Pokaż cały numer - Farmaceutyczny Przegląd Naukowy
Pokaż cały numer - Farmaceutyczny Przegląd Naukowy
Pokaż cały numer - Farmaceutyczny Przegląd Naukowy
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Farm Przegl Nauk, 2009,2<br />
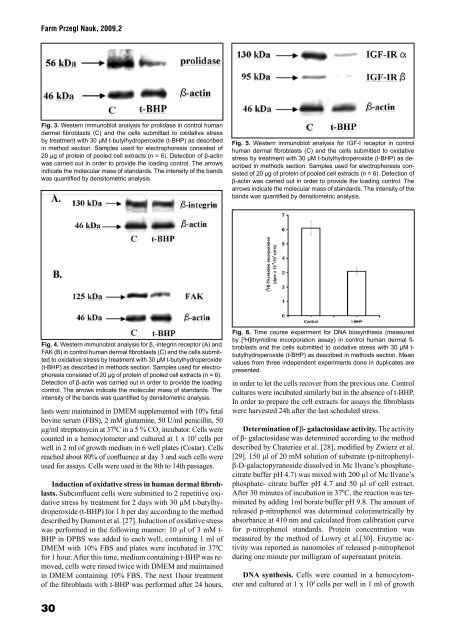
Fig. 3. Western immunoblot analysis for prolidase in control human<br />
dermal fibroblasts (C) and the cells submitted to oxidative stress<br />
by treatment with 30 µM t-butylhydroperoxide (t-BHP) as described<br />
in method section. Samples used for electrophoresis consisted of<br />
20 µg of protein of pooled cell extracts (n = 6). Detection of β-actin<br />
was carried out in order to provide the loading control. The arrows<br />
indicate the molecular mass of standards. The intensity of the bands<br />
was quantified by densitometric analysis.<br />
Fig. 4. Western immunoblot analysis for β 1 -integrin receptor (A) and<br />
FAK (B) in control human dermal fibroblasts (C) and the cells submitted<br />
to oxidative stress by treatment with 30 µM t-butylhydroperoxide<br />
(t-BHP) as described in methods section. Samples used for electrophoresis<br />
consisted of 20 µg of protein of pooled cell extracts (n = 6).<br />
Detection of β-actin was carried out in order to provide the loading<br />
control. The arrows indicate the molecular mass of standards. The<br />
intensity of the bands was quantified by densitometric analysis.<br />
lasts were maintained in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal<br />
bovine serum (FBS), 2 mM glutamine, 50 U/ml penicillin, 50<br />
µg/ml streptomycin at 37 0 C in a 5 % CO 2 incubator. Cells were<br />
counted in a hemocytometer and cultured at 1 x 10 5 cells per<br />
well in 2 ml of growth medium in 6 well plates (Costar). Cells<br />
reached about 80% of confluence at day 3 and such cells were<br />
used for assays. Cells were used in the 8th to 14th passages.<br />
Induction of oxidative stress in human dermal fibroblasts.<br />
Subconfluent cells were submitted to 2 repetitive oxidative<br />
stress by treatment for 2 days with 30 µM t-butylhydroperoxide<br />
(t-BHP) for 1 h per day according to the method<br />
described by Dumont et al. [27]. Induction of oxidative stress<br />
was performed in the following manner: 10 µl of 3 mM t-<br />
BHP in DPBS was added to each well, containing 1 ml of<br />
DMEM with 10% FBS and plates were incubated in 37 0 C<br />
for 1 hour. After this time, medium containing t-BHP was removed,<br />
cells were rinsed twice with DMEM and maintained<br />
in DMEM containing 10% FBS. The next 1hour treatment<br />
of the fibroblasts with t-BHP was performed after 24 hours,<br />
30<br />
Fig. 5. Western immunoblot analysis for IGF-I receptor in control<br />
human dermal fibroblasts (C) and the cells submitted to oxidative<br />
stress by treatment with 30 µM t-butylhydroperoxide (t-BHP) as described<br />
in methods section. Samples used for electrophoresis consisted<br />
of 20 µg of protein of pooled cell extracts (n = 6). Detection of<br />
β-actin was carried out in order to provide the loading control. The<br />
arrows indicate the molecular mass of standards. The intensity of the<br />
bands was quantified by densitometric analysis.<br />
Fig. 6. Time course experiment for DNA biosynthesis (measured<br />
by [ 3 H]thymidine incorporation assay) in control human dermal fibroblasts<br />
and the cells submitted to oxidative stress with 30 µM tbutylhydroperoxide<br />
(t-BHP) as described in methods section. Mean<br />
values from three independent experiments done in duplicates are<br />
presented.<br />
in order to let the cells recover from the previous one. Control<br />
cultures were incubated similarly but in the absence of t-BHP.<br />
In order to prepare the cell extracts for assays the fibroblasts<br />
were harvested 24h after the last scheduled stress.<br />
Determination of β- galactosidase activity. The activity<br />
of β- galactosidase was determined according to the method<br />
described by Chateriee et al. [28], modified by Zwierz et al.<br />
[29]. 150 µl of 20 mM solution of substrate (p-nitrophenylβ-D-galactopyranoside<br />
dissolved in Mc Ilvane’s phosphate-<br />
citrate buffer pH 4.7) was mixed with 200 µl of Mc Ilvane’s<br />
phosphate- citrate buffer pH 4.7 and 50 µl of cell extract.<br />
After 30 minutes of incubation in 37 0 C, the reaction was terminated<br />
by adding 1ml borate buffer pH 9.8. The amount of<br />
released p-nitrophenol was determined colorimetrically by<br />
absorbance at 410 nm and calculated from calibration curve<br />
for p-nitrophenol standards. Protein concentration was<br />
measured by the method of Lowry et al.[30]. Enzyme activity<br />
was reported as nanomoles of released p-nitrophenol<br />
during one minute per milligram of supernatant protein.<br />
DNA synthesis. Cells were counted in a hemocytometer<br />
and cultured at 1 x 10 5 cells per well in 1 ml of growth