Innehåll 1 Sannolikhetsteori - Matematikcentrum
Innehåll 1 Sannolikhetsteori - Matematikcentrum
Innehåll 1 Sannolikhetsteori - Matematikcentrum
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
1 SANNOLIKHETSTEORI<br />
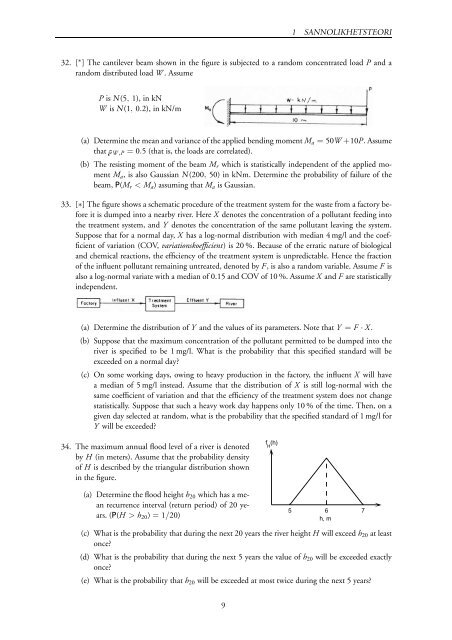
32. [ ∗ ] The cantilever beam shown in the figure is subjected to a random concentrated load P and a<br />
random distributed load W . Assume<br />
P is N(5, 1), in kN<br />
W is N(1, 0.2), in kN/m<br />
(a) Determine the mean and variance of the applied bending moment M a = 50W+10P. Assume<br />
thatÖW,P = 0.5 (that is, the loads are correlated).<br />
(b) The resisting moment of the beam M r which is statistically independent of the applied moment<br />
M a , is also Gaussian N(200, 50) in kNm. Determine the probability of failure of the<br />
beam, P(M r < M a ) assuming that M a is Gaussian.<br />
33. [∗] The figure shows a schematic procedure of the treatment system for the waste from a factory before<br />
it is dumped into a nearby river. Here X denotes the concentration of a pollutant feeding into<br />
the treatment system, and Y denotes the concentration of the same pollutant leaving the system.<br />
Suppose that for a normal day, X has a log-normal distribution with median 4 mg/l and the coefficient<br />
of variation (COV, variationskoefficient) is 20 %. Because of the erratic nature of biological<br />
and chemical reactions, the efficiency of the treatment system is unpredictable. Hence the fraction<br />
of the influent pollutant remaining untreated, denoted by F, is also a random variable. Assume F is<br />
also a log-normal variate with a median of 0.15 and COV of 10 %. Assume X and F are statistically<br />
independent.<br />
(a) Determine the distribution of Y and the values of its parameters. Note that Y = F · X .<br />
(b) Suppose that the maximum concentration of the pollutant permitted to be dumped into the<br />
river is specified to be 1 mg/l. What is the probability that this specified standard will be<br />
exceeded on a normal day<br />
(c) On some working days, owing to heavy production in the factory, the influent X will have<br />
a median of 5 mg/l instead. Assume that the distribution of X is still log-normal with the<br />
same coefficient of variation and that the efficiency of the treatment system does not change<br />
statistically. Suppose that such a heavy work day happens only 10 % of the time. Then, on a<br />
given day selected at random, what is the probability that the specified standard of 1 mg/l for<br />
Y will be exceeded<br />
34. The maximum annual flood level of a river is denoted<br />
by H (in meters). Assume that the probability density<br />
of H is described by the triangular distribution shown<br />
in the figure.<br />
f H<br />
(h)<br />
(a) Determine the flood height h 20 which has a mean<br />
recurrence interval (return period) of 20 years.<br />
(P(H > h 20 ) = 1/20)<br />
5 6 7<br />
h, m<br />
(c) What is the probability that during the next 20 years the river height H will exceed h 20 at least<br />
once<br />
(d) What is the probability that during the next 5 years the value of h 20 will be exceeded exactly<br />
once<br />
(e) What is the probability that h 20 will be exceeded at most twice during the next 5 years<br />
9