Curso de Equações Diferenciais Ordinárias - Unesp
Curso de Equações Diferenciais Ordinárias - Unesp
Curso de Equações Diferenciais Ordinárias - Unesp
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
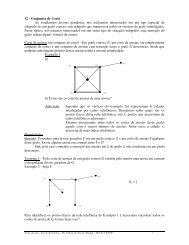
7) Classifique a singularida<strong>de</strong> (0, 0) dos campos:<br />
[ ] [ ]<br />
−5 3<br />
−5 3<br />
a)<br />
d)<br />
[<br />
2 7<br />
] [<br />
2 −7<br />
]<br />
−5 3<br />
−5 3<br />
b)<br />
e)<br />
[<br />
−2 5<br />
] [<br />
−7 4<br />
]<br />
−<br />
3 1<br />
3 1<br />
c) 2 4<br />
−1 − 1 g) 2 4<br />
1<br />
2<br />
−1<br />
2<br />
8) Estabeleça condições sobre a constante µ <strong>de</strong> modo que (0, 0) seja um<br />
centro [ ] −µ 1<br />
.<br />
−1 µ<br />
9) Estabeleça condições sobre a constante µ <strong>de</strong> modo que (0, 0) seja um foco<br />
atrator [<br />
0 1<br />
]<br />
−1 µ<br />
10) Prove que (0, 0) é sempre uma singularida<strong>de</strong> repulsora <strong>de</strong><br />
[<br />
µ<br />
]<br />
1<br />
−1 1<br />
on<strong>de</strong> µ é uma constante real e µ ≠ 1. Quando é que (0, 0) é um ponto <strong>de</strong> sela<br />
E foco repulsor<br />
11) Seja γ = γ (t) uma trajetória do campo linear<br />
[ ]<br />
α −β<br />
β<br />
α<br />
passando por um ponto p 0 . Estabeleça condições sobre α e β que garantam que<br />
lim γ (t) = 0<br />
t→+∞<br />
12) Prove que (0, 0) é uma singularida<strong>de</strong> atratora do campo<br />
X (x, y) = ( αx − βy + y 2 , βx + αy − xy ) .<br />
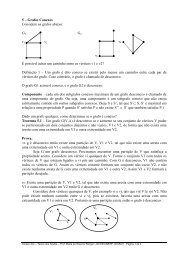
13) Classifique as singularida<strong>de</strong>s dos campos:<br />
a)X (x, y) = (1 − 2xy, 2xy − y) e)X (x, y) = ( x 2 − y 2 − 1, 2y )<br />
b)X (x, y) = ( y − x 2 + 2, x 2 − xy ) f)X (x, y) = ( 2x − y 2 , −y + xy )<br />
c)X (x, y) = ( −3x + y 2 + 2, x 2 − y 2) g)X (x, y) = ( xy − 3y − 4, y 2 − x 2)<br />
d)X (x, y) = ( −2xy, y − x + xy − y 3)<br />
14) Prove que a equação diferencial não linear <strong>de</strong> 2 a or<strong>de</strong>m<br />
(<br />
1 + α 2 x 2) x ′′ +<br />
(<br />
β 2 + (x ′ ) 2) x = 0<br />
97