Curso de Equações Diferenciais Ordinárias - Unesp
Curso de Equações Diferenciais Ordinárias - Unesp
Curso de Equações Diferenciais Ordinárias - Unesp
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
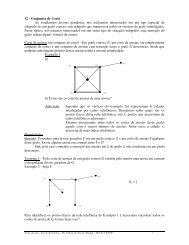
2.3 Equações Separáveis<br />
Uma EDO <strong>de</strong> primeira or<strong>de</strong>m<br />
y ′ = f (x, y)<br />
é dita SEPARÁVEL se for possível escrevermos<br />
f (x, y) = M (x)<br />
N (y) .<br />
Exemplos:<br />
1)<br />
é separável.<br />
y ′ = x e y<br />
2)<br />
não é separável.<br />
y ′ = sin (xy)<br />
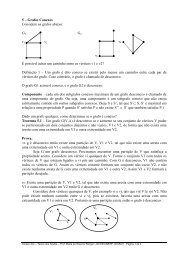
Soluções <strong>de</strong> Equações Separáveis:<br />
Dada a equação<br />
temos que<br />
e assim<br />
∫<br />
y ′ = M (x)<br />
N (y)<br />
N (y) y ′ = M (x)<br />
∫<br />
N (y) y ′ dx = M (x) dx<br />
Fazendo a mudança <strong>de</strong> variável, na primeira primitiva, dada por<br />
y = y (x)<br />
temos que<br />
e assim<br />
∫<br />
dy = y ′ dx<br />
∫<br />
N (y) dy = M (x) dx<br />
e as soluções da EDO são dadas implicitamente por<br />
g (y) − h (x) = c.<br />
12