Jaarboek no. 89. 2010/2011 - Koninklijke Maatschappij voor ...
Jaarboek no. 89. 2010/2011 - Koninklijke Maatschappij voor ...
Jaarboek no. 89. 2010/2011 - Koninklijke Maatschappij voor ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
tering and leaner exhibit decreased susceptibility<br />
for CSD, manifesting as an increased threshold for<br />
inducing a CSD event. Functionally, these mutations<br />
convey clear electrophysiological loss-of-function<br />
effects to the channels. In contrast, in keeping with a<br />
gain-of-function effect in FHM1, the R192Q k<strong>no</strong>ckin<br />
mice exhibited a decreased threshold for inducing a<br />
CSD event. Together, these findings suggest a direct<br />
positive correlation between channel function and<br />
spreading depression: more Ca2+ influx leads to an<br />
increased susceptibility for spreading depression<br />
in the cortex. This may have clinical significance, as<br />
decreasing calcium channel activity to wild-type<br />
levels in the brain might help rescue the migraine<br />
brain.<br />
B. Na + /K + -ATPase α2 transporter (FHM2)<br />
To date, 45 mutations in the ATP1A2 gene have been<br />
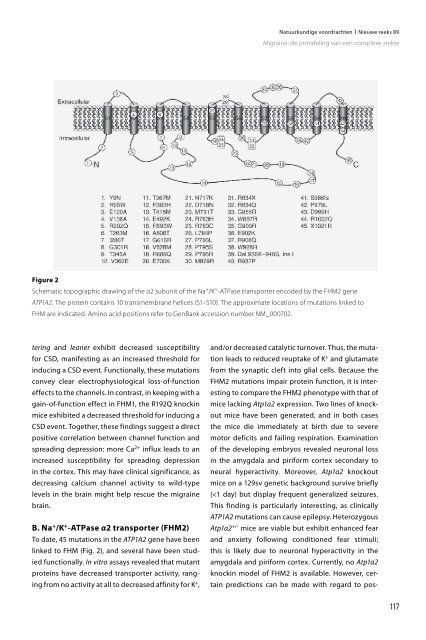
linked to FHM (Fig. 2), and several have been studied<br />
functionally. In vitro assays revealed that mutant<br />
proteins have decreased transporter activity, ranging<br />
from <strong>no</strong> activity at all to decreased affinity for K + ,<br />
Natuurkundige <strong>voor</strong>drachten I Nieuwe reeks 89<br />
Migraine: de ontrafeling van een complexe ziekte<br />
Figure 2<br />
Schematic topographic drawing of the α2 subunit of the Na + /K + -ATPase transporter encoded by the FHM2 gene<br />
ATP1A2. The protein contains 10 transmembrane helices (S1–S10). The approximate locations of mutations linked to<br />
FHM are indicated. Ami<strong>no</strong> acid positions refer to GenBank accession number NM_000702.<br />
and/or decreased catalytic tur<strong>no</strong>ver. Thus, the mutation<br />
leads to reduced reuptake of K + and glutamate<br />
from the synaptic cleft into glial cells. Because the<br />
FHM2 mutations impair protein function, it is interesting<br />
to compare the FHM2 phe<strong>no</strong>type with that of<br />
mice lacking Atp1a2 expression. Two lines of k<strong>no</strong>ckout<br />
mice have been generated, and in both cases<br />
the mice die immediately at birth due to severe<br />
motor deficits and failing respiration. Examination<br />
of the developing embryos revealed neuronal loss<br />
in the amygdala and piriform cortex secondary to<br />
neural hyperactivity. Moreover, Atp1a2 k<strong>no</strong>ckout<br />
mice on a 129sv genetic background survive briefly<br />
(