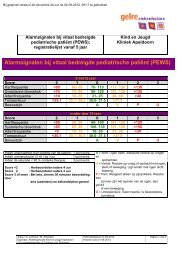
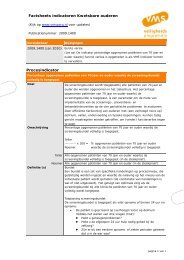
POSTOPERATIEVE PIJNBEHANDELINGMEDICATIENiveau 2Er zijn aanwijzingen dat een vroege ‘agressieve’ postoperatieve pijnbehandelingde kans op overgang naar een chronisch pijntype kan doen verminderen.A2 Katz 1992 89Overige overwegingenVeel studies zijn begin 90-er jaren verricht met het éénmalig toedienen van het analgeticum<strong>voor</strong> en/of na de nociceptieve stimulus (ingreep). Het lijkt steeds duidelijker te worden dateen éénmalige pre-emptieve therapie weinig tot geen effect zal hebben, omdat de afferenteneuronale activiteit op spinaalniveau zich ook <strong>voor</strong>tzet na de ingreep vanwege de inflammatoirerespons bij het beschadigde weefsel. Deze postoperatieve verhoogde neuronale activiteit dientdan ook goed behandeld te worden door middel van goede, gecontinueerde postoperatievepijnbehandeling van voldoende kwaliteit en intensiteit wil de pre-emptieve pijnbehandelingenige zin hebben. 85-87Er is onvoldoende klinisch bewijs <strong>voor</strong> het pre-emptieve gebruik van opioïden, NSAID’s ofparacetamol. Er kan echter een farmacokinetische reden zijn om standaard preoperatief testarten met toediening van NSAID’s of paracetamol. Hierbij kan gedacht worden aan kortdurendeingrepen met naar verwachting matige postoperatieve pijn, opdat <strong>postoperatief</strong> reedseen voldoende hoge plasmaspiegel aanwezig is.AanbevelingOp grond van de bestaande literatuur adviseert de werkgroep het alleen pre-emptievegebruik van paracetamol, NSAID’s en opioïden niet. Ingebed in de totale (multimodale)postoperatieve pijnbehandeling kan het perspectieven bieden.Literatuur1. Carr D, Goudas LC. Acute pain. Lancet 1999;353:2051-8.2. Kehlet H. In: Cousins MJ, Bridenbaugh PO (eds). Neural blockade in clinical anesthesia and management of pain,3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven Publishers;1998.3. Woodhouse A, Mather LE. The minimum effective concentration of opioids: a revisitation with patient-controlledanalgesia fentanyl. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2000;25:259-67.4. MacIntyre PE, Jarvis DA. Age is the best predictor of postoperative morphine requirements. Pain 1996;64:357-64.5. Upton RN, Semple TJ, McIntyre PE. Pharmacokinetic optimisation of opioid treatment in acute pain therapy. ClinPharmacokin 1997;33:225-44.6. Forman WB. Opioid analgesic drugs in the elderly (review). Clin Geriatr Med 1996;12(3): 489-500.7. Egbert AM. Postoperative pain management in the frail elderly (review). Clin Geriatr Med 1996;12(3):583-99.8. Tyler DC, Pomietto M, Womack W. Variation in opioid use during PCA in adolescents. Paediatr Anaesth 1996;6:33-8 .9. Sarton E, Olofsen E, Romberg R, Hartigh J den, Kest B, Nieuwenhuijs D, et al. Sex differences in morphine analgesia:an experimental study in healthy volunteers. Anesthesiology 2000;93:1245-54.10. Zhou HH, Sheller JR, Nu H, Wood M, Wood AJ. Ethnic differences in response to morphine. Clin Pharmacol Ther1993;54:507-13.11. Nieuwenhuyzen MC van den, Engbers FH, Burm AG, Vletter AA, Kleef JW van, Bovill JG. Target-controlled infusionof alfentanil for postoperative analgesia: contribution of plasma protein binding to intra-patient and inter-patientvariability. Br J Anaesth 1999;82:580-5.12. McQuay HJ. Opioids in pain management. Lancet 1999;353:2229-32.13. McQuay HJ, Moore RA. An evidence-based resource for pain relief. Oxford;Oxford University Press.14. Porter J, Jick H. Addiction rate in patients treated with narcotics. N Engl J Med 1980;302:123.15. McQuay HJ, Carroll D, Moore RA. Injected morphine in postoperative pain; a quantitative systematic review. J PainSymptom Manage 1999;17:164-74.16. Moore A, Collins S, Carroll D, McQuay H, Edwards J. Single dose paracetamol (acetominophen), with and withoutcodeine, for postoperative pain (Cochrane review). In: The Cochrane Library, Issue 2, 2000;Oxford:Update Software.17. Collins SL, Edwards JE, Moore RA, McQuay HJ. Single dose dextropropoxyphene alone and with paracetamol(acetominophen) for postoperative pain (Cochrane review). In: The Cochrane Library, Issue 4, 2001;Oxford:UpdateSoftware.18. Edwards JE, McQuay HJ, Moore RA. Single dose dihydrocodeine for postoperative pain (Cochrane review). In: TheCochrane Library, Issue 4, 2000;Oxford:Update Software.19. Moore RA, McQuay HJ. Single patient data meta-analysis of 3543 postoperative patients: oral tramadol versusplacebo, codeine and combination analgesics. Pain 1997;69:287-94.20. Rainer TH, Jacobs P, Ng YC, Cheung NK, Tam M, Lam PK, et al. Cost effectiveness analysis of intravenous ketarolacand morphine for treating pain after limb injury: double blind randomized trial. BMJ 2000;321:1247-51.21. Woodhouse A, Ward ME, Mather LE. Intra-subject variability in postoperative patient controlled analgesia (PCA):is the patient equally satisfied with morphine, pethidine and fentanyl? Pain 1999;80(3):545-53.22. Faura CC, Collins SL, Moore RA, McQuay HJ. Systematic review of factors affecting the ratios for morphine and itsmajor metabolites. Pain 1998;74:43-53.23. Morlion B, Ebner E, Weber A, Finke W, Puchstein C. Influence of bolus size on efficacy of postoperative patient-controlledanalgesia with piritramide. Br J Anaesth 1999;82:52-5.24. Albrecht S, Fechner J, Geisslinger G, Maass AB, Upadhyaya B, Moecke H, et AL. postoperative pain control followingremifentanil-based anaesthesia for major abdominal surgery. Anaesthesia 2000;55:315-22.25. Kietzmann D, Bouillon T, Hamm C, Schwabe K, Schenk H, Gundert-Remy U, et al. Pharmacodynamic modelling ofthe analgesic effects of piritramide in postoperative patients. Acta Anaesthiol Scand 1997;41:888-94.26. Chui PT, Gin T. A double blind randomized trial comparing postoperative analgesia after perioperative loadingdoses of methadone or morphine. Anaesth Intensive Care 1992;20:46-51.27. Laur DF, Sinkovich J, Betley K. A comparison of intraoperative morphine sulfate and methadone hydrochloride onpostoperative visual analogue scale pain scores and narcotic requirements. CRNA 1995;6:21-5.28. Smith LA, Carroll D, Edwards JE, Moore RA, McQuay HJ. Single dose ketorolac and pethidine in acute postoperativepain: systematic review with meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth 2000 Jan;84(1):48-58.29. Elborne D, Wiseman RA. Types of intra-muscular opioids for maternal pain relief in labour (Cochrane review). In:The Cochrane Library, Issue 4, 2001;Oxford:Update Software.30. Kehlet H, Rung GW, Callesen T. Postoperative opioid analgesia: time for a reconsideration? J Clin Anesth 1996;8(6):441-5.31. Rosenberg J, Kehlet H. Postoperative mental confusion, association with postoperative hypoxemia. Surgery 1993Jul;114(1):76-81.7071
POSTOPERATIEVE PIJNBEHANDELINGMEDICATIE32. Camu F. Side effects of opioids in postoperative pain treatment. Acta Anaesth Belg 1996;47:105-9.33. Mulroy MF. Monitoring opioids (review). Reg Anesth 1996;21(6 suppl):89-93.34. Reeder MK, Goldman MD, Loh L, Muir AD, Casey KR, Lehane JR. Late postoperative nocturnal dips in oxygen saturationin patients undergoing major abdominal vascular surgery. Anesthesia 1992;47:110-5.35. Choi HJ, Little MS, Garber SZ, Tremper KK. Pulse oximetry for monitoring during ward analgesia: epidural morphineversus parenteral narcotics. J Clin Monit 1989;5(2):87-9.36. Nozaki-Taguchi N, Oka T, Kochi T, Taguchi N, Mizuguchi T. Apnoea and oximetric desaturation in patients receivingepidural morphine after gastrectomy: a comparison of intermittent bolus and patient controlled administration.Anaesth Intensive Care 1993;21(3):292-7.37. Motamed C, Spencer A, Farhat F, Bourgain JL, Lasser P, Jayr C. Postoperative hypoxemia: continuous extraduralinfusion of bupivacaine and morphine vs patient controlled analgesia with intravenous morphine. Br J Anaesth1998;80(6):742-7.38. Wheatley RG, Shepherd D, Jackson IJ, Madej TH, Hunter D. Hypoxemia and pain relief after upper abdominal surgery:comparison of i.m. and patient controlled analgesia. Br J Anaesth 1992;69(6):558-61.39. Wheatley RG, Somerville ID, Sapsford DJ, Jones JG. Postoperative hypoxemia: comparison of extradural, i.m. andpatient controlled opioid analgesia. Br J Anaesth 1990;64(3):267-75.40. Bailey PL, et al. Effects of intrathecal morphine on the ventilatory respons to hypoxia. N Engl J Med 2000;343:1228-34.41. Jorgensen H, Wetterslev J, Moiniche S, Dahl JB. Epidural local anaesthetics versus opioid-base analgesic regimenson postoperative paralysis, PONV and pain after abdominal surgery (Cochrane review). In: The Cochrane Library,Issue 4, 2000;Oxford:Update Software.42. Liu SS, Carpenter RL, Mackey DC, Thirlby RC, Rupp SM, Shine TS, et al. Effects of perioperative analgesic techniqueon rate of recovery after colon surgery. Anesthesiology 1995;83(4):757-65.43. Thorn SE, Wattwil M, Lindberg G, Sawe J. Systemic and central effects of morphine on gastroduodenal motility.Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 1996;40(2):177-86.44. Grass JA, Sakima NT, Valley M, Fischer K, Jackson C, Walsh P, et al. Assessment of ketarolac as an adjuvant to fentanylpatient-controlled analgesia after radical retropubic prostatectomy. Anesthesiology 1993;78:642-8.45. Thoren T, Sundberg A, Wattwil M, Garvill JE, Jurgensen U. Effects of epidural bupivacaine and epidural morphineon bowel function and pain after hysterectomy. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 1989;33:181-5.46. Slappendel R, Weber EW, Benraad B, Limbeek J van, Dirksen R. Itching after intrathecal morphine. Incidence andtreatment. Eur J Aneasthesiol 2000;17(10):616-21.47. Charuluxananan S. Ondansetron for treatment of ontrathecal morphine-induced pruritus after caesarean delivery.Reg Anesth Pain Med 2000;25:535-9.48. Choi JH, Lee J, Choi JH, Bishop MJ. Epidural naloxone reduces pruritus and nausea without affecting analgesia byepidural morphine in bupivacaine. Can J Anaesth 2000;47:33-7.49. Colbert S, O’Hanlon DM, Galvin S, Chambers F, Moriarty DC. The effect of rectal diclofenac on pruritus in patientsreceiving intrathecal morphine. Anaesthesia 1999;54:948-52.50. Kehlet H. Multimodal approach tot control postoperative pathofysiology and rehabilitation. Br J Anaesthesia1997;78:606-17.51. Edwards JE, Moore RA, McQuay HJ. Single dose oxycodone and oxycodone plus paracetamol (acetominophen) foracute postoperative pain (Cochrane review). In: The Cochrane Library, Issue 4, 2000;Oxford:Update Software.52. Peduto VA, Ballabio M, Stefanini S. Efficacy of proparacetamol in the treatment of postoperative pain. Morphine-sparingeffect in orthopedic surgery. Italian Collaborative Group on Propacetamol. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 1998;42:293-8.53. Schug SA, Sidebotham DA, McGuinnety M, Thomas J, Fox L. Acetominophen as an adjunct to morphine by patientcontrolled analgesia in the management of acute postoperative pain. Anesth Analg 1998;87(2):368-72.54. Cobby TF, Crighton IM, Kyriakides K, Hobbs GJ. Rectal paracetamol has a significant morphine-sparing effect afterhysterectomy. Br J Anaesth 1999;83:253-6.55. Rao AS, Cardosa M, Inbasegaran K. Morphine sparing effect of ketoprofen after abdominal surgery. AnaesthIntensive Care 2000;28:22-6.56. Rapanos T, Murphy P, Szalai JP, Burlacoff L, Lam-McCulloch J, Kay J. Rectal indomethacin reduces postoperativepain and morphine use after cardiac surgery. Can J Anaesth 1999;46:725-30.57. Wideman GL, et al. Analgesic efficacy of a combination of hydrocodone with ibuprofen in postoperative pain. ClinPharmacol Ther 1999;65:66-76.58. Wideman GL, Keffer M, Morris E, Doyle RT Jr, Jiang JG, Beaver WT. Ketorolac potentiates morphine in postoperativepatient-controlled analgesia. Pain 1997;73:401-6.59. Montgomery JE, Sutherland CJ, Kestin IG, Sneyd JR. Morphine consumption in patients receiving paracetamol anddiclofenac alone and in combination. Br J Anaesth 1996;77:445-7.60. Moren J, Francois T, Blanloeil Y, Pinaud M. The effects of a NSAID (ketoprofen) on morphine respiratory depression:a double blind, randomized study in volenteers. Anesth Analg 1997;85:400-5.61. Stamer UM, Grond S, Maier C. Responders and non-responders to postoperative pain treatment: the loading dosepredicts analgesic needs. Eur J Anaesthesiol 1999;16:103-10.62. McArdle CS. Continuous and patient controlled analgesic infusions. In: Doyle, eds. 1986 International Symposiumon Pain Control. Royal Society of Medicine International Congress and Symposium Series 1986;123:17-23.63. Aubrun F, Monsel S, Langeron O, Coriat P, Riou B. Postoperative titration of intravenous morphine. Eur J Aneasthesiol2001;18:159-65.64. Bourke M, Hayes A, Doyle M, McCarroll M. A comparison of regularly administered sustained release oral morphinewith intramuscular morphine for control of postoperative pain. Anesth Analg 2000;90(2):427-30.65. Smith G, Power I. Audit and bridging the analgesic gap. Anesthesia 1998;53:521-2.66. D’Haese J, Vanlersberghe C, Umbrain V, Camu F. Pharmaco-economic evaluation of a disposable patient controlledanalgesia device and intramuscular analgesia in surgical patients. Eur J Anaesthesiol 1998;15(3):297-303.67. Snell CC, Fothergill-Bourbonnais F, Durocher-Hendriks S. Patient controlled analgesia and intramuscular injections:a comparison of patient pain experiences and postoperative outcomes. J Adv Nurs 1997;25(4):681-90.68. Choiniere M, Rittenhouse BE, Perreault S, Chartrand D, Rousseau P, Smith B, et al. Efficacy and costs of patientcontrolled analgesia versus regularly administered intramuscular opioid therapy. Anesthesiology 1998;89 (6):1377-88.69. Lavand’Homme P, Kock M de. Practical guidelines on the postoperative use of patient controlled analgesia in theelderly. Drugs Aging 1998;13(1):9-16.70. Egbert AM, Parks LH, Short LM, Burnett ML. Randomized trial of postoperative patient controlled analgesia vsintramuscular narcotics in frail elderly men. Arch Intern Med 1990;150(9):1897-903.71. Cooper IM. Morphine for postoperative analgesia. A comparison of intramuscular and subcutaneous routes ofadministration. Aneaesth Intensive Care 1996;24(5):574-8.72. Gopinathan C, Sockalingham I, Fung MA, Peat S, Hanna MH. A comparative study of patient controlled epiduraldiamorphine, subcutaneous diamorphine and an epidural diamorphine/bupivacaine combination for postoperativepain. Eur J Anaesthesiol 2000;17(3):189-96.7273