- Page 1: ISTITUZIONI DI FISICAMATEMATICACors
- Page 4 and 5: 5 Funzioni sferiche . . . . . . . .
- Page 7 and 8: Capitolo IEQUAZIONI DELLA FISICAMAT
- Page 9 and 10: ha la seguente rappresentazione:∆
- Page 11 and 12: dove L ∈ (0, +∞). Ponendoψ(r,
- Page 13 and 14: nelle variabili (x, y, z) per k > 0
- Page 15 and 16: 3 Equazione di HelmholtzIn questa p
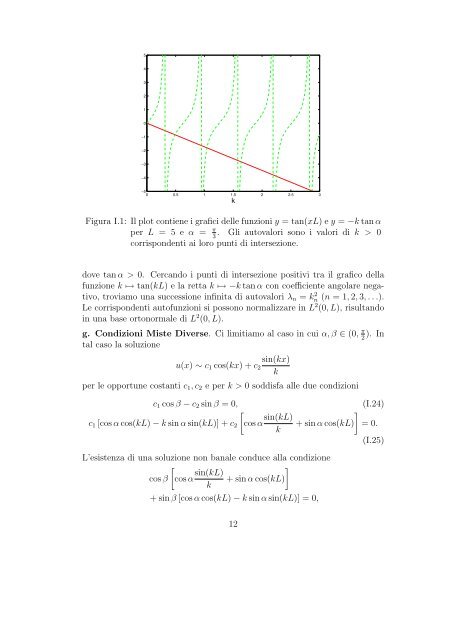
- Page 17: L’altra condizione u(L) = 0 condu
- Page 21 and 22: dove a 2 è la diffusività termica
- Page 23 and 24: I coefficienti di Fourier si calcol
- Page 25: per l’equazione delle onde.Per l
- Page 28 and 29: per n, m > n(ε), ossia se lim n,m
- Page 30 and 31: d. (αϕ + βψ, χ) = α(ϕ, χ) +
- Page 32 and 33: Appena trovata una base ortonormale
- Page 34 and 35: ossia∫1 π|f(x)| 2 dx =2π −π
- Page 36 and 37: Proposizione II.3 Siano X, Y spazi
- Page 38 and 39: Sia X uno spazio di Banach compless
- Page 40 and 41: Teorema II.7 Sia T ∈ L(X) un oper
- Page 42 and 43: 5.4 Operatori autoaggiunti non limi
- Page 45 and 46: Capitolo IIIEQUAZIONI DIFFERENZIALI
- Page 47 and 48: Essendo w(x) ≠ 0 (per ogni x ∈
- Page 49 and 50: Spieghiamo ora il Metodo di Frobeni
- Page 51 and 52: poichè in alcuni casi si trovano d
- Page 53 and 54: per |z| abbastanza piccola, dove il
- Page 55 and 56: Quindi la sostituzione y(x) = x −
- Page 57 and 58: come dovevasi dimostrare. La funzio
- Page 59 and 60: e dunque [vedi la (A.10) nell’App
- Page 61 and 62: dove ν > −1. Allora∫ 1xJ ν (
- Page 63 and 64: Siccome µ −ν [αJ ν (µ) + β
- Page 65 and 66: 3025201510587654321000 1 2 3 4 5 1
- Page 67 and 68: È anche abbastanza facile trovare
- Page 69 and 70:
Consideriamo ora le funzioni sferic
- Page 71 and 72:
soddisfano la (II.74) per λ = l(l
- Page 73 and 74:
si ottiene∫ 1(−1) l+1(P l+1 , x
- Page 75 and 76:
5.3 Funzioni di Legendre associateS
- Page 77 and 78:
convergente in L 2 (S 2 ). I coeffi
- Page 79 and 80:
Confrontando i coefficienti di z n+
- Page 81 and 82:
Derivando la (II.95) n + 1 volte e
- Page 83 and 84:
40502000−20−40−50−60−80
- Page 85 and 86:
otteniamo le seguenti espressioni p
- Page 87 and 88:
∫ 1−1U n (x)U m (x) √ 1 − x
- Page 89 and 90:
dove q è un polinomio di grado n
- Page 91:
++n∑(α j−1 p j−1 (x)p j (y)
- Page 94 and 95:
dove K ∗ (x, y) = K(y, x), sono d
- Page 96 and 97:
Da questa disuguaglianza segue che
- Page 98 and 99:
(1/Mm(Ω)) − ε}, per ε > 0 qual
- Page 100 and 101:
Risolviamo ora l’equazione di Vol
- Page 102 and 103:
Dimostrazione. Come è noto, ogni s
- Page 104 and 105:
Conformemente al Lemma III.5, la su
- Page 106 and 107:
ECC. Supponiamo di aver trovato i n
- Page 108 and 109:
Introduciamo ora la successione di
- Page 110 and 111:
Teorema IV.8 (Teorema di Hilbert-Sc
- Page 112 and 113:
L’operatore L è hermitiano, cio
- Page 114 and 115:
Calcolando la derivata si trovau
- Page 116 and 117:
e quindiw(x) = v 1 (0, λ)v 2(0,
- Page 118 and 119:
segue che u 0 ∈ C[0, l], poichè
- Page 120 and 121:
Le condizioni al contorno (IV.2) si
- Page 122 and 123:
implica l’impossibilità di conve
- Page 124 and 125:
Quindi il problema (IV.26)-(IV.27)
- Page 126 and 127:
120
- Page 128 and 129:
dove a 00 (x) = 0 (essendo t la coo
- Page 130 and 131:
Tutte le funzioni f di classe C 2 (
- Page 132 and 133:
2. Sia f ∈ M L . Ponendo u = f e
- Page 134 and 135:
3.1 Equazioni di Laplace e di Poiss
- Page 136 and 137:
Sostituendo le condizioni al contor
- Page 138 and 139:
Risolvendo la (V.34) sotto la condi
- Page 140 and 141:
Utilizzando il linguaggio dell’el
- Page 142 and 143:
L’equazione (V.48) è un’equazi
- Page 144 and 145:
dove abbiamo utilizzato ∑ ∞n=1
- Page 146 and 147:
3.1.fEquazione di Laplace nella sfe
- Page 148 and 149:
nella forma∫u(x) = E(x, y)f(y) dy
- Page 150 and 151:
4 Equazioni parabolicheL’equazion
- Page 152 and 153:
doveG(x, y; t) = 2 ∞∑e −n2 (
- Page 154 and 155:
e applicando la solita separazione
- Page 156 and 157:
dove u(x) = −u(−x) per x ∈ R
- Page 158 and 159:
Quindiu(x, t) = 1 ∫ ∞e i(x·ξ)
- Page 160 and 161:
dove ψ 0 (x) = 1/ √ mis(Ω) è l
- Page 162 and 163:
L’equazione delle onde (V.97) con
- Page 164 and 165:
da Γ(z) = Γ(z + 1)/z, poi nella s
- Page 166 and 167:
Il teorema A.1 può essere applicat
- Page 168 and 169:
162
- Page 170 and 171:
Quindi φ ν (z) è una soluzione d
- Page 172 and 173:
dove χ = z −( 1ν + 1 )π, otten
- Page 174 and 175:
dove A(k, θ, θ ′ ) è l’ampie
- Page 176 and 177:
L’equazione (C.5) può essere ris
- Page 178 and 179:
Per trovare i stati limite richiedi
- Page 180 and 181:
2 Oscillatore armonicoa. Utilizzand
- Page 182 and 183:
isultando in polinomi in x di grado
- Page 184 and 185:
altre parole,⎧⎪⎨ E n = −κ
- Page 186 and 187:
Siano f, g ∈ L 1 (R n ). Inoltre,
- Page 188 and 189:
L’equazione (D.4) dimostra che F
- Page 190 and 191:
(d) Se f ∈ S ′ , allora ogni de
- Page 192 and 193:
La trasformazione inversa di Fourie
- Page 194 and 195:
3.1 Proprietà della trasformazione
- Page 196 and 197:
190
- Page 198 and 199:
Osservando ora che tutti gli aperti
- Page 200 and 201:
3. Se f, g : R n → C sono misurab
- Page 202 and 203:
Esempio E.2 Sia f : R + → R defin
- Page 204 and 205:
Teorema E.6 (Fubini) Sia f : R n+m
- Page 206 and 207:
Sia f : G → C una funzione analit
- Page 208 and 209:
e quindi f ′ (w) = 0. Siccome w
- Page 210 and 211:
204
- Page 212 and 213:
Abbiamo bisogno di alcune informazi
- Page 214:
[13] I.N. Sneddon, Special Function