Prise en Charge de la Fibrillation Auriculaire - Cardiologie ...
Prise en Charge de la Fibrillation Auriculaire - Cardiologie ...
Prise en Charge de la Fibrillation Auriculaire - Cardiologie ...
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
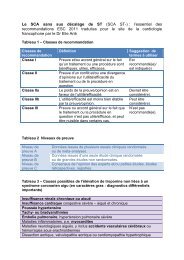
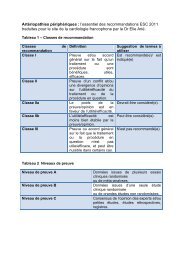
Choix d’un antiarythmique pour le contrôle <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> FARecommandations Niveau Gra<strong>de</strong>Les médicam<strong>en</strong>ts anti-arythmiques suivants sont recommandés pour lecontrôle du rythme chez les pati<strong>en</strong>ts <strong>en</strong> FA, <strong>en</strong> fonction <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong>cardiopathie sous-jac<strong>en</strong>te:amiodaronedronedarone I Aflecaini<strong>de</strong> I Apropaf<strong>en</strong>one I AsotalolIAL’amiodarone est plus efficace <strong>en</strong> terme <strong>de</strong> mainti<strong>en</strong> du rythme sinusalque le sotalol, <strong>la</strong> propafénone, le flécaïni<strong>de</strong> (par analogie), ou <strong>la</strong>Adronédarone (niveau A), mais <strong>en</strong> raison <strong>de</strong> sa toxicité, elle doit êtreIutilisée lorsque les autres ag<strong>en</strong>ts ont échoué ou sont contre-indiqués(niveau C).Chez les pati<strong>en</strong>ts <strong>en</strong> insuffisance cardiaque sévère, c<strong>la</strong>sse NYHA III et IVou c<strong>la</strong>sse NYHA II instable (décomp<strong>en</strong>sation durant le mois précéd<strong>en</strong>t),l'amiodarone doit être le médicam<strong>en</strong>t <strong>de</strong> choix. I BEn cas <strong>de</strong> cardiopathie significative sous-jac<strong>en</strong>te, le traitem<strong>en</strong>tantiarythmique initial doit être choisi parmi <strong>la</strong> dronédarone, le flécaïni<strong>de</strong>,<strong>la</strong> propafénone et le sotalol. I AIALes β-bloquants sont recommandés pour <strong>la</strong> prév<strong>en</strong>tion <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> FAadrénergique.Si un médicam<strong>en</strong>t anti-arythmique ne parvi<strong>en</strong>t pas à réduire le taux <strong>de</strong>srécidives <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> FA à un niveau cliniquem<strong>en</strong>t acceptable, l'utilisation d’unautre médicam<strong>en</strong>t anti-arythmique doit être <strong>en</strong>visagée.IIIaCCLa dronédarone doit être <strong>en</strong>visagée afin <strong>de</strong> réduire les hospitalisationscardiovascu<strong>la</strong>ires chez les pati<strong>en</strong>ts avec FA non perman<strong>en</strong>te et <strong>de</strong>sfacteurs <strong>de</strong> risque cardiovascu<strong>la</strong>ires.IIaBLes β-bloquants doiv<strong>en</strong>t être <strong>en</strong>visagés pour le contrôle du rythme (et <strong>de</strong><strong>la</strong> fréqu<strong>en</strong>ce) chez les pati<strong>en</strong>ts prés<strong>en</strong>tant un premier épiso<strong>de</strong> <strong>de</strong> FA. IIa CLe disopyrami<strong>de</strong> peut être <strong>en</strong>visagé chez les pati<strong>en</strong>ts avec une FA vagale.IIbB