Connecteurs de commande M 23 / Boîtiers
Connecteurs de commande M 23 / Boîtiers
Connecteurs de commande M 23 / Boîtiers
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
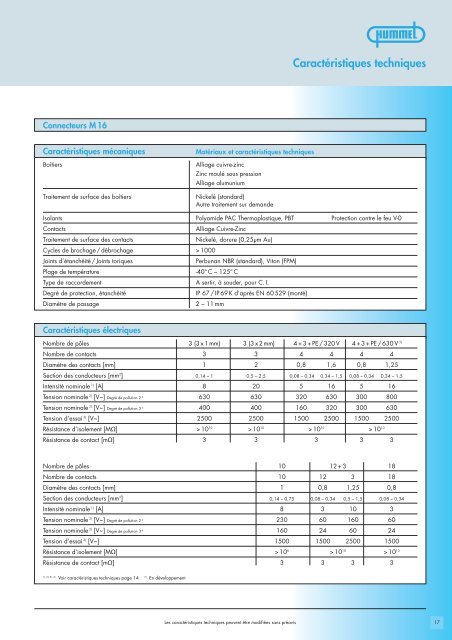
Caractéristiques techniques<br />
<strong>Connecteurs</strong> M 16<br />
Caractéristiques mécaniques<br />
<strong>Boîtiers</strong><br />
Traitement <strong>de</strong> surface <strong>de</strong>s boîtiers<br />
Matériaux et caractéristiques techniques<br />
Alliage cuivre-zinc<br />
Zinc moulé sous pression<br />
Alliage alumunium<br />
Nickelé (standard)<br />
Autre traitement sur <strong>de</strong>man<strong>de</strong><br />
Isolants Polyami<strong>de</strong> PAC Thermoplastique, PBT Protection contre le feu V-0<br />
Contacts<br />
Alliage Cuivre-Zinc<br />
Traitement <strong>de</strong> surface <strong>de</strong>s contacts<br />
Nickelé, dorure (0,25µm Au)<br />
Cycles <strong>de</strong> brochage / débrochage > 1000<br />
Joints d’étanchéité / Joints toriques<br />
Perbunan NBR (standard), Viton (FPM)<br />
Plage <strong>de</strong> température<br />
-40° C – 125° C<br />
Type <strong>de</strong> raccor<strong>de</strong>ment A sertir, à sou<strong>de</strong>r, pour C. I.<br />
Degré <strong>de</strong> protection, étanchéité<br />
IP 67 / IP 69 K d’après EN 60 529 (monté)<br />
Diamètre <strong>de</strong> passage<br />
2 – 11 mm<br />
Caractéristiques électriques<br />
Nombre <strong>de</strong> pôles<br />
Nombre <strong>de</strong> contacts<br />
Diamètre <strong>de</strong>s contacts [mm]<br />
Section <strong>de</strong>s conducteurs [mm 2 ]<br />
Intensité nominale 1) [A]<br />
Tension nominale 2) [V~] Degré <strong>de</strong> pollution 2 4)<br />
Tension nominale 2) [V~] Degré <strong>de</strong> pollution 3 4)<br />
Tension d’essai 3) [V~]<br />
Résistance d’isolement [MΩ]<br />
Résistance <strong>de</strong> contact [mΩ]<br />
3 (3 x 1 mm) 3 (3 x 2 mm) 4 + 3 + PE / 320 V 4 + 3 + PE / 630 V 5)<br />
3 3 4 4 4 4<br />
1 2 0,8 1,6 0,8 1,25<br />
0,14 – 1 0,5 – 2,5 0,08 – 0,34 0,34 – 1,5 0,08 – 0,34 0,34 – 1,5<br />
8 20 5 16 5 16<br />
630 630 320 630 300 800<br />
400 400 160 320 300 630<br />
2500 2500 1500 2500 1500 2500<br />
> 10 10 > 10 10 > 10 10 > 10 10<br />
3 3 3 3 3<br />
Nombre <strong>de</strong> pôles<br />
Nombre <strong>de</strong> contacts<br />
Diamètre <strong>de</strong>s contacts [mm]<br />
Section <strong>de</strong>s conducteurs [mm 2 ]<br />
Intensité nominale 1) [A]<br />
Tension nominale 2) [V~] Degré <strong>de</strong> pollution 2 4)<br />
Tension nominale 2) [V~] Degré <strong>de</strong> pollution 3 4)<br />
Tension d’essai 3) [V~]<br />
Résistance d’isolement [MΩ]<br />
Résistance <strong>de</strong> contact [mΩ]<br />
10 12 + 3 18<br />
10 12 3 18<br />
1 0,8 1,25 0,8<br />
0,14 – 0,75 0,08 – 0,34 0,5 – 1,5 0,08 – 0,34<br />
8 3 10 3<br />
<strong>23</strong>0 60 160 60<br />
160 24 60 24<br />
1500 1500 2500 1500<br />
> 10 6 > 10 10 > 10 10<br />
3 3 3 3<br />
1), 2), 3), 4)<br />
Voir caractéristiques techniques page 14<br />
5)<br />
En développement<br />
Les caractéristiques techniques peuvent être modifiées sans préavis<br />
17