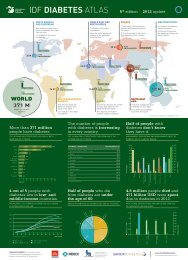
Autosurveillance - International Diabetes Federation
Autosurveillance - International Diabetes Federation
Autosurveillance - International Diabetes Federation
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Directive sur l’autosurveillance glycémique<br />
dans le diabète de type 2 non traité par l’insuline<br />
9. Bibliographie<br />
1. <strong>International</strong> <strong>Diabetes</strong> <strong>Federation</strong>. <strong>Diabetes</strong> Facts<br />
and Figures. 2008 Accessed November 1, 06<br />
2. United Nations GA. Resolution 61/225. <strong>Diabetes</strong><br />
Day. 2007. Ref Type: Bill/Resolution<br />
3. <strong>Diabetes</strong> Control and Complications Trial (DCCT)<br />
Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment<br />
of diabetes on the development and progression<br />
of long-term complications in insulin-dependent<br />
diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:977-986.<br />
4. <strong>Diabetes</strong> Control and Complications Trial (DCCT)<br />
Research Group. The relationship of glycemic<br />
exposure (HbA 1c<br />
) to the risk of development and<br />
progression of retinopathy in the diabetes control<br />
and complications trial. <strong>Diabetes</strong>. 1995;44:968-983.<br />
5. Ohkubo Y, Kishikawa H, Araki E et al. Intensive<br />
insulin therapy prevents the progression of diabetic<br />
microvascular complications in Japanese patients<br />
with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: a<br />
randomized prospective 6-year study. <strong>Diabetes</strong> Res<br />
Clin Pract. 1995;28:103-117.<br />
6. UK Prospective <strong>Diabetes</strong> Study (UKPDS) Group.<br />
Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas<br />
or insulin compared with conventional treatment<br />
and risk of complications in patients with type 2<br />
diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet. 1998;352:837-853.<br />
7. Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J et al. Intensive<br />
blood glucose control and vascular outcomes<br />
in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med.<br />
2008;358:2560-2572.<br />
8. Coutinho M, Gerstein HC, Wang Y et al. The<br />
relationship between glucose and incident<br />
cardiovascular events. A metaregression analysis of<br />
published data from 20 studies of 95,783 individuals<br />
followed for 12.4 years. <strong>Diabetes</strong> Care. 1999;22:233-240.<br />
9. Stettler C, Allemann S, Juni P et al. Glycemic control<br />
and macrovascular disease in types 1 and 2 diabetes<br />
mellitus: Meta-analysis of randomized trials. Am<br />
Heart J. 2006;152:27-38.<br />
10. Anselmino M, Ohrvik J, Malmberg K et al. Glucose<br />
lowering treatment in patients with coronary<br />
artery disease is prognostically important not only<br />
in established but also in newly detected diabetes<br />
mellitus: a report from the Euro Heart Survey on<br />
<strong>Diabetes</strong> and the Heart. Eur Heart J. 2008;29:177-184.<br />
11. Nathan DM, Cleary PA, Backlund JY et al. Intensive<br />
diabetes treatment and cardiovascular disease<br />
in patients with type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med.<br />
2005;353:2643-2653.<br />
33