La dystocie cervicale et la stagnation de la dilatation
La dystocie cervicale et la stagnation de la dilatation
La dystocie cervicale et la stagnation de la dilatation
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
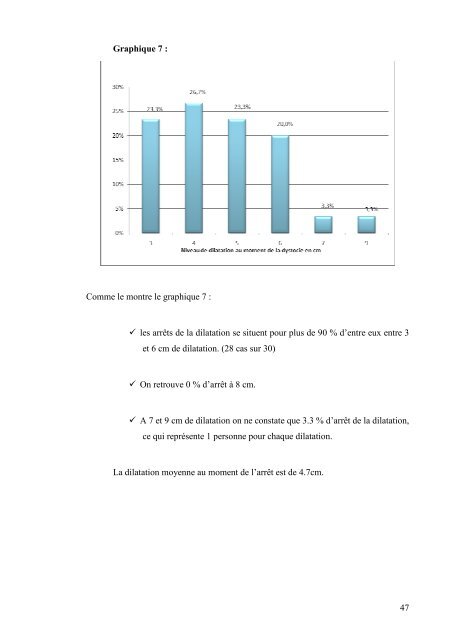
Graphique 7 :<br />
Comme le montre le graphique 7 :<br />
les arrêts <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> di<strong>la</strong>tation se situent pour plus <strong>de</strong> 90 % d’entre eux entre 3<br />
<strong>et</strong> 6 cm <strong>de</strong> di<strong>la</strong>tation. (28 cas sur 30)<br />
On r<strong>et</strong>rouve 0 % d’arrêt à 8 cm.<br />
A 7 <strong>et</strong> 9 cm <strong>de</strong> di<strong>la</strong>tation on ne constate que 3.3 % d’arrêt <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> di<strong>la</strong>tation,<br />
ce qui représente 1 personne pour chaque di<strong>la</strong>tation.<br />
<strong>La</strong> di<strong>la</strong>tation moyenne au moment <strong>de</strong> l’arrêt est <strong>de</strong> 4.7cm.<br />
47