Tema 3. Señales y sistemas en tiempo discreto. Introducción: ⢠Las ...
Tema 3. Señales y sistemas en tiempo discreto. Introducción: ⢠Las ...
Tema 3. Señales y sistemas en tiempo discreto. Introducción: ⢠Las ...
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
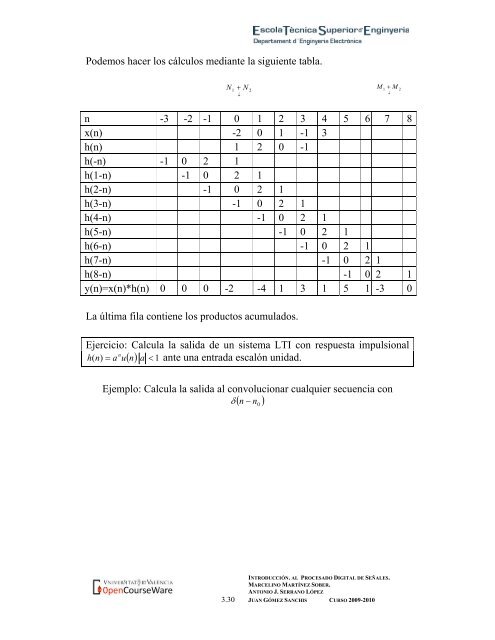
Podemos hacer los cálculos mediante la sigui<strong>en</strong>te tabla.N1+ NM21+ M2↓↓n -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8x(n) -2 0 1 -1 3h(n) 1 2 0 -1h(-n) -1 0 2 1h(1-n) -1 0 2 1h(2-n) -1 0 2 1h(3-n) -1 0 2 1h(4-n) -1 0 2 1h(5-n) -1 0 2 1h(6-n) -1 0 2 1h(7-n) -1 0 2 1h(8-n) -1 0 2 1y(n)=x(n)*h(n) 0 0 0 -2 -4 1 3 1 5 1 -3 0La última fila conti<strong>en</strong>e los productos acumulados.Ejercicio: Calcula la salida de un sistema LTI con respuesta impulsionalnh( n)= a u( n) a < 1 ante una <strong>en</strong>trada escalón unidad.Ejemplo: Calcula la salida al convolucionar cualquier secu<strong>en</strong>cia conδ ( n − n 0)INTRODUCCIÓN. AL PROCESADO DIGITAL DE SEÑALES.MARCELINO MARTÍNEZ SOBER.ANTONIO J. SERRANO LÓPEZ<strong>3.</strong>30 JUAN GÓMEZ SANCHIS CURSO 2009-2010