Untitled - Roche Trasplantes
Untitled - Roche Trasplantes
Untitled - Roche Trasplantes
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
EARLY DIAGNOSIS OF CHRONIC ALLOGRAFT NEPHROPATHY<br />
BY MEANS OF PROTOCOL BIOPSIES<br />
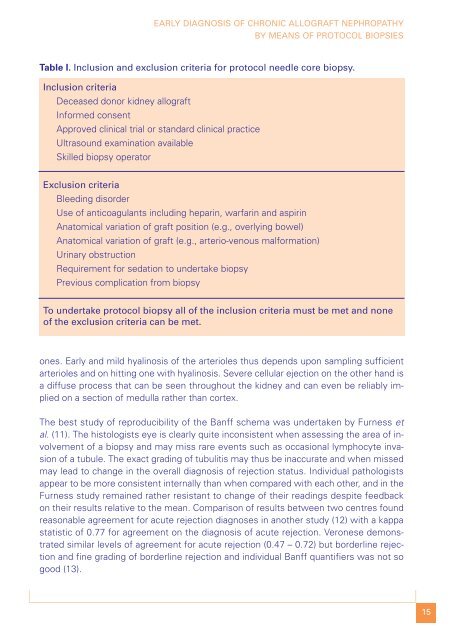
Table I. Inclusion and exclusion criteria for protocol needle core biopsy.<br />
Inclusion criteria<br />
Deceased donor kidney allograft<br />
Informed consent<br />
Approved clinical trial or standard clinical practice<br />
Ultrasound examination available<br />
Skilled biopsy operator<br />
Exclusion criteria<br />
Bleeding disorder<br />
Use of anticoagulants including heparin, warfarin and aspirin<br />
Anatomical variation of graft position (e.g., overlying bowel)<br />
Anatomical variation of graft (e.g., arterio-venous malformation)<br />
Urinary obstruction<br />
Requirement for sedation to undertake biopsy<br />
Previous complication from biopsy<br />
To undertake protocol biopsy all of the inclusion criteria must be met and none<br />
of the exclusion criteria can be met.<br />
ones. Early and mild hyalinosis of the arterioles thus depends upon sampling sufficient<br />
arterioles and on hitting one with hyalinosis. Severe cellular ejection on the other hand is<br />
a diffuse process that can be seen throughout the kidney and can even be reliably implied<br />
on a section of medulla rather than cortex.<br />
The best study of reproducibility of the Banff schema was undertaken by Furness et<br />
al. (11). The histologists eye is clearly quite inconsistent when assessing the area of involvement<br />
of a biopsy and may miss rare events such as occasional lymphocyte invasion<br />
of a tubule. The exact grading of tubulitis may thus be inaccurate and when missed<br />
may lead to change in the overall diagnosis of rejection status. Individual pathologists<br />
appear to be more consistent internally than when compared with each other, and in the<br />
Furness study remained rather resistant to change of their readings despite feedback<br />
on their results relative to the mean. Comparison of results between two centres found<br />
reasonable agreement for acute rejection diagnoses in another study (12) with a kappa<br />
statistic of 0.77 for agreement on the diagnosis of acute rejection. Veronese demonstrated<br />
similar levels of agreement for acute rejection (0.47 – 0.72) but borderline rejection<br />
and fine grading of borderline rejection and individual Banff quantifiers was not so<br />
good (13).<br />
15