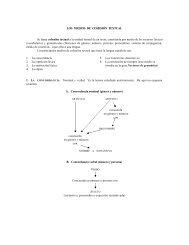
No cumple el axioma de completitud ya que si tomamos una parte ...
No cumple el axioma de completitud ya que si tomamos una parte ...
No cumple el axioma de completitud ya que si tomamos una parte ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Caso 2: Si los <strong>de</strong>nominadores <strong>de</strong> las fracciones son diferentes, se proce<strong>de</strong> <strong>si</strong>guiendo la<br />
<strong>si</strong>guiente regla.<br />
sean a,<br />
b,<br />
c,<br />
d ∈ R,<br />
Ejemplo:<br />
2 3<br />
+ =<br />
5 6<br />
2<br />
con b,<br />
d ≠ 0,<br />
( 6)<br />
+ 5(<br />
3)<br />
12 + 15 27<br />
= =<br />
5(<br />
6)<br />
30 30<br />
entonces<br />
a c ad ± bc<br />
± =<br />
b d bd<br />
MULTIPLICACION DE FRACCIONES<br />
Para multiplicar fracciones se multiplica numerador con numerador y <strong>de</strong>nominador con<br />
<strong>de</strong>nominador es <strong>de</strong>cir, la multiplicación <strong>de</strong> fracciones es lineal.<br />
a c ac<br />
sean a,<br />
b,<br />
c,<br />
d ∈ R, con b,<br />
d ≠ 0,<br />
entonces ⋅ =<br />
b d bd<br />
Ejemplo:<br />
5 9<br />
× =<br />
2 4<br />
5<br />
2<br />
( 9)<br />
=<br />
( 4)<br />
8<br />
45<br />
DIVISION DE FRACCIONES<br />
Para dividir fracciones se multiplica en cruz, numerador <strong>de</strong> la primera fracción por<br />
<strong>de</strong>nominador <strong>de</strong> la segunda fracción y <strong>de</strong>nominador <strong>de</strong> la primera por numerador <strong>de</strong> la<br />
segunda es <strong>de</strong>cir, la divi<strong>si</strong>ón <strong>de</strong> fracciones es cruzada.<br />
a c ad<br />
sean a,<br />
b,<br />
c,<br />
d ∈ R, con b,<br />
c,<br />
d ≠ 0,<br />
entonces ÷ =<br />
b d bc<br />
Ejemplo:<br />
5 9 5<br />
÷ =<br />
3 7 3<br />
( 7)<br />
35<br />
=<br />
( 9)<br />
27<br />
Existe <strong>una</strong> forma <strong>de</strong> transformar las divi<strong>si</strong>ones en multiplicaciones, esta con<strong>si</strong>ste en invertir<br />
<strong>el</strong> or<strong>de</strong>n <strong>de</strong> la segunda fracción, es <strong>de</strong>cir <strong>el</strong> numerador pasa a ser <strong>de</strong>nominador y <strong>el</strong><br />
<strong>de</strong>nominador a ser numerador.<br />
67