Silyl Ethers - Thieme Chemistry
Silyl Ethers - Thieme Chemistry
Silyl Ethers - Thieme Chemistry
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Trimethylsilyl cyanide (TMSCN) is a reagent used for silylation where the presence of a<br />
base must be avoided. [26] Since the byproduct, hydrogen cyanide, is volatile and not sufficiently<br />
acidic to be deleterious, silylation can be carried out with the neat reagent or in a<br />
neutral solution. The reagent rapidly silylates alcohols, phenols and carboxylic acids, but<br />
reacts only slowly with amines and thiols. Amides are not silylated with this reagent. An<br />
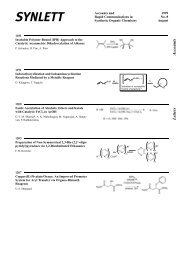
example illustrating the application of this reagent is the conversion of the sensitive<br />
calicheamicinone precursor 5 into its trimethylsilyl ether 7 via the tris(silyl ether) 6<br />
(Scheme 3). [27] It is noteworthy that only the primary trimethylsilyl ether of intermediate<br />
6 is cleaved during workup in the presence of aqueous acetic acid.<br />
Scheme 3 <strong>Silyl</strong>ation with Trimethylsilyl Cyanide [27]<br />
TESO<br />
NHCO2Me<br />
OH<br />
FOR PERSONAL USE ONLY<br />
374 Science of Synthesis 4.4 Silicon Compounds<br />
OBoc OBoc<br />
Me 3SiCN<br />
TESO<br />
HO TMSO<br />
5 6<br />
AcOH, H2O, THF<br />
99%<br />
NHCO2Me<br />
OTMS<br />
TESO<br />
HO<br />
OBoc<br />
7<br />
NHCO2Me<br />
OTMS<br />
Methyl 11-(tert-Butoxycarbonyloxy)-13-(2-hydroxyethylidene)-1-(triethylsiloxy)-8á-<br />
(trimethylsiloxy)bicyclo[7.3.1]trideca-4,9,11-triene-2,6-diyn-10-ylcarbamate (7): [27]<br />
A soln of 5 (465 mg, 0.85 mmol) in TMSCN (1 mL) was stirred for 30 min and the volatiles<br />
were evaporated in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in a mixture of THF (50 mL), H 2O<br />
(10 mL), and glacial AcOH (1 mL). The mixture was stirred for 30 min (with close monitoring<br />
by TLC, Et 2O/petroleum ether 1:1), diluted with Et 2O (150 mL), washed with sat. aq<br />
NaHCO 3 (2 ” 50 mL), dried (MgSO 4), filtered, and evaporated in vacuo to give 7 as a pale<br />
yellow, solid foam; yield: 518 mg (99%).<br />
4.4.17.1.4 Method 4:<br />
<strong>Silyl</strong>ation ofAlcohols with N,O-Bis(trimethylsilyl)acetamide<br />
N,O-Bis(trimethylsilyl)acetamide (BSA) is a relatively unselective reagent that can convert<br />
hindered alcohols into their trimethylsilyl ethers when used in dimethylformamide at elevated<br />
temperature (80±1008C). [28] The byproduct acetamide must be removed, often requiring<br />
chromatography for purification of the silyl ether. The related reagent N,O-bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide,<br />
[29] although used less frequently, has the advantage that<br />
the byproduct, trifluoroacetamide, is removed more easily since it is quite volatile. An application<br />
of N,O-bis(trimethylsilyl)acetamide is seen in the conversion of the alcohol 8<br />
into its trimethylsilyl ether 9 (Scheme 4), an intermediate in a synthetic route to azinomycin.<br />
[30]<br />
White, J. D.; Carter, R. G., SOS, (2002) 4, 371. 2002 Georg <strong>Thieme</strong> Verlag KG