Silyl Ethers - Thieme Chemistry
Silyl Ethers - Thieme Chemistry
Silyl Ethers - Thieme Chemistry
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
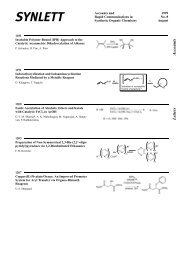
Scheme 22 Selective <strong>Silyl</strong>ation of Secondary Alcohols with tert-Butyldimethylsilyl Trifluoromethanesulfonate<br />
[54]<br />
HO<br />
HO OH<br />
H<br />
H<br />
TBDMSOTf, Et3N<br />
DMAP, CH2Cl2 −20<br />
87%<br />
oC, 30 min<br />
TBDMSO<br />
44 45<br />
HO OTBDMS<br />
H<br />
(1á,3â,4aá,5á,8â,8aá)-8-(tert-Butyldimethylsiloxy)-3-(tert-butyldimethylsiloxymethyl)-5isopropyl-3-methyldecahydro-1-naphthol<br />
(45): [54]<br />
To a stirred mixture of triol 44 (92 mg, 0.36 mmol), Et 3N (109 mg, 1.08 mmol), and DMAP<br />
(2 mg, 0.016 mmol) in CH 2Cl 2 (5 mL) at ±20 8C, was added TBDMSOTf (190 mg, 0.72 mmol).<br />
The mixture was stirred at ±208C for 30 min, diluted with Et 2O (40 mL), washed with 5%<br />
HCl (2 mL), brine (5 mL) and H 2O (5 mL), dried (Na 2SO 4), and concentrated in vacuo. Flash<br />
chromatography of the residue (silica gel, EtOAc/hexane 5:95) afforded 45 as a colorless<br />
oil; yield: 152 mg (87%).<br />
4.4.17.3.3 Method 3:<br />
Migration ofa tert-Butyldimethylsilyl Group from<br />
a tert-Butyldimethylsilyl Ether to an Alcohol<br />
The tert-butyldimethylsilyl group of a tert-butyldimethylsilyl ether will migrate to the oxygen<br />
atom of an adjacent alcohol under basic conditions if the new tert-butyldimethylsilyl<br />
ether is sterically less crowded than its precursor. [14] Thus, the direction of migration is<br />
invariably from a secondary to a primary alcohol or from a tertiary to either a secondary<br />
or primary alcohol. Migration between 1,2-substituted and 1,3-substituted diol derivatives<br />
is particularly common, although transfer of a tert-butyldimethylsilyl group between<br />
oxygens that span four or more carbons can occur if the oxygens are in spatial<br />
proximity. [16] The mechanism usually envisioned for these migrations involves intramolecular<br />
attack by an alkoxide oxygen on silicon to produce a pentacoordinate intermediate<br />
that collapses toward the more thermodynamically stable tert-butyldimethylsilyl<br />
ether. While silyl migration between oxygen atoms can pose an inconvenience in certain<br />
polyhydroxylated systems such as carbohydrates, where site-specific silylation may be desired,<br />
a virtue can be made of this chemistry in the deprotection of a silyl ether that may<br />
be difficult to cleave. Thus, if the silyl group can be forced to move to a less sterically<br />
crowded oxygen, its cleavage can become more facile.<br />
An example of an efficient migration of a tert-butyldimethylsilyl group is seen in the<br />
rearrangement of secondary tert-butyldimethylsilyl ether 46 to its isomeric primary silyl<br />
ether 47 (Scheme 23). [55]<br />
Scheme 23 Rearrangement of a Secondary tert-Butyldimethylsilyl Ether<br />
to a Primary tert-Butyldimethylsilyl Ether [55]<br />
OTBDMS<br />
F3C OH<br />
46<br />
FOR PERSONAL USE ONLY<br />
4.4.17 <strong>Silyl</strong> <strong>Ethers</strong> 387<br />
t-BuOK, THF/DMF (1:4)<br />
−78 oC, 4 h<br />
99%<br />
OH<br />
47<br />
H<br />
F 3C OTBDMS<br />
Another example, in this case involving migration of the tert-butyldimethylsilyl group<br />
from a tertiary to a secondary alcohol, occurred in the course of an approach to the core<br />
structure of esperamicin A. [56] The rearrangement was triggered by S,S-diphenylsulfil-<br />
for references see p 410<br />
White, J. D.; Carter, R. G., SOS, (2002) 4, 371. 2002 Georg <strong>Thieme</strong> Verlag KG