watervulnerability
watervulnerability watervulnerability
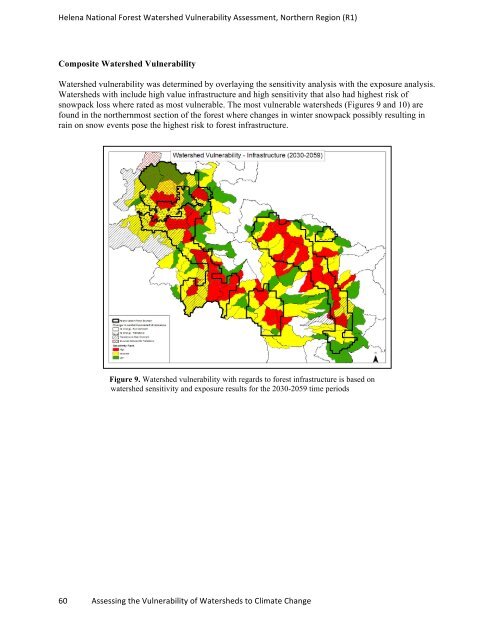
Helena National Forest Watershed Vulnerability Assessment, Northern Region (R1) Composite Watershed Vulnerability Watershed vulnerability was determined by overlaying the sensitivity analysis with the exposure analysis. Watersheds with include high value infrastructure and high sensitivity that also had highest risk of snowpack loss where rated as most vulnerable. The most vulnerable watersheds (Figures 9 and 10) are found in the northernmost section of the forest where changes in winter snowpack possibly resulting in rain on snow events pose the highest risk to forest infrastructure. Figure 9. Watershed vulnerability with regards to forest infrastructure is based on watershed sensitivity and exposure results for the 2030-2059 time periods 60 Assessing the Vulnerability of Watersheds to Climate Change
Helena National Forest Watershed Vulnerability Assessment, Northern Region (R1) Figure 10. Watershed vulnerability with regards to forest infrastructure is based on watershed sensitivity and exposure results for the 2070-2099 time periods CONNECTIONS TO OTHER ASSESSMENTS AND POTENTIAL APPLICATIONS • The WVA will provide a basis for incorporating climate change considerations into project planning and implementation. Identified climate change considerations may also be designed into forest plan desired conditions, objectives, and standards and guidelines. • Information from the WVA, while not specifically part of the watershed condition framework, can be used to help identify priority watersheds for future restoration activities. • Completing the WVA will aide in the completion of the climate change scorecard. The WVA analysis helps fulfill element 6 (vulnerability assessment), element 7 (adaptation activities), and element 8 (monitoring). • The WVA utilized work done by the Fisheries Watershed Baseline for the bull trout and Cutthroat trout sensitivity analysis. CRITIQUE What important questions were not considered? 1. The watershed vulnerability assessment focused only on water resources and did not consider predicted changes to terrestrial resources. While this analysis was designed to focus on water resources, composite effects on terrestrial ecosystems can have significant influence on watershed hydrology. 2. Did not account for all resilience factors and did not use all climate exposure factors, including flow metrics. 61 Assessing the Vulnerability of Watersheds to Climate Change
- Page 14 and 15: NF (Region 8) relied on information
- Page 16 and 17: level of uncertainty. Though there
- Page 18 and 19: climate (Casola et al. 2005). Only
- Page 20 and 21: sensitivity. Most were derived from
- Page 22 and 23: The sensitivity evaluation typicall
- Page 24 and 25: in exposure. The result of combinin
- Page 26 and 27: highest priority for management act
- Page 28 and 29: to information affected the assessm
- Page 30 and 31: with and rely on in many resource d
- Page 32 and 33: Pilot National Forest Reports Conte
- Page 34 and 35: Assessment of Watershed Vulnerabili
- Page 36 and 37: Gallatin National Forest Watershed
- Page 38 and 39: Gallatin National Forest Watershed
- Page 40 and 41: Gallatin National Forest Watershed
- Page 42 and 43: Gallatin National Forest Watershed
- Page 44 and 45: Gallatin National Forest Watershed
- Page 46 and 47: Gallatin National Forest Watershed
- Page 48 and 49: Gallatin National Forest Watershed
- Page 50 and 51: Assessment of Watershed Vulnerabili
- Page 52 and 53: Helena National Forest Watershed Vu
- Page 54 and 55: Helena National Forest Watershed Vu
- Page 56 and 57: Helena National Forest Watershed Vu
- Page 58 and 59: Helena National Forest Watershed Vu
- Page 60 and 61: Helena National Forest Watershed Vu
- Page 62 and 63: Helena National Forest Watershed Vu
- Page 66 and 67: Helena National Forest Watershed Vu
- Page 68 and 69: Assessment of Watershed Vulnerabili
- Page 70 and 71: Grand Mesa, Uncompahgre and Gunniso
- Page 72 and 73: Grand Mesa, Uncompahgre and Gunniso
- Page 74 and 75: Grand Mesa, Uncompahgre and Gunniso
- Page 76 and 77: Grand Mesa, Uncompahgre and Gunniso
- Page 78 and 79: Grand Mesa, Uncompahgre and Gunniso
- Page 80 and 81: Grand Mesa, Uncompahgre and Gunniso
- Page 82 and 83: Grand Mesa, Uncompahgre and Gunniso
- Page 84 and 85: Grand Mesa, Uncompahgre and Gunniso
- Page 86 and 87: Grand Mesa, Uncompahgre and Gunniso
- Page 88 and 89: Grand Mesa, Uncompahgre and Gunniso
- Page 90 and 91: Grand Mesa, Uncompahgre and Gunniso
- Page 92 and 93: Grand Mesa, Uncompahgre and Gunniso
- Page 94 and 95: Grand Mesa, Uncompahgre and Gunniso
- Page 96 and 97: Grand Mesa, Uncompahgre and Gunniso
- Page 98 and 99: Grand Mesa, Uncompahgre and Gunniso
- Page 100 and 101: Grand Mesa, Uncompahgre and Gunniso
- Page 102 and 103: Grand Mesa, Uncompahgre and Gunniso
- Page 104 and 105: Grand Mesa, Uncompahgre and Gunniso
- Page 106 and 107: Grand Mesa, Uncompahgre and Gunniso
- Page 108 and 109: Grand Mesa, Uncompahgre and Gunniso
- Page 110 and 111: Grand Mesa, Uncompahgre and Gunniso
- Page 112 and 113: Grand Mesa, Uncompahgre and Gunniso
Helena National Forest Watershed Vulnerability Assessment, Northern Region (R1)<br />
Composite Watershed Vulnerability<br />
Watershed vulnerability was determined by overlaying the sensitivity analysis with the exposure analysis.<br />
Watersheds with include high value infrastructure and high sensitivity that also had highest risk of<br />
snowpack loss where rated as most vulnerable. The most vulnerable watersheds (Figures 9 and 10) are<br />
found in the northernmost section of the forest where changes in winter snowpack possibly resulting in<br />
rain on snow events pose the highest risk to forest infrastructure.<br />
Figure 9. Watershed vulnerability with regards to forest infrastructure is based on<br />
watershed sensitivity and exposure results for the 2030-2059 time periods<br />
60 Assessing the Vulnerability of Watersheds to Climate Change