XIX Sympozjum Srodowiskowe PTZE - materialy.pdf
XIX Sympozjum Srodowiskowe PTZE - materialy.pdf
XIX Sympozjum Srodowiskowe PTZE - materialy.pdf
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>XIX</strong> <strong>Sympozjum</strong> <strong>PTZE</strong>, Worliny 2009<br />
DIRECT PREISACH HYSTERESIS MODELS<br />
FOR FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS<br />
OF EDDY CURRENT FIELD<br />
Daniel Marcsa, Miklos Kuczmann<br />
Széchenyi István Egyetem, Laboratory of Electromagnetic Fields<br />
Egyetem tér 1, Győr, H-9026, Hungary<br />
The full paper deals with the numerical analysis of the Problem No. 32 of TEAM Workshops<br />
[1] based on the eddy current field computation taking the ferromagnetic hysteresis account.<br />
The direct (H-based) scalar Preisach hysteresis model [2,4] is integrated on a two-dimensional<br />
time-stepping finite element analysis [2,3,4]. The interface between the Preisach model and<br />
the finite element eddy current field formulation is the Fixed-Point iterative technique [2-5],<br />
which seems to be the most widely used numerical scheme for handling the nonlinearities<br />
introduced by the magnetic hysteresis phenomenon. Here, the problem is a nonlinear eddy<br />
current field problem.<br />
The two-dimensional time-stepping eddy current field potential formulations is the T,Φ – Φ -<br />
potential formulation [3] with direct model of nonlinear constitutive relations. The T,Φ – Φ -<br />
formulation is make it possible the direct model of constitutive relations [2,4], because of the<br />
primary quantity of this formulation is the magnetic field intensity H. In this formulation the<br />
nonlinear constitutive relations between H and B is the following<br />
B µ H + R , (1)<br />
= FP<br />
where µFP is a properly chosen constant, the ideal permeability (Fixed-Point coefficient), and<br />
R is a residual nonlinearity (Fixed-Point residual), which has to be determined iteratively.<br />
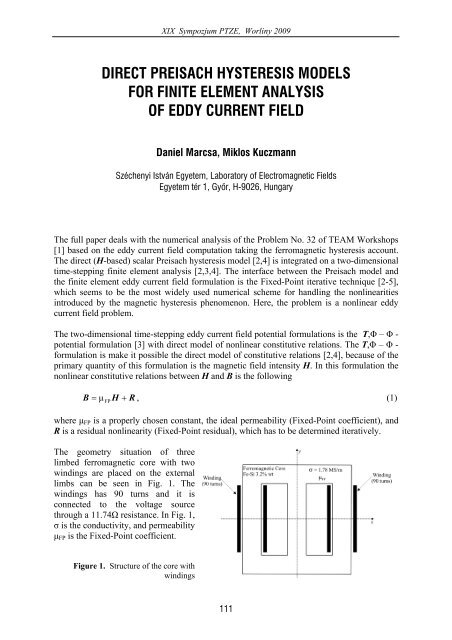
The geometry situation of three<br />
limbed ferromagnetic core with two<br />
windings are placed on the external<br />
limbs can be seen in Fig. 1. The<br />
windings has 90 turns and it is<br />
connected to the voltage source<br />
through a 11.74Ω resistance. In Fig. 1,<br />
σ is the conductivity, and permeability<br />
µFP is the Fixed-Point coefficient.<br />
Figure 1. Structure of the core with<br />
windings<br />
111