Geologic Time and Earth History - Elmhurst College
Geologic Time and Earth History - Elmhurst College
Geologic Time and Earth History - Elmhurst College
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Geologic</strong> <strong>Time</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Earth</strong> <strong>History</strong><br />
Dr. R. B. Schultz
<strong>Geologic</strong> <strong>Time</strong><br />
How do geologists determine how old rocks are?<br />
Relative age dating -- determine whether the rock is older or younger than<br />
other rocks relative to one another<br />
Absolute age dating -- use radiometric dating techniques to determine how<br />
old rock is in the exact number of years<br />
Not all rocks can be dated absolutely, so combinations of techniques are used.<br />
By examining layers of sedimentary rock, geologists developed a time scale for<br />
dividing up earth history.<br />
Early in the 20 th century, radiometric-dating techniques allowed scientists to<br />
put absolute dates on divisions in the geologic time scale.<br />
In this segment, we will learn how geologists:<br />
Determine the relative ages of rock units,<br />
Determined <strong>and</strong> named the divisions of the geologic time scale, <strong>and</strong><br />
Use radiometric techniques can be used to date some rocks.
So, what is Absolute Age Dating?<br />
Uses radiometric Dating Techniques<br />
Use naturally-occurring radioactive isotopes<br />
Isotope: form of an element that has additional neutrons<br />
Radioisotope -- isotope that spontaneously decays, giving off radiation<br />
Rate of Radioactive Decay is important:<br />
Radioisotopes decay at a constant rate.<br />
Rate of decay is measured by half-life<br />
Half-life: Half life: time it takes for one-half of the radioactive material to decay.<br />
Decay products<br />
Radioisotopes may decay to form a different isotope or a stable isotope.<br />
Stable isotope is called the "daughter daughter" formed from decay of radioactive "parent parent"<br />
Exactly how is this accomplished?<br />
Radioisotopes are trapped in minerals when they crystallize.<br />
Radioisotopes decay through time, <strong>and</strong> stable isotopes are formed.<br />
Scientists determine the ratio of parent isotope to daughter product which reveals the<br />
number of half-lives that has elapsed.<br />
Common isotopes used in age dating<br />
U-Pb -- half-life of U-238 is 4.5 b.y.<br />
K-Ar -- half-life of K-40 is 1.3 b.y.<br />
Rb-Sr -- half-life of Rb-87 is 47 b.y.<br />
Carbon 14 -- half-life of C-14 is 5730 yrs
Absolute Dating Example<br />
If one knows the half-life of a given isotope, <strong>and</strong> can accurately measure the<br />
quantity of the isotope present in the rock, one can deduce how long it has<br />
taken to decay down to the present amount in the rock.<br />
Example: All living things have carbon, including carbon-14 (radioactive<br />
isotope). In that way, there is a known ratio of carbon-14 to carbon-12 in all<br />
living things.<br />
If a rock has 0.5 (one-half) of the original carbon 14 material in it, one can<br />
deduce that, knowing the half-life of carbon-14 is 5730 years, the rock must<br />
have decayed (lost) 50% of its original carbon-14 material <strong>and</strong> is now 5730<br />
years old.<br />
In a period of 5730 years from now, the rock will contain .25 (25%) of its<br />
original carbon 14-material, <strong>and</strong> will be 11,460 years old.<br />
Theoretically, there will always be some trace of carbon 14 present in the<br />
rock…it will never decay totally.
Gradualists vs. Catastrophists<br />
Interpreting the rock record:<br />
James Ussher (1581-1656), Archbishop of Armagh, Primate of All Irel<strong>and</strong>, <strong>and</strong><br />
Vice-Chancellor of Trinity <strong>College</strong> in Dublin was highly regarded in his day as a<br />
churchman <strong>and</strong> as a scholar.<br />
Having established the first day of creation as Sunday 26 October 4004 BC at<br />
9:00 a.m., Ussher calculated the dates of other biblical events, concluding,<br />
for example, that Adam <strong>and</strong> Eve were driven from Paradise on Monday 10<br />
November 4004 BC, <strong>and</strong> that the ark touched down on Mt Ararat on 5 May 1491<br />
BC `on a Wednesday'.<br />
In the 1600’s, prior to geologic principles, Archbishop James Ussher calculated<br />
the age of the <strong>Earth</strong> at 6006 years old <strong>and</strong> was not questioned until nearly 100<br />
years later.<br />
Principle of Uniformitarianism:<br />
James Hutton, late 1700s – (considered to be "Father of Geology") questioned<br />
Ussher’s calculations <strong>and</strong> debated his “scientific methods”.<br />
Hutton realized that most sedimentary layers were deposited from gradual,<br />
day-to-day processes. He realized that it took a long time to form these rocks.<br />
This was far different from what others believed prior to this time.<br />
"Present is the key to the past" -- whatever processes are occurring today<br />
(plate tectonics, volcanism, mountain building, earthquakes, sedimentation)<br />
also occurred in the past <strong>and</strong> probably at the same (or very comparable) rates.<br />
Hutton wrote “Theory of the <strong>Earth</strong>, or an Investigation of the Laws Observable<br />
in the Composition, Dissolution <strong>and</strong> Restoration of L<strong>and</strong> upon the Globe” <strong>and</strong><br />
began a major controversy.
What is Relative Age Dating?<br />
The comparing of rock units to decipher their age relative to one another<br />
James Hutton used many of the following principles which underlie modern geology:<br />
Principle of Superposition<br />
Rock layer above is younger than the ones below it.<br />
Oldest on bottom, youngest on top<br />
Principle of Original Horizontality<br />
Sedimentary layers are deposited in approximately horizontal sheets.<br />
If layers are folded, episode of deformation must have occurred after rocks formed.<br />
Principle of Crosscutting Relationships<br />
Any feature (e.g. fault or intrusion) that cuts across rocks is younger than the youngest<br />
rock that is cut.<br />
Principle of Faunal Succession<br />
Organisms have evolved <strong>and</strong> gone extinct through time<br />
Fossil content of rock changes in a systematic way, reflecting evolutionary changes<br />
Fossil content can be used to help determine age of rock <strong>and</strong> correlate rocks.<br />
Paraphrased as "Organisms within rock units change with time".
Example of Relative Age Dating <strong>and</strong> Correlation
Relative Age Dating
Original<br />
Horizontality<br />
Illustration of Relative Age Principles<br />
Superposition<br />
Cross Cutting<br />
Relations
Correlation<br />
Correlation is determining<br />
that rocks are within the<br />
same formation in a<br />
different geographic<br />
location (may mean rocks<br />
are the same age)
Illustration of Principle of Faunal Succession
James Hutton also noticed that not only were the rock layers that were<br />
present important, but rock layers that were missing were also important.<br />
Unconformities<br />
Unconformities are surfaces in rock that represent periods of erosion or nondeposition.<br />
In other words, time has been left out of the physical geologic rock record.<br />
There are three (3) principal types of unconformities:<br />
Angular Unconformity<br />
Rocks above <strong>and</strong> below unconformity have different orientations.<br />
Rocks are at an angle <strong>and</strong> truncate at a horizontal layer.<br />
Easiest of the three types to recognize because the units are at an angle<br />
truncated with the units above them.<br />
Nonconformity<br />
Rocks in a horizontal fashion were eroded down to igneous bedrock material<br />
at which time subsequent deposition of sedimentary layers commenced.<br />
Represents the greatest amount of time left out of the geologic rock record.<br />
Disconformity<br />
Rocks in a nearly horizontal fashion were eroded <strong>and</strong> an erosional profile<br />
remains covered by subsequent sedimentary deposition.<br />
Most difficult to recognize because the units are nearly horizontal <strong>and</strong> only a<br />
small discontinuous layer can be observed (rubble zone or soil profile).<br />
Represents the least amount of time left out of the geologic rock record.
Unconformity Types Using Gr<strong>and</strong> Canyon as Example
Gr<strong>and</strong> Canyon Flyby
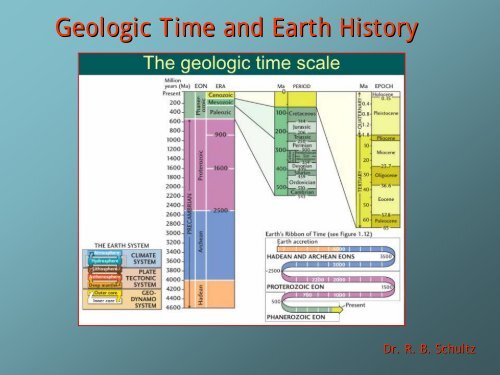
What is the <strong>Geologic</strong> <strong>Time</strong> Scale?<br />
A global scale constructed to correlate world-wide rock layers<br />
Developed in 1800s from relative dating of rocks<br />
More recently, radiometric techniques have allowed us to determine<br />
ages of units in years before present.<br />
Many of the names relate back to localities in Engl<strong>and</strong> (Ex: Devonian<br />
from Devonshire) or ancient peoples (Ordovcian from Olduvai)<br />
See this website for details of naming:<br />
http://www.geotech.org/survey/geotech/geotech6.html<br />
Divisions of <strong>Geologic</strong> <strong>Time</strong> Scale:<br />
Eons �Eras � Periods � Epochs
The <strong>Geologic</strong> <strong>Time</strong> Scale<br />
Most recent<br />
“Ice Age”<br />
“Humans”<br />
arrive<br />
Major Mass<br />
Extinction<br />
Age of<br />
Dinosaurs<br />
Major Mass<br />
Extinction<br />
Age of Coal<br />
Formation<br />
Age of Fishes<br />
First multicelled<br />
organisms<br />
Origin of the <strong>Earth</strong><br />
4.55 Billion years
How Do We Know What Killed the Dinosaurs?<br />
Investigating a small clay layer in Gubbio, Italy, Dr. Walter L. Alvarez discovered a layer<br />
with an unusually high concentration of iridium.<br />
This layer was found at the Cretaceous-Tertiary (K-T) Boundary. The Cretaceous period<br />
ended 65 million years ago. With the end of the Cretaceous period, so can the end of the<br />
dinosaurs <strong>and</strong> most other forms of life.<br />
Iridium is a dense <strong>and</strong> rare metal, <strong>and</strong> it is the most corrosion-resistant metal known to<br />
man. Iridium can be found in the core of the earth, but the levels found at the K-T<br />
Boundary were too high. Normally, iridium is found in concentrations of 0.3 parts per<br />
billion. The clay layer at Gubbio had concentration 30 times higher. Iridium is also found,<br />
in much higher levels, in asteroids.<br />
Alvarez <strong>and</strong> his team, which included his father Dr. Luis Alvarez, proposed that an<br />
asteroid hit the earth, throwing up a dust layer that encircled the earth <strong>and</strong> lead to the<br />
extinction of the dinosaurs.<br />
Since Alvarez’s proposal, more than 100 iridium rich deposits at the K-T Boundary have<br />
been found around the world. These additional sites support the theory set forth by Dr.<br />
Alvarez <strong>and</strong> his team.<br />
Additionally, a site for the asteroid impact has been proposed. It is believed that the 180mile<br />
crater in Chicxulub, on the Yucatan Peninsula, is the site of the asteroid that brought<br />
an end to the dinosaurs <strong>and</strong> most life forms at the end of the Cretaceous Period. This site<br />
was discovered in 1960, but it was not revealed until 1990, where it was met with very<br />
little interest.<br />
Today however, many scientists accept the buried 180-mile crater as the impact site of<br />
the asteroid, <strong>and</strong> many scientists also believe that this asteroid caused the extinction of<br />
the dinosaurs.
What Killed the Dinosaurs?
Can these meteorites hit anywhere on <strong>Earth</strong>?<br />
YES! The probability that the <strong>Earth</strong> will be struck<br />
again is 100%! We just don’t don t know when.
Key Terminology<br />
Relative age dating Absolute age dating<br />
Isotope Radioisotope<br />
Half-life Half life Daughter product<br />
Parent Material Archbishop Ussher<br />
James Hutton Uniformitarianism (Uniformity)<br />
Superposition Cross cutting relationships<br />
Original horizontality Faunal succession<br />
Correlation Unconformity<br />
Angular unconformity Disconformity<br />
Nonconformity <strong>Geologic</strong> time scale<br />
Eon Era<br />
Period Epoch<br />
Mass extinction Walter Alvarez