the advanced concept of small satellite integrated navigation system ...
the advanced concept of small satellite integrated navigation system ...
the advanced concept of small satellite integrated navigation system ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
GPS & GLONASS constellation and user motion model<br />
User<br />
attitude<br />
simulator<br />
E tr<br />
S<br />
User<br />
ephemerise<br />
generator<br />
X tr<br />
Calculator <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
"true" antennae <strong>system</strong> position<br />
in <strong>the</strong> inertial frame<br />
errors <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>system</strong><br />
initialization<br />
ephemerise<br />
errors<br />
User "On-Board" S<strong>of</strong>tware<br />
E ref<br />
s<br />
re f<br />
X s<br />
X ref<br />
ant<br />
S<br />
E* s<br />
X* s<br />
X tr<br />
ΔX N S<br />
ant<br />
GPS & GLONASS<br />
ephemerise<br />
generator<br />
X tr<br />
N S<br />
Definition <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> observed<br />
GPS & GLONASS <strong>satellite</strong>s<br />
X tr<br />
O N S<br />
Simulator <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
GPS & GLONASS<br />
<strong>navigation</strong>al message<br />
ref<br />
X (-30)<br />
O N S<br />
Integration <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> observed<br />
GPS & GLONASS <strong>satellite</strong>s<br />
reference trajectories<br />
ref<br />
X (t)<br />
O N S<br />
Formation <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
reference<br />
measurement results<br />
φ ref<br />
Calculator <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
reference antennae <strong>system</strong><br />
position in <strong>the</strong> inertial frame User attitude<br />
data processing<br />
algorithm<br />
OUTPUT<br />
DATA<br />
X tr<br />
O N S<br />
X tr<br />
set <strong>of</strong><br />
measurement errors<br />
Formation <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> "true"<br />
measurement results<br />
ant<br />
φ tr<br />
ref ref<br />
ρ , δρ<br />
User position & velocity<br />
data processing<br />
algorithm<br />
tr tr<br />
ρ , δρ<br />
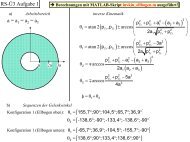
Fig. 4 Simplified diagram <strong>of</strong> simulation<br />
instant using all <strong>the</strong> observed <strong>navigation</strong>al <strong>satellite</strong>s, are<br />
considered as a complete sample to be processed by <strong>the</strong><br />
LMS method. As <strong>the</strong> result, it is not necessary to<br />
involve complete ma<strong>the</strong>matical model <strong>of</strong> angular<br />
<strong>satellite</strong> motion in <strong>the</strong> attitude determination algorithm.<br />
The simplified diagram <strong>of</strong> simulation is given in Fig.<br />
4. The following notations are used in this figure:<br />
X is <strong>the</strong> vector <strong>of</strong> «true» TUD <strong>satellite</strong> position and<br />
tr<br />
S<br />
velocity components in <strong>the</strong> absolute inertial frame<br />
(IF2000),<br />
E is <strong>the</strong> vector <strong>of</strong> «true» TUD <strong>satellite</strong> Euler angles,<br />
tr<br />
S<br />
tr<br />
X NS is <strong>the</strong> vector <strong>of</strong> «true» GLONASS and GPS<br />
<strong>satellite</strong>s ephemerides,<br />
tr<br />
X ant is <strong>the</strong> vector <strong>of</strong> «true» antenna position in <strong>the</strong><br />
IF2000 frame (see below in detail),<br />
tr<br />
X ONS is <strong>the</strong> vector <strong>of</strong> «true» observed <strong>navigation</strong>al<br />
<strong>satellite</strong>s (ONS) ephemerides,<br />
tr<br />
ρ is <strong>the</strong> vector <strong>of</strong> «true» pseudorange measurement<br />
results, obtained from <strong>the</strong> observed <strong>navigation</strong>al<br />
<strong>satellite</strong>s,<br />
tr<br />
δρ is <strong>the</strong> vector <strong>of</strong> «true» pseudorange rate<br />
measurement results, obtained from <strong>the</strong> observed<br />
<strong>navigation</strong>al <strong>satellite</strong>s,<br />
tr<br />
Φ is <strong>the</strong> vector <strong>of</strong> «true» carrier phase difference<br />
measurement results, calculated for <strong>the</strong> observed<br />
<strong>navigation</strong>al <strong>satellite</strong>s,<br />
ref<br />
X ONS is <strong>the</strong> vector <strong>of</strong> observed <strong>navigation</strong>al <strong>satellite</strong>s<br />
ephemerides, which corresponds to <strong>the</strong> <strong>navigation</strong>al<br />
message,<br />
ref<br />
X NS is <strong>the</strong> vector <strong>of</strong> observed <strong>navigation</strong>al <strong>satellite</strong>s<br />
short term («reference») ephemerides, calculated by <strong>the</strong><br />
<strong>satellite</strong> onboard computer,<br />
ref<br />
X S is <strong>the</strong> user «reference» state vector, calculated by<br />
<strong>the</strong> onboard computer bases on <strong>the</strong> previous<br />
estimations,<br />
ref<br />
E S is <strong>the</strong> vector <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> «reference» <strong>satellite</strong> Euler<br />
angles, calculated by onboard computer based on <strong>the</strong><br />
previous estimations and angular motion model,<br />
ref<br />
X ant is <strong>the</strong> vector <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> «reference» antenna position<br />
in <strong>the</strong> IF2000, calculated by onboard computer, using<br />
ref ref<br />
XS<br />
and ES<br />
data,<br />
ref ref ref<br />
ρ , δρ , ϕ are corresponding reference<br />
measurement data, generated based on <strong>the</strong><br />
corresponding reference vectors<br />
ref ref ref ref<br />
XS<br />
, Xant<br />
, ES<br />
, XONS<br />
.<br />
* *<br />
E S , XS<br />
are <strong>the</strong> vectors <strong>of</strong> estimations <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> user<br />
attitude, position and velocity.<br />
tr tr tr<br />
To obtain <strong>the</strong> values <strong>of</strong> XS<br />
, ES<br />
, X NS , <strong>the</strong> most<br />
accurate and complete models <strong>of</strong> motion as well as<br />
high-accuracy integration method are used.<br />
Ma<strong>the</strong>matical Models and Algorithms<br />
Let us emphasize, that for simulation <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
considered <strong>navigation</strong> <strong>system</strong> one has to create <strong>the</strong><br />
following ma<strong>the</strong>matical models and algorithms:<br />
• GLONASS and GPS constellation model;<br />
• GLONASS and GPS <strong>satellite</strong> observability model;<br />
• user orbital and angular motion models;<br />
• <strong>navigation</strong>al message and receiver antennae <strong>system</strong><br />
models;<br />
• algorithm <strong>of</strong> user position and velocity<br />
determination;<br />
• algorithm <strong>of</strong> user attitude determination.<br />
All <strong>the</strong> mentioned models have been created,<br />
considering wide set <strong>of</strong> uncontrollable factors and<br />
errors, such as GLONASS and GPS ephemerides<br />
maintenance <strong>system</strong>atic errors caused by <strong>the</strong> errors <strong>of</strong><br />
orbit determination <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>navigation</strong> <strong>satellite</strong>s by <strong>the</strong>