Analytical Chemistry Chemical Cytometry Quantitates Superoxide
Analytical Chemistry Chemical Cytometry Quantitates Superoxide
Analytical Chemistry Chemical Cytometry Quantitates Superoxide
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
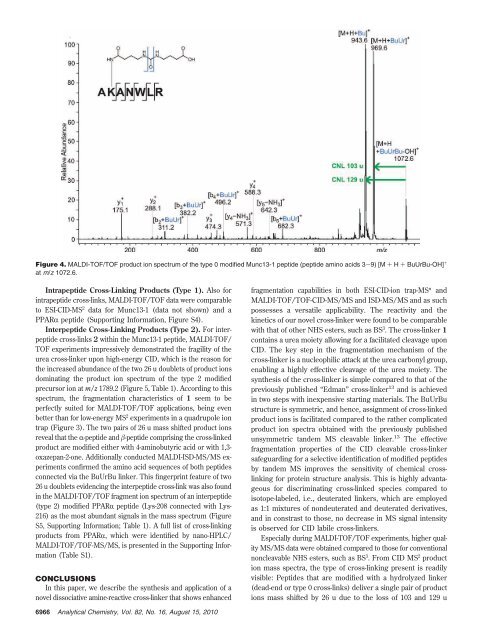
Figure 4. MALDI-TOF/TOF product ion spectrum of the type 0 modified Munc13-1 peptide (peptide amino acids 3-9) [M + H + BuUrBu-OH] +<br />
at m/z 1072.6.<br />
Intrapeptide Cross-Linking Products (Type 1). Also for<br />
intrapeptide cross-links, MALDI-TOF/TOF data were comparable<br />
to ESI-CID-MS 2 data for Munc13-1 (data not shown) and a<br />
PPARR peptide (Supporting Information, Figure S4).<br />
Interpeptide Cross-Linking Products (Type 2). For interpeptide<br />
cross-links 2 within the Munc13-1 peptide, MALDI-TOF/<br />
TOF experiments impressively demonstrated the fragility of the<br />
urea cross-linker upon high-energy CID, which is the reason for<br />
the increased abundance of the two 26 u doublets of product ions<br />
dominating the product ion spectrum of the type 2 modified<br />
precursor ion at m/z 1789.2 (Figure 5, Table 1). According to this<br />
spectrum, the fragmentation characteristics of 1 seem to be<br />
perfectly suited for MALDI-TOF/TOF applications, being even<br />
better than for low-energy MS 2 experiments in a quadrupole ion<br />
trap (Figure 3). The two pairs of 26 u mass shifted product ions<br />
reveal that the R-peptide and �-peptide comprising the cross-linked<br />
product are modified either with 4-aminobutyric acid or with 1,3oxazepan-2-one.<br />
Additionally conducted MALDI-ISD-MS/MS experiments<br />
confirmed the amino acid sequences of both peptides<br />
connected via the BuUrBu linker. This fingerprint feature of two<br />
26 u doublets evidencing the interpeptide cross-link was also found<br />
in the MALDI-TOF/TOF fragment ion spectrum of an interpeptide<br />
(type 2) modified PPARR peptide (Lys-208 connected with Lys-<br />
216) as the most abundant signals in the mass spectrum (Figure<br />
S5, Supporting Information; Table 1). A full list of cross-linking<br />
products from PPARR, which were identified by nano-HPLC/<br />
MALDI-TOF/TOF-MS/MS, is presented in the Supporting Information<br />
(Table S1).<br />
CONCLUSIONS<br />
In this paper, we describe the synthesis and application of a<br />
novel dissociative amine-reactive cross-linker that shows enhanced<br />
6966 <strong>Analytical</strong> <strong>Chemistry</strong>, Vol. 82, No. 16, August 15, 2010<br />
fragmentation capabilities in both ESI-CID-ion trap-MS n and<br />
MALDI-TOF/TOF-CID-MS/MS and ISD-MS/MS and as such<br />
possesses a versatile applicability. The reactivity and the<br />
kinetics of our novel cross-linker were found to be comparable<br />
with that of other NHS esters, such as BS 3 . The cross-linker 1<br />
contains a urea moiety allowing for a facilitated cleavage upon<br />
CID. The key step in the fragmentation mechanism of the<br />
cross-linker is a nucleophilic attack at the urea carbonyl group,<br />
enabling a highly effective cleavage of the urea moiety. The<br />
synthesis of the cross-linker is simple compared to that of the<br />
previously published “Edman” cross-linker 13 and is achieved<br />
in two steps with inexpensive starting materials. The BuUrBu<br />
structure is symmetric, and hence, assignment of cross-linked<br />
product ions is facilitated compared to the rather complicated<br />
product ion spectra obtained with the previously published<br />
unsymmetric tandem MS cleavable linker. 13 The effective<br />
fragmentation properties of the CID cleavable cross-linker<br />
safeguarding for a selective identification of modified peptides<br />
by tandem MS improves the sensitivity of chemical crosslinking<br />
for protein structure analysis. This is highly advantageous<br />
for discriminating cross-linked species compared to<br />
isotope-labeled, i.e., deuterated linkers, which are employed<br />
as 1:1 mixtures of nondeuterated and deuterated derivatives,<br />
and in constrast to those, no decrease in MS signal intensity<br />
is observed for CID labile cross-linkers.<br />
Especially during MALDI-TOF/TOF experiments, higher quality<br />
MS/MS data were obtained compared to those for conventional<br />
noncleavable NHS esters, such as BS 3 . From CID MS 2 product<br />
ion mass spectra, the type of cross-linking present is readily<br />
visible: Peptides that are modified with a hydrolyzed linker<br />
(dead-end or type 0 cross-links) deliver a single pair of product<br />
ions mass shifted by 26 u due to the loss of 103 and 129 u