- Page 1 and 2:
Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6745-6750 Let
- Page 3 and 4:
purchased from Invitrogen-Molecular
- Page 5 and 6:
Figure 3. Electropherograms of TPP-
- Page 7 and 8:
Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6751-6755 Res
- Page 9 and 10:
(pH 8.0) with cysteine and cystamin
- Page 11 and 12:
Figure 4. Ion mobility mass spectra
- Page 13 and 14:
GOx glucose + O298 gluconic acid +
- Page 15 and 16:
coater at 2000 rpm for 20 s, and th
- Page 17 and 18:
Figure 5. Comparison of cyclic volt
- Page 19 and 20:
in channels with either no grooves
- Page 21 and 22:
indicators of atmospheric processin
- Page 23 and 24:
Figure 1. GC/MS total ion chromatog
- Page 25 and 26:
Table 2. Concentrations and Stable
- Page 27 and 28:
on a substrate are preferred. 20-24
- Page 29 and 30:
Figure 4. SERS analysis of NAADP co
- Page 31 and 32:
Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6775-6781 Hig
- Page 33 and 34:
tion, 2 µL of proprionaldehyde wer
- Page 35 and 36:
Figure 4. Analysis of 2a by HPLC-MS
- Page 37 and 38:
eaction of 1a with PBH can be condu
- Page 39 and 40:
Numerous references had demonstrate
- Page 41 and 42:
Figure 1. TEM images of the prepare
- Page 43 and 44:
Figure 4. Schematic representation
- Page 45 and 46:
esult in a big SPR signal change wi
- Page 47 and 48:
also reduces chemical noise, which
- Page 49 and 50:
Table 1. Extraction Yields, Liquid
- Page 51 and 52:
scanning of AMPP amides of the anal
- Page 53 and 54:
Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6797-6806 δ
- Page 55 and 56:
Figure 1. Schematic view of the pre
- Page 57 and 58:
from the specimen and enclosed in a
- Page 59 and 60:
Figure 4. (A) IRMS mass-44 chromato
- Page 61 and 62:
Table 3. Ambient Measurement Result
- Page 63 and 64:
Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6807-6813 Dir
- Page 65 and 66:
Polymerase (1 U per sample). Reacti
- Page 67 and 68:
of which was constant for all ampli
- Page 69 and 70:
analytically useful signals at less
- Page 71 and 72:
carbon black and RP-C18 for the ext
- Page 73 and 74:
solution in an equal volume, and 1
- Page 75 and 76:
Table 2. Concentrations and Ratios
- Page 77 and 78:
Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6821-6829 Mac
- Page 79 and 80:
mg/mL protein, followed by separati
- Page 81 and 82:
Figure 2. Productivity of SEQUST an
- Page 83 and 84:
Figure 4. High-resolution MS/MS spe
- Page 85 and 86:
Figure 6. Characterization of PSMs
- Page 87 and 88:
containing T-T mismatches. 23 Based
- Page 89 and 90:
Figure 1. Extinction spectra of sol
- Page 91 and 92:
Figure 3. (A) The value of Ex650 nm
- Page 93 and 94:
Figure 5. Extinction spectra and co
- Page 95 and 96:
wished to explore the dehydration o
- Page 97 and 98:
constant medium for separation; we
- Page 99 and 100:
Figure 2. Standards of (Pi)n, n ) 1
- Page 101 and 102:
Figure 5. Quantitative calibration
- Page 103 and 104:
Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6847-6853 Met
- Page 105 and 106:
Figure 1. 226 Ra spectrum by liquid
- Page 107 and 108:
Table 1. Counting Properties and De
- Page 109 and 110:
Table 3. Analysis of 226 Ra in Sedi
- Page 111 and 112:
mercial microarray scanner and fabr
- Page 113 and 114:
Figure 2. Optical transmission meas
- Page 115 and 116:
Figure 5. Volcano plots detailing t
- Page 117 and 118:
data as well. The 41 genes in Table
- Page 119 and 120:
corresponding compound if its chemi
- Page 121 and 122: Figure 1. Schematic illustration of
- Page 123 and 124: Table 1. Absolute Quantification Re
- Page 125 and 126: ment. Therefore, the long-time drea
- Page 127 and 128: Figure 1. Chemically actuated micro
- Page 129 and 130: Figure 2. Influence of a surfactant
- Page 131 and 132: Figure 5. Device to eject and mix s
- Page 133 and 134: Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6877-6886 Imm
- Page 135 and 136: NaCl, phosphate buffer saline (PBS)
- Page 137 and 138: Figure 2. Product ion mass spectra
- Page 139 and 140: -70 °C resolved the problem, givin
- Page 141 and 142: Table 1. Intraday Precision and Acc
- Page 143 and 144: Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6887-6894 Fer
- Page 145 and 146: Figure 1. Infrared spectra of (A) u
- Page 147 and 148: Figure 3. Cyclic voltammograms obta
- Page 149 and 150: Figure 6. Calculated charge from ch
- Page 151 and 152: Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6895-6903 Ele
- Page 153 and 154: Table 1. Chemical Structure, pKa Va
- Page 155 and 156: pH with a tilted baseline (Figure 1
- Page 157 and 158: Table 2. Linearity and Detection Li
- Page 159 and 160: ascorbic acid (AA), uric acid (UA),
- Page 161 and 162: the multielement capabilities, the
- Page 163 and 164: RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Sulfur Detec
- Page 165 and 166: Table 2. Molecular Properties and C
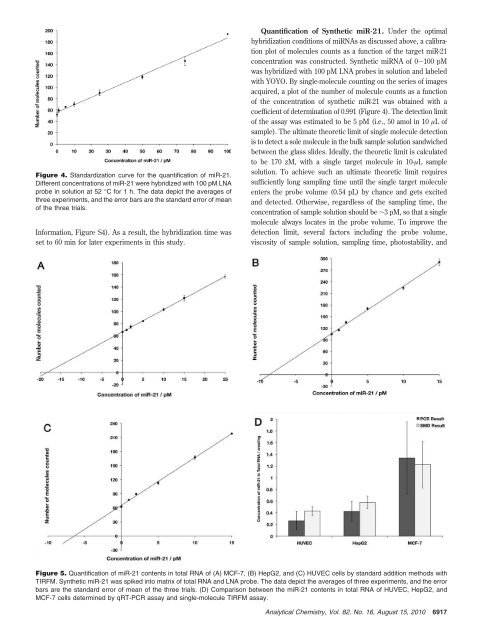
- Page 167 and 168: Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6911-6918 Dir
- Page 169 and 170: dilution and hybridization buffer.
- Page 171: solution under appropriate incubati
- Page 175 and 176: Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6919-6925 Ele
- Page 177 and 178: the ×10 objective, to have a large
- Page 179 and 180: Figure 2. With a suitable removal o
- Page 181 and 182: the NB signal in a much better foot
- Page 183 and 184: Scheme 1. Reactions of Selenium Rea
- Page 185 and 186: Figure 2. (a) ESI-MS spectrum showi
- Page 187 and 188: Figure 4. (a) ESI-MS spectrum showi
- Page 189 and 190: Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6933-6939 Dif
- Page 191 and 192: trode 28 by a finite element using
- Page 193 and 194: Figure 4. Comparison between simula
- Page 195 and 196: Figure 6. Comparison between simula
- Page 197 and 198: educed in the vicinity of double bo
- Page 199 and 200: Figure 2. Normalized product ion ab
- Page 201 and 202: Figure 4. EID (a) and IRMPD (b) of
- Page 203 and 204: Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6947-6957 Ide
- Page 205 and 206: Figure 1. Schematic flowchart showi
- Page 207 and 208: difference, ppm compound Table 1. I
- Page 209 and 210: isoforms, its successful use, in th
- Page 211 and 212: Figure 5. Extracted ion current ESI
- Page 213 and 214: m/z 1172.935 was observed for Ser14
- Page 215 and 216: linked products via affinity tags.
- Page 217 and 218: Scheme 2. Fragmentation Mechanism o
- Page 219 and 220: Figure 1. (A) ESI-LTQ-CID-MS 2 prod
- Page 221 and 222: Figure 3. (A) ESI-LTQ-CID-MS 2 prod
- Page 223 and 224:
Figure 5. (A) MALDI-TOF/TOF product
- Page 225 and 226:
Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6969-6975 Ana
- Page 227 and 228:
Figure 3. Equilibrium response as a
- Page 229 and 230:
Figure 6. The average measured resp
- Page 231 and 232:
for the fill time, and we find that
- Page 233 and 234:
nucleotide tails. 3-5 Thus, the amo
- Page 235 and 236:
allow the use of higher aptamer con
- Page 237 and 238:
quent ligation of the aptamers afte
- Page 239 and 240:
Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6983-6990 Imp
- Page 241 and 242:
Figure 2. Configuration editor wind
- Page 243 and 244:
Figure 4. Dependencies between volu
- Page 245 and 246:
Since the time for liquid expulsion
- Page 247 and 248:
Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6991-6999 Int
- Page 249 and 250:
Figure 1. Representation of the Car
- Page 251 and 252:
Table 2. Capillary Electrophoresis
- Page 253 and 254:
Figure 4. (A) Typical raw electroph
- Page 255 and 256:
field. DNA profiles were delivered
- Page 257 and 258:
Another approach to handle this lim
- Page 259 and 260:
(principal components, PCs) in whic
- Page 261 and 262:
Figure 5. Relevant score plots and
- Page 263 and 264:
CONCLUSIONS In this paper we have i
- Page 265 and 266:
electroactive-species loaded liposo
- Page 267 and 268:
Figure 2. Qdot-based FLFTS response
- Page 269 and 270:
Figure 6. Fluorescence imaging of Q
- Page 271 and 272:
Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7015-7020 Sel
- Page 273 and 274:
Table 1. Effect of 1 D-LC Condition
- Page 275 and 276:
Figure 3. Peak-production rate vers
- Page 277 and 278:
Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7021-7026 Cel
- Page 279 and 280:
luciferase (T7 control vector) was
- Page 281 and 282:
Figure 3. Inhibitory effects of luc
- Page 283 and 284:
Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7027-7034 Pat
- Page 285 and 286:
Electrochemistry. Electrochemical m
- Page 287 and 288:
Figure 2. SEM images of Au substrat
- Page 289 and 290:
Table 3. Film Thickness Measurement
- Page 291 and 292:
Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7035-7043 Qua
- Page 293 and 294:
Figure 1. (A) FL spectra of BSPOTPE
- Page 295 and 296:
Figure 4. (A) Variation in the FL i
- Page 297 and 298:
Figure 6. (A) FL spectra of BSPOTPE
- Page 299 and 300:
Scheme 1. Proposed Mechanism for Fl
- Page 301 and 302:
one or more drawbacks including poo
- Page 303 and 304:
Figure 2. Free fluorophores do not
- Page 305 and 306:
Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7049-7052 Dev
- Page 307 and 308:
Figure 2. Comparative analysis of d