NOx-Reduktion durch katalytische Naßoxidation ... - DGE GmbH
NOx-Reduktion durch katalytische Naßoxidation ... - DGE GmbH
NOx-Reduktion durch katalytische Naßoxidation ... - DGE GmbH
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Umweltschutz<br />
Environmental<br />
protection<br />
Protection de<br />
l’environnement<br />
Verfahrenstechnik<br />
Chemical<br />
Engineering<br />
Génie<br />
Chimique<br />
Anlagenbau<br />
Plant engineering<br />
and construction<br />
Construction<br />
d’installations<br />
industrielles<br />
Dr.-Ing. Günther Engineering <strong>GmbH</strong><br />
<strong>NOx</strong>-<strong>Reduktion</strong> <strong>durch</strong> <strong>katalytische</strong> <strong>Naßoxidation</strong><br />
Reducing <strong>NOx</strong> by Means of Catalytic Wet Oxidation<br />
Réduction de <strong>NOx</strong> par oxydation catalytique humide<br />
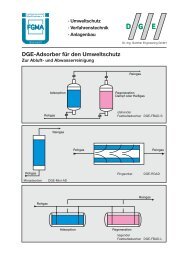
Anlage für ein 3,5 m 3 Beizbad mit Meßtechnik<br />
Plant for a 3.5 m 3 pickling bath with measuring<br />
equipment<br />
Installation pour un bain de decapage de<br />
3,5 m 3 avec matériel de mésure<br />
Reingas NO, NO2<br />
Clean gas NO, NO2<br />
Gaz purifié NO, NO2<br />
Rohgas NO, NO2<br />
Crude gas NO, NO2<br />
Gaz brut NO, NO2<br />
KATOX Kolonne<br />
(KATOX) / Column<br />
Catalytic oxidation<br />
(KATOX) / colonne<br />
(oxydation catalytique)<br />
HNO3 > 20 %<br />
HNO3 > 20 %<br />
HNO3 > 20 %<br />
Prozeßschema<br />
Process diagram<br />
Schéma de procédé<br />
Tropfenabscheider<br />
Mist collector<br />
Séparateur de gouttes<br />
Katalysator 2<br />
Calalyst 2<br />
Catalyseur 2<br />
2. Stufe<br />
Second stage<br />
2 e étage<br />
Katalysator 1<br />
Calalyst 1<br />
Catalyseur 1<br />
1. Stufe<br />
First stage<br />
1 er étage<br />
Oxidationsmittel<br />
Oxidising agent<br />
Agent d’oxydation<br />
Kreislaufpumpe<br />
Recycling pump<br />
Pompe de circulation<br />
<strong>DGE</strong>-<strong>NOx</strong>-Abbauprozeß · <strong>DGE</strong> Process for reducing <strong>NOx</strong><br />
Processus de dégradation <strong>DGE</strong> - <strong>NOx</strong><br />
Katalytische NO-Oxidation · Catalytic NO oxidation · Oxydation catalytique de NO<br />
NO-Umsatz<br />
100<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
20<br />
0<br />
18:10 18:20 18:30 18:40 18:50<br />
1. Stufe<br />
First stage<br />
1 er étage<br />
Uhrzeit · Time · Durée<br />
2. Stufe<br />
Second stage<br />
2 e étage<br />
Diagramm: NO-Abbau<br />
Diagram: NO reduction<br />
Diagramme: dégradation de NO<br />
1. und 2. Stufe<br />
First and Second stage<br />
1 er et 2 e étage<br />
<strong>DGE</strong> <strong>GmbH</strong> · Hufelandstraße 33 · D-06886 Lutherstadt Wittenberg · Tel.: 0049-34 91-66 18 41 · Fax: 0049-34 91-66 18 42<br />
eMail: <strong>DGE</strong>-INFO@t-online.de · Internet: http://www.dge-wittenberg.com
Umweltschutz<br />
Environmental<br />
protection<br />
Protection de<br />
l’environnement<br />
Verfahrenstechnik<br />
Chemical<br />
Engineering<br />
Génie<br />
Chimique<br />
Anlagenbau<br />
Plant engineering<br />
and construction<br />
Construction<br />
d’installations<br />
industrielles<br />
Dr.-Ing. Günther Engineering <strong>GmbH</strong><br />
<strong>NOx</strong>-<strong>Reduktion</strong> <strong>durch</strong> <strong>katalytische</strong> <strong>Naßoxidation</strong><br />
Reducing <strong>NOx</strong> by Means of Catalytic Wet Oxidation<br />
Réduction de <strong>NOx</strong> par oxydation catalytique humide<br />
Bei Beizvorgängen in Galvanikbetrieben<br />
der Chemischen Industrie,<br />
bei Stickstoffprozessen und anderen<br />
Anwendungsfällen entstehen nitrose<br />
Abgase, die gereinigt werden<br />
müssen. Allgemein erfolgt diese<br />
Reinigung <strong>durch</strong> Wäsche mit NaOH/<br />
H 2 O 2 . Dies führt zu einer erheblichen<br />
Salzfracht für das Abwasser. Eine<br />
andere Methode besteht in der<br />
<strong>katalytische</strong>n Umsetzung <strong>durch</strong><br />
Zugabe von Ammoniak zu Stickstoff.<br />
Beide Techniken reduzieren die<br />
<strong>NOx</strong>-Emissionen mit erheblichen<br />
Betriebskosten.<br />
Der <strong>DGE</strong>-Prozeß zur <strong>NOx</strong>-Reduzierung<br />
basiert auf einer ein- oder<br />
mehrstufigen Prozeßführung mit<br />
Wertstoffrückgewinnung.<br />
In der ersten Stufe erfolgt in einer<br />
Waschkolonne <strong>durch</strong> Zugabe von<br />
H 2 O 2 die katalytisch beschleunigte<br />
Umsetzung der Komponenten<br />
NO und NO 2 zu HNO 3 entsprechend<br />
nachstehenden Summengleichungen:<br />
2 NO + 3 H 2 O 2 ➞ 2 HNO 3 + 2 H 2 O<br />
2 NO 2 + H 2 O 2 ➞ 2 HNO 3<br />
Die dabei entstehende Salpetersäure<br />
kann einer weiteren Verwendung<br />
zugeführt oder für den Kreislaufprozeß<br />
verwendet werden.<br />
Für die <strong>katalytische</strong> Umsetzung<br />
stehen drei verschiedene<br />
Katalysatortypen zur Verfügung, die<br />
den einzelnen Anwendungsgebieten<br />
angepaßt sind.<br />
In einer ggf. zweiten nach- oder<br />
vorgeschalteten Waschstufe können<br />
noch andere Inhaltsstoffe entfernt<br />
werden.<br />
In pickling processes in electroplating<br />
shops of the chemical industry,<br />
nitrous waste gases develop in<br />
nitrogen processes and other<br />
applications. These gases have to<br />
be purified. In general, purifying is<br />
done by scrubbing with NaOH/<br />
H 2 O 2 , However, this leads to a<br />
significant amount of salt freight for<br />
the waste water. There is another<br />
method which consists of catalytic<br />
conversion by adding ammonia to<br />
nitrogen. Both of these techniques<br />
reduce the <strong>NOx</strong> emissions, but at<br />
significant operating costs.<br />
The <strong>DGE</strong> Process for reducing <strong>NOx</strong><br />
ist based upon a single- or multiplestage<br />
process with material recovery.<br />
The first stage takes place in a<br />
scrubber column by adding H 2 O 2<br />
and includes the catalytically<br />
accelerated conversion of the<br />
components NO and NO 2 to HNO 3<br />
according to the following empirical<br />
equation:<br />
2 NO + 3 H 2 O 2 ➞ 2 HNO 3 + 2 H 2 O<br />
2 NO 2 + H 2 O 2 ➞ 2 HNO 3<br />
The nitric acid formed in this process<br />
may be applied elsewhere or<br />
be used in the recirculation process.<br />
There are three different types of<br />
catalysts available for catalytic<br />
conversion that are adapted to the<br />
individual areas of application.<br />
Furthermore, if there is a second<br />
downstream or upstream scrubbing<br />
stage, it is also possible to remove<br />
other constituents.<br />
Le décapage dans les ateliers de<br />
galvanisation, le traitement de<br />
l’azote dans l’industrie chimique et<br />
d’autres applications donnent des<br />
gaz d’évacuation nitreux qui doivent<br />
être purifiés. D’une façon<br />
générale, ce nettoyage est exécuté<br />
par lavage avec NaOH/H 2 O 2 qui<br />
donne une charge de sel importante<br />
dans l’eau de sortie. Une<br />
autre méthode consiste à procéder<br />
à la dégradation catalytique par<br />
adjonction d’ammoniaque pour<br />
obtenir de l’azote. Ces deux techniques<br />
réduisent les émissions de<br />
<strong>NOx</strong> moyennant un coût de fonctionnement<br />
élevé.<br />
Le processus <strong>DGE</strong> de réduction<br />
de <strong>NOx</strong> repose sur le traitement à<br />
un et plusieurs étages avec recyclage<br />
des produits à la sortie.<br />
Le premier étage est constitué<br />
d’une colonne de lavage; le<br />
traitement est réalisé par adjonction<br />
de H 2 O 2 pour provoquer la<br />
transformation catalytique accélérée<br />
des composants NO et NO 2<br />
pour donner HNO 3 selon les équations<br />
suivantes:<br />
2 NO + 3 H 2 O 2 ➞ 2 HNO 3 + 2 H 2 O<br />
2 NO 2 + H 2 O 2 ➞ 2 HNO 3<br />
L’acide nitrique ainsi obtenue peut<br />
être injectée dans un autre<br />
traitement ou être réutilisée dans le<br />
procédé en circuit fermé.<br />
Trois types de catalyseur sont<br />
utilisés pour la dégradation<br />
catalytique, chacun étant réglé<br />
pour l’utilisation spécifique.<br />
Il est possible d’intégrer un<br />
deuxième étage de lavage en aval<br />
ou en amont pour prélever<br />
d’autres composants.<br />
<strong>DGE</strong> <strong>GmbH</strong> · Hufelandstraße 33 · D-06886 Lutherstadt Wittenberg · Tel.: 0049-34 91-66 18 41 · Fax: 0049-34 91-66 18 42<br />
eMail: <strong>DGE</strong>-INFO@t-online.de · Internet: http://www.dge-wittenberg.com