Book of Extended summaries ISDA
Book of Extended summaries ISDA Book of Extended summaries ISDA
International Conference on Reimagining Rainfed Agro-ecosystems: Challenges & Opportunities during 22-24, December 2022 at ICAR-CRIDA, Hyderabad design with eight treatments and three replications. There were eight treatments viz, T1 is RDF (No spray), T2 is RDF + 1% urea spraying, T3 is RDF + 1% DAP spraying, T4 is RDF + 1% 19:19:19 (N,P,K) spraying, T5 is RDF + 1% 00:52:34 (N,P,K) spraying, T6 is RDF + 13:00:45 (N,P,K) spraying, T7 is RDF + 1% 13:40:13 (N,P,K) spraying and T8- control (no RDF, no spray). Foliar application of fertilizers (1%) is done at the flowering and pod development stage. The treatments were allotted randomly in each replication. Therecommendeddoseoffertilizer (25:50:25 NPK kg ha -1 ) was applied at the time of sowing through Urea, SSP, and MOP. The recommended cultural practices and plant protectionmeasureswereproperlytakenfrom timetotime.The plants were used for measuring phenological characteristics like plant height, the number of branches plant and number of nodule plants, the seed index by taking 100 seeds, and weight for working out the seed index on electric balance.Protein content was determined by multiplying the percent of N in the grain sample by a constant factor of 6.25 as described by A.O.A.C. (1975).The statistical method of analysis of variance was used for analyzing the data and the “F” test of significance was used for testing the null hypothesis to determine whether the observed treatment effects were real and discernible from chance effects. Results Data in respect of plant height and number of branches plant -1 influenced by different treatment. The plant height (cm)differed significantly due to different foliar applications of fertilizers in gram, T4 - RDF + 1% 19:19:19 NPK spraying at flowering and pod development recorded significantly highest plant height (59.73) cm which was found at par with T2 - RDF + 1% Urea spraying at flowering and pod development (58.77) cm however it was significantly higher than all other treatments. Significantly lowest (42.87) cm plant height was recorded with T8 - Control (No RDF, No spray). In the present study, the data revealed an increase in plant height through foliar application of 19:19:19and urea may be attributed to increasing the N status in the plant system. The number of branches plant -1 of gram was significantly influenced due to different foliar fertilizers application, T4 - RDF + 1% 19:19:19 NPK spraying at flowering and pod development recorded a significantly higher number of branches (24.20) which was found at par with T5 - RDF + 00:52:34 NPK spraying at flowering and pod development (23.40) however, it was significantly higher than all other treatments. significantly the lowest number of branches (13.19) recorded with T8 - Control (No RDF, No spray). The maximum number of branches might be due to the increased number of nodes and the development of plants due to the treatment effect and increase in the availability of nitrogen which encouraged the carbohydrate synthesis in grams as there was the availability of applied nitrogen. Data on the number of nodule plant -1 as Sustainable soil management for resilient rainfed agro-ecosystem: conservation agriculture, organic farming, INM, soil-microorganisms-plant interactions 545 | Page
International Conference on Reimagining Rainfed Agro-ecosystems: Challenges & Opportunities during 22-24, December 2022 at ICAR-CRIDA, Hyderabad influenced by various treatments. The mean number of nodule plant -1 was not influenced significantly by various foliar applications of fertilizers in gram. However, the mean number of nodule plant -1 at 30, 45, 60, 75, and 90 DAS were 16.98, 36.16, 40.47, 20.81, and 9.74 respectively. The seed index was not influenced significantly due to foliage-applied fertilizers. The highest seed index (8.53 g) was recorded with T5 - RDF + 1% 00:52:34 (NPK) spraying at flowering and pod development stage followed by T4 - RDF + 1% 19:19:19 (NPK) spraying at flowering and pod development (8.42 g) and T7 - RDF + 1% 13:40:13 (NPK) spraying at flowering and pod development (8.27 g). The lowest seed index (7.20 g) was recorded with T4 - Control (No RDF, No spray). The protein content (%) differed significantly due to different foliage applied fertilizers in gram, T4- RDF + 1% 19:19:19 NPK spraying at flowering and pod development recorded significantly highest protein content (19.68%) which was found at par with T7 - RDF + 1% 13:40:13 (NPK) spraying at flowering and pod development (19.37%) and T3- RDF + 1% DAP (NPK) spraying at flowering and pod development (18.75%). Significantly lowest (16.87%) protein content recorded with T8 - Control (No RDF, No spray). An increase in protein content may be due to the most important role of nitrogen in plants is mainly in its presence in the nucleic acid which is the protein structure. In addition, nitrogen is also found in chlorophyll molecules. Chlorophyllconverts sunlight energy into assimilates through photosynthesis. Therefore, the nitrogen supply to the plant will influence the amount of protein. Conclusion The foliage application of 1% 19:19:19 (NPK) or 1% 00:52:34 (NPK) or 1% 13:40:13 (NPK) spraying at flowering and pod development stage along with RDF was found beneficial and productive for improving phenological characters of a gram. For higher quality gram foliage application of 1% 19:19:19 (NPK) or 1%, 13:40:13 (NPK) or 1% DAP along with RDF was found beneficial. References A. O. A. C. 1975. Association of official Analytical chemist, Washington, D.C. U.S.A. Jaybal, A., Revathy, M. and Saxena, M. G. 1999. Effect of foliar nutrition on nutrient uptake pattern in soybean. Andhra Agric. J. 46:243-244. 546 | Page Sustainable soil management for resilient rainfed agro-ecosystem: conservation agriculture, organic farming, INM, soilmicroorganisms-plant interactions
- Page 507 and 508: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 509 and 510: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 511 and 512: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 513 and 514: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 515 and 516: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 517 and 518: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 519 and 520: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 521 and 522: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 523 and 524: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 525 and 526: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 527 and 528: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 529 and 530: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 531 and 532: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 533 and 534: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 535 and 536: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 537 and 538: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 539 and 540: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 541 and 542: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 543 and 544: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 545 and 546: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 547 and 548: International Conference on Reimagi
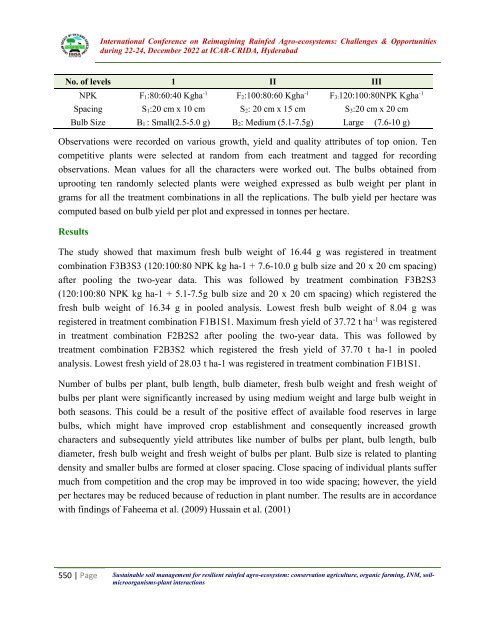
- Page 549 and 550: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 551 and 552: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 553 and 554: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 555 and 556: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 557: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 561 and 562: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 563 and 564: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 567: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 571 and 572: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 573 and 574: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 575 and 576: Resource conservation and rainfed a
- Page 577 and 578: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 579 and 580: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 581 and 582: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 583 and 584: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 585 and 586: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 587 and 588: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 589 and 590: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 591 and 592: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 593 and 594: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 595 and 596: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 597 and 598: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 599 and 600: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 601 and 602: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 603 and 604: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 605 and 606: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 607 and 608: International Conference on Reimagi
International Conference on Reimagining Rainfed Agro-ecosystems: Challenges & Opportunities<br />
during 22-24, December 2022 at ICAR-CRIDA, Hyderabad<br />
influenced by various treatments. The mean number <strong>of</strong> nodule plant -1 was not influenced<br />
significantly by various foliar applications <strong>of</strong> fertilizers in gram. However, the mean number <strong>of</strong><br />
nodule plant -1 at 30, 45, 60, 75, and 90 DAS were 16.98, 36.16, 40.47, 20.81, and 9.74<br />
respectively. The seed index was not influenced significantly due to foliage-applied fertilizers.<br />
The highest seed index (8.53 g) was recorded with T5 - RDF + 1% 00:52:34 (NPK) spraying at<br />
flowering and pod development stage followed by T4 - RDF + 1% 19:19:19 (NPK) spraying at<br />
flowering and pod development (8.42 g) and T7 - RDF + 1% 13:40:13 (NPK) spraying at<br />
flowering and pod development (8.27 g). The lowest seed index (7.20 g) was recorded with T4 -<br />
Control (No RDF, No spray). The protein content (%) differed significantly due to different<br />
foliage applied fertilizers in gram, T4- RDF + 1% 19:19:19 NPK spraying at flowering and pod<br />
development recorded significantly highest protein content (19.68%) which was found at par<br />
with T7 - RDF + 1% 13:40:13 (NPK) spraying at flowering and pod development (19.37%) and<br />
T3- RDF + 1% DAP (NPK) spraying at flowering and pod development (18.75%). Significantly<br />
lowest (16.87%) protein content recorded with T8 - Control (No RDF, No spray). An increase in<br />
protein content may be due to the most important role <strong>of</strong> nitrogen in plants is mainly in its<br />
presence in the nucleic acid which is the protein structure. In addition, nitrogen is also found in<br />
chlorophyll molecules. Chlorophyllconverts sunlight energy into assimilates through<br />
photosynthesis. Therefore, the nitrogen supply to the plant will influence the amount <strong>of</strong> protein.<br />
Conclusion<br />
The foliage application <strong>of</strong> 1% 19:19:19 (NPK) or 1% 00:52:34 (NPK) or 1% 13:40:13 (NPK) spraying at<br />
flowering and pod development stage along with RDF was found beneficial and productive for improving<br />
phenological characters <strong>of</strong> a gram. For higher quality gram foliage application <strong>of</strong> 1% 19:19:19 (NPK) or<br />
1%, 13:40:13 (NPK) or 1% DAP along with RDF was found beneficial.<br />
References<br />
A. O. A. C. 1975. Association <strong>of</strong> <strong>of</strong>ficial Analytical chemist, Washington, D.C. U.S.A.<br />
Jaybal, A., Revathy, M. and Saxena, M. G. 1999. Effect <strong>of</strong> foliar nutrition on nutrient uptake pattern in<br />
soybean. Andhra Agric. J. 46:243-244.<br />
546 | Page Sustainable soil management for resilient rainfed agro-ecosystem: conservation agriculture, organic farming, INM, soilmicroorganisms-plant<br />
interactions