Book of Extended summaries ISDA
Book of Extended summaries ISDA Book of Extended summaries ISDA
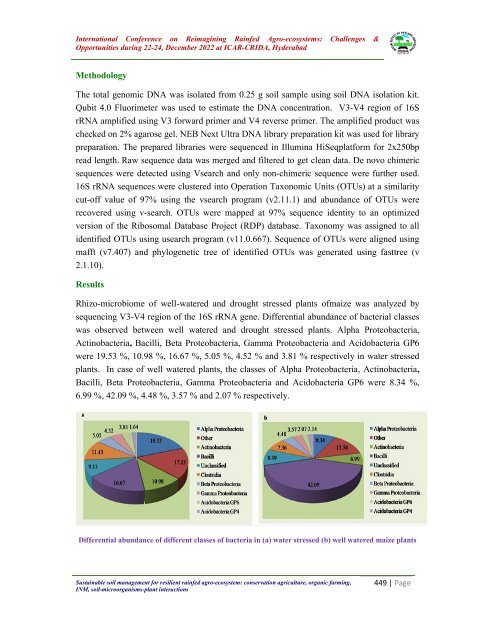
International Conference on Reimagining Rainfed Agro-ecosystems: Challenges & Opportunities during 22-24, December 2022 at ICAR-CRIDA, Hyderabad impact on the production and productivity. Drought is one of the main environmental factors that negatively affect plant growth and development and productivity. In plants, drought is associated with other stresses, for example, osmotic stress produced by dehydration, which diminishes cell expansion. A microbial consortium involves two or more microbial groups living symbiotically. Consortia can be endosymbiotic or ectosymbiotic. Microbial consortium is specially formulated microbial inoculants. It contains N- fixing, P and Zn solubilizing and K mobilizing and plant growth promoting bacteria. To increase the productivity of sorghum in kharif season, an experiment was conducted to study the response of microbial consortia on productivity of sorghum (sorghum bicolar L.) and soil quality under rainfed conditions of Marathawadaregion. Methodology The study was conducted at research farm of All India Coordinated Research Project on Dry Land Agriculture, VNMKV, Parbhani during kharif season 2018-20. The experiment comprises of seven treatments including two types of microbial consortia culture (C1 & C2) along with three methods (seed, soil and seed + soil) of culture application and was laid out in a randomized block design with three replications. Microbial consortia culture (C1& C2) was procured from ICAR-CRIDA, Hyderabad before sowing of the experiment. For seed treatment, microbial consortia culture (C 1&C 2 ) were applied @ 250g 10 Kg -1 of seed and for soil application 2.5 kg culture powder ha -1 were applied,immediately before sowing. The recommended doses of chemical fertilizer were applied at the time of sowing. Results Yield and monetary returns: Application of microbial consortia significantly increased grain yield, straw yield and returns of sorghum. Application of microbial consortia C 2 in T 6 (Seed treatment + Soil appication of consortia 2) gave grain and straw yield i.e. 2510 and 7279 Kg ha -1 respectively as compared to other treatment. However, it was at par with treatment T 3 (Seed tresatment + Soil application of consortia 1). Similar trend was recorded in case of gross returns (GR), net returns (NR) and B: C ratio. The production of proline and osmoregulantsenabled the crop to withstand the water stress due to dry spell. These isolates were capable of increasing shoot and leaf biomass, shoot length and photosynthesis. (Kavya et al. 2015) Grain yield, straw yield (Kgha -1 ), GMR, NMR and B: C ratio as influenced with use of Consortia culture in sorghum Treatments Grain yield (Kg ha -1 ) Straw yield (Kg ha -1 ) G R (Rs.) N R (Rs.) B:C Ratio T 1: Seed treatment (C 1) 1952 4489 63243 38943 2.60 446 | Page Sustainable soil management for resilient rainfed agro-ecosystem: conservation agriculture, organic farming, INM, soil-microorganisms-plant interactions
International Conference on Reimagining Rainfed Agro-ecosystems: Challenges & Opportunities during 22-24, December 2022 at ICAR-CRIDA, Hyderabad T 2: Soil application (C 1) 2140 5136 69978 45078 2.81 T 3: Seed treatment+ Soil application(C 1) 2485 6709 83494 58094 3.28 T 4: Seed treatment (C 2) 1997 5592 67699 43399 2.78 T 5: Soil application (C 2) 2018 6054 69621 44721 2.79 T 6: Seed treatment + Soil application (C 2) 2510 7279 85842 60542 3.39 T 7: Absolute control 1938 5233 65118 42818 2.92 SE 359 2521 2421 2801 0.69 CD 1106 7767 7462 8630 2.14 C 1 – Consortia culture 1 C 2 – Consortia culture 2 Proline content: Proline content in sorghum leaf after harvest was significantly high (1.89 ug g-1) with treatment T6followed by treatment T3. The effect of microbial culture on proline content in sorghum leaf after dry spell was non-significant. Similar results were reported by Kalindee Shinde and Borkar. (2013) in sorghum seed bacterialization with four rhizobacterial isolate viz., Serratia marcescens L1SC8, Pseudomonas putida L3SC1, Enterobacter cloacae L1CcC1 and Serratia marcescens. L2FmA4 were found beneficial to mitigate drought stress effect in sorghum. Proline content (ug g -1 ) in sorghum leaf at after dry spell and at harvest stage as Influenced with use of consortia culture Treatments Proline content at flowering stage (ug g -1 ) Proline content at Harvest (ug g -1 ) T 1: Seed treatment of consortia (C 1) 0.90 1.09 T 2: Soil application of consortia (C 1) 0.69 1.03 T 3: Seed treatment + Soil application of consortia (C 1) 0.80 1.10 T 4: Seed treatment of consortia (C 2) 0.86 1.18 T 5: Soil application of consortia (C 2) 0.85 1.12 T 6: Seed treatment + Soil application of consortia (C 2) 0.79 1.89 T 7: Absolute control 0.07 0.88 SE 0.02 0.44 CD 0.06 1.36 C 1 – Consortia culture 1 C 2 – Consortia culture 2 Sustainable soil management for resilient rainfed agro-ecosystem: conservation agriculture, organic farming, INM, soil-microorganisms-plant interactions 447 | Page
- Page 408 and 409: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 410 and 411: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 412 and 413: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 414 and 415: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 416 and 417: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 418 and 419: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 420 and 421: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 422 and 423: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 424 and 425: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 426 and 427: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 428 and 429: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 430 and 431: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 432 and 433: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 434 and 435: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 436 and 437: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 438 and 439: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 440 and 441: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 442 and 443: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 444 and 445: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 446 and 447: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 448 and 449: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 450 and 451: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 452 and 453: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 454 and 455: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 456 and 457: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 460 and 461: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 462 and 463: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 464 and 465: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 466 and 467: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 468 and 469: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 470 and 471: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 472 and 473: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 475 and 476: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 477 and 478: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 479 and 480: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 481 and 482: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 483 and 484: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 485 and 486: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 487 and 488: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 489 and 490: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 491 and 492: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 493 and 494: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 495 and 496: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 497 and 498: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 499 and 500: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 501 and 502: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 503 and 504: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 505 and 506: International Conference on Reimagi
- Page 507 and 508: International Conference on Reimagi
International Conference on Reimagining Rainfed Agro-ecosystems: Challenges &<br />
Opportunities during 22-24, December 2022 at ICAR-CRIDA, Hyderabad<br />
impact on the production and productivity. Drought is one <strong>of</strong> the main environmental factors that<br />
negatively affect plant growth and development and productivity. In plants, drought is associated<br />
with other stresses, for example, osmotic stress produced by dehydration, which diminishes cell<br />
expansion. A microbial consortium involves two or more microbial groups living symbiotically.<br />
Consortia can be endosymbiotic or ectosymbiotic. Microbial consortium is specially formulated<br />
microbial inoculants. It contains N- fixing, P and Zn solubilizing and K mobilizing and plant<br />
growth promoting bacteria. To increase the productivity <strong>of</strong> sorghum in kharif season, an<br />
experiment was conducted to study the response <strong>of</strong> microbial consortia on productivity <strong>of</strong><br />
sorghum (sorghum bicolar L.) and soil quality under rainfed conditions <strong>of</strong> Marathawadaregion.<br />
Methodology<br />
The study was conducted at research farm <strong>of</strong> All India Coordinated Research Project on Dry<br />
Land Agriculture, VNMKV, Parbhani during kharif season 2018-20. The experiment comprises<br />
<strong>of</strong> seven treatments including two types <strong>of</strong> microbial consortia culture (C1 & C2) along with<br />
three methods (seed, soil and seed + soil) <strong>of</strong> culture application and was laid out in a randomized<br />
block design with three replications. Microbial consortia culture (C1& C2) was procured from<br />
ICAR-CRIDA, Hyderabad before sowing <strong>of</strong> the experiment. For seed treatment, microbial<br />
consortia culture (C 1&C 2 ) were applied @ 250g 10 Kg -1 <strong>of</strong> seed and for soil application 2.5 kg<br />
culture powder ha -1 were applied,immediately before sowing. The recommended doses <strong>of</strong><br />
chemical fertilizer were applied at the time <strong>of</strong> sowing.<br />
Results<br />
Yield and monetary returns:<br />
Application <strong>of</strong> microbial consortia significantly increased grain yield, straw yield and returns <strong>of</strong><br />
sorghum. Application <strong>of</strong> microbial consortia C 2 in T 6 (Seed treatment + Soil appication <strong>of</strong><br />
consortia 2) gave grain and straw yield i.e. 2510 and 7279 Kg ha -1 respectively as compared to<br />
other treatment. However, it was at par with treatment T 3 (Seed tresatment + Soil application <strong>of</strong><br />
consortia 1). Similar trend was recorded in case <strong>of</strong> gross returns (GR), net returns (NR) and B: C<br />
ratio. The production <strong>of</strong> proline and osmoregulantsenabled the crop to withstand the water stress<br />
due to dry spell. These isolates were capable <strong>of</strong> increasing shoot and leaf biomass, shoot length<br />
and photosynthesis. (Kavya et al. 2015)<br />
Grain yield, straw yield (Kgha -1 ), GMR, NMR and B: C ratio as influenced with use <strong>of</strong><br />
Consortia culture in sorghum<br />
Treatments<br />
Grain yield<br />
(Kg ha -1 )<br />
Straw yield<br />
(Kg ha -1 )<br />
G R<br />
(Rs.)<br />
N R<br />
(Rs.)<br />
B:C Ratio<br />
T 1: Seed treatment (C 1) 1952 4489 63243 38943 2.60<br />
446 | Page Sustainable soil management for resilient rainfed agro-ecosystem: conservation agriculture, organic farming, INM,<br />
soil-microorganisms-plant interactions