Water Quality in Slovenia - Agencija RS za okolje
Water Quality in Slovenia - Agencija RS za okolje
Water Quality in Slovenia - Agencija RS za okolje
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
S U R F A C E W A T E R S<br />
In the years 2003 to 2006, the monitor<strong>in</strong>g network consisted of monitor<strong>in</strong>g sites <strong>in</strong> lakes and monitor<strong>in</strong>g<br />
sites at the lakes’ <strong>in</strong>flows and outflows. The sampl<strong>in</strong>g of lakes was carried out at selected depths along<br />
the water column. The monitor<strong>in</strong>g programme was primarily adjusted to monitor eutrophication,<br />
which is the ma<strong>in</strong> problem <strong>in</strong> most natural and artificial lakes of the Temperate Zone on a carbonate<br />
geological layer, to which all lakes and reservoirs <strong>in</strong> <strong>Slovenia</strong> also belong. In the lakes and their <strong>in</strong>flows,<br />
the status of nutrients and general physico-chemical parameters were primarily monitored. Analyses<br />
of pollutants, heavy metals and pesticides were only carried out <strong>in</strong> some <strong>in</strong>flows and outflows where,<br />
tak<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>to account the pressures <strong>in</strong> the catchment area, an <strong>in</strong>creased concentration of <strong>in</strong>dividual<br />
pollutants <strong>in</strong> water was to be expected. The lakes were evaluated accord<strong>in</strong>g to OECD criteria (33),<br />
which classify the lakes <strong>in</strong>to five trophic categories, based on the average annual concentration of<br />
total phosphorus and nitrogen, the average annual and m<strong>in</strong>imum transparency, and the average<br />
annual and maximum concentration of chlorophyll-a. Other pressures that have to be taken <strong>in</strong>to<br />
consideration <strong>in</strong> the ecological status classification of lakes or the ecological potential of artificial<br />
reservoirs as required by the <strong>Water</strong> Framework Directive, were not evaluated while an appropriate<br />
methodology is still <strong>in</strong> the course of preparation. Among biological quality elements, the status of<br />
phytoplankton, macrophytes, phytobenthos and benthic <strong>in</strong>vertebrates was monitored. In the years<br />
2003 to 2006 the f<strong>in</strong>al assessment of lake status was made accord<strong>in</strong>g to the status of phytoplankton<br />
(one of the OECD criteria), which is expressed by the average and maximum annual concentration<br />
of chlorophyll-a. The sampl<strong>in</strong>g of macrophytes, phytobenthos and benthic <strong>in</strong>vertebrates was carried<br />
out at selected sites <strong>in</strong> the shore zone accord<strong>in</strong>g to new methodology, adapted for the assessment<br />
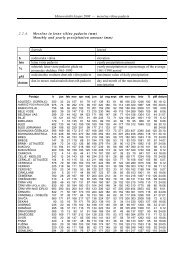
of the ecological status of lakes. A detailed programme outl<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g the monitor<strong>in</strong>g of water quality for<br />
each <strong>in</strong>dividual lake is presented <strong>in</strong> the annual Programme for monitor<strong>in</strong>g the quality of lakes (32).<br />
Lake Bled<br />
29