A Monte Carlo pencil beam scanning model for proton ... - Creatis
A Monte Carlo pencil beam scanning model for proton ... - Creatis
A Monte Carlo pencil beam scanning model for proton ... - Creatis
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
5206 L Grevillot et al<br />
Beam extent σ x (mm)<br />
θ (mrad)<br />
10<br />
5<br />
0<br />
-5<br />
(a)<br />
-10<br />
-150 -100 -50 0 50 100 150<br />
4<br />
2<br />
0<br />
-2<br />
-4<br />
(b)<br />
f(x,y)<br />
-4 -2 0 2 4<br />
x (mm)<br />
1<br />
0.9<br />
0.8<br />
0.7<br />
0.6<br />
0.5<br />
0.4<br />
0.3<br />
0.2<br />
0.1<br />
0<br />
Position along the <strong>beam</strong> path z (mm)<br />
θ (mrad)<br />
4<br />
2<br />
0<br />
-2<br />
-4<br />
(c)<br />
f(x,y)<br />
-4 -2 0 2 4<br />
x (mm)<br />
1<br />
0.9<br />
0.8<br />
0.7<br />
0.6<br />
0.5<br />
0.4<br />
0.3<br />
0.2<br />
0.1<br />
0<br />
θ (mrad)<br />
4<br />
2<br />
0<br />
-2<br />
-4<br />
(d)<br />
f(x,y)<br />
-4 -2 0 2 4<br />
x (mm)<br />
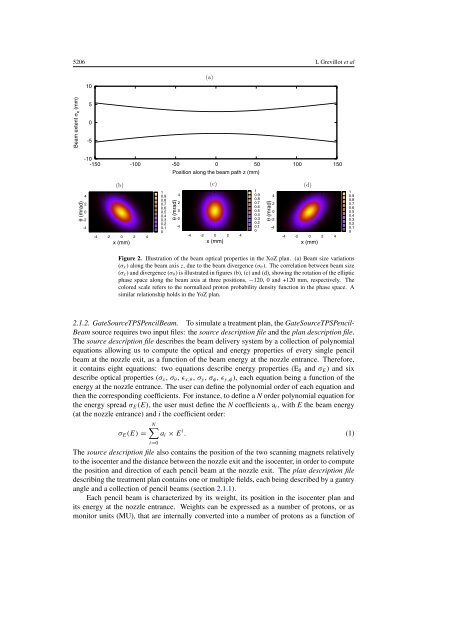
Figure 2. Illustration of the <strong>beam</strong> optical properties in the XoZ plan. (a) Beam size variations<br />
(σx) along the <strong>beam</strong> axis z, due to the <strong>beam</strong> divergence (σθ ). The correlation between <strong>beam</strong> size<br />
(σx) and divergence (σθ ) is illustrated in figures (b), (c) and (d), showing the rotation of the elliptic<br />
phase space along the <strong>beam</strong> axis at three positions, −120, 0 and +120 mm, respectively. The<br />
colored scale refers to the normalized <strong>proton</strong> probability density function in the phase space. A<br />
similar relationship holds in the YoZ plan.<br />
2.1.2. GateSourceTPSPencilBeam. To simulate a treatment plan, the GateSourceTPSPencil-<br />
Beam source requires two input files: the source description file and the plan description file.<br />
The source description file describes the <strong>beam</strong> delivery system by a collection of polynomial<br />
equations allowing us to compute the optical and energy properties of every single <strong>pencil</strong><br />
<strong>beam</strong> at the nozzle exit, as a function of the <strong>beam</strong> energy at the nozzle entrance. There<strong>for</strong>e,<br />
it contains eight equations: two equations describe energy properties (E0 and σE) and six<br />
describe optical properties (σx, σθ, ɛx,θ, σy, σφ, ɛy,φ), each equation being a function of the<br />
energy at the nozzle entrance. The user can define the polynomial order of each equation and<br />
then the corresponding coefficients. For instance, to define a N order polynomial equation <strong>for</strong><br />
the energy spread σE(E), the user must define the N coefficients ai, with E the <strong>beam</strong> energy<br />
(at the nozzle entrance) and i the coefficient order:<br />
N�<br />
σE(E) = ai × E i . (1)<br />
i=0<br />
The source description file also contains the position of the two <strong>scanning</strong> magnets relatively<br />
to the isocenter and the distance between the nozzle exit and the isocenter, in order to compute<br />
the position and direction of each <strong>pencil</strong> <strong>beam</strong> at the nozzle exit. The plan description file<br />
describing the treatment plan contains one or multiple fields, each being described by a gantry<br />
angle and a collection of <strong>pencil</strong> <strong>beam</strong>s (section 2.1.1).<br />
Each <strong>pencil</strong> <strong>beam</strong> is characterized by its weight, its position in the isocenter plan and<br />
its energy at the nozzle entrance. Weights can be expressed as a number of <strong>proton</strong>s, or as<br />
monitor units (MU), that are internally converted into a number of <strong>proton</strong>s as a function of<br />
1<br />
0.9<br />
0.8<br />
0.7<br />
0.6<br />
0.5<br />
0.4<br />
0.3<br />
0.2<br />
0.1<br />
0