Instruction in Functional Assessment, 2014a
Instruction in Functional Assessment, 2014a
Instruction in Functional Assessment, 2014a
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Instruction</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Functional</strong> <strong>Assessment</strong> Chapter 2<br />
90% of 176 <strong>in</strong>patient cases of <strong>in</strong>dividuals with <strong>in</strong>tellectual disability and severe challeng<strong>in</strong>g<br />
behaviors were identified as a result of conduct<strong>in</strong>g a series of more <strong>in</strong>dividually-tailored or<br />
idiosyncratic FAn.<br />
Researchers have attempted to address the difficulties with conduct<strong>in</strong>g FAn, such as<br />
the ethical issues when target<strong>in</strong>g harmful behaviors (Hanley, 2012). As one approach, procedures<br />
may be modified to reduce the threat of harm to the <strong>in</strong>dividual due to provocation<br />
of the challeng<strong>in</strong>g behavior dur<strong>in</strong>g the assessment conditions. For <strong>in</strong>stance, conditions may<br />
be a s<strong>in</strong>gle trial (rather than 5-m<strong>in</strong> sessions) and embedded <strong>in</strong> naturally-occurr<strong>in</strong>g ongo<strong>in</strong>g<br />
activities <strong>in</strong> the <strong>in</strong>dividual’s environment (Bloom et al., 2011; Bloom, Lambert, Dayton,<br />
& Samaha, 2013). Other approaches entail measur<strong>in</strong>g precursor behaviors <strong>in</strong>stead of the<br />
actual challeng<strong>in</strong>g behavior (Fritz et al., 2013) or latency to engage <strong>in</strong> the challeng<strong>in</strong>g behavior<br />
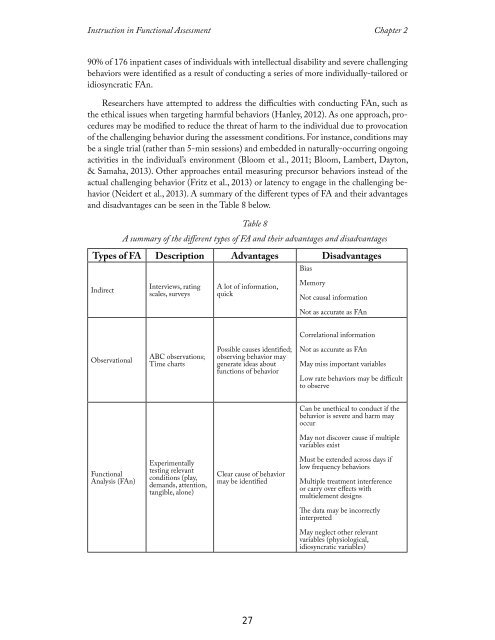
(Neidert et al., 2013). A summary of the different types of FA and their advantages<br />
and disadvantages can be seen <strong>in</strong> the Table 8 below.<br />
Table 8<br />
A summary of the different types of FA and their advantages and disadvantages<br />
Types of FA Description Advantages Disadvantages<br />
Bias<br />
Indirect<br />
Interviews, rat<strong>in</strong>g<br />
scales, surveys<br />
A lot of <strong>in</strong>formation,<br />
quick<br />
Memory<br />
Not causal <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Not as accurate as FAn<br />
Correlational <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Observational<br />
ABC observations;<br />
Time charts<br />
Possible causes identified;<br />
observ<strong>in</strong>g behavior may<br />
generate ideas about<br />
functions of behavior<br />
Not as accurate as FAn<br />
May miss important variables<br />
Low rate behaviors may be difficult<br />
to observe<br />
Can be unethical to conduct if the<br />
behavior is severe and harm may<br />
occur<br />
May not discover cause if multiple<br />
variables exist<br />
<strong>Functional</strong><br />
Analysis (FAn)<br />
Experimentally<br />
test<strong>in</strong>g relevant<br />
conditions (play,<br />
demands, attention,<br />
tangible, alone)<br />
Clear cause of behavior<br />
may be identified<br />
Must be extended across days if<br />
low frequency behaviors<br />
Multiple treatment <strong>in</strong>terference<br />
or carry over effects with<br />
multielement designs<br />
The data may be <strong>in</strong>correctly<br />
<strong>in</strong>terpreted<br />
May neglect other relevant<br />
variables (physiological,<br />
idiosyncratic variables)<br />
27