3. FOOD ChEMISTRy & bIOTEChNOLOGy 3.1. Lectures
3. FOOD ChEMISTRy & bIOTEChNOLOGy 3.1. Lectures
3. FOOD ChEMISTRy & bIOTEChNOLOGy 3.1. Lectures
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Chem. Listy, 102, s265–s1311 (2008) Food Chemistry & Biotechnology<br />
HO HO<br />
OH<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
R= α/β-H 1a<br />
α-CH3 1b<br />
OR<br />
HO O<br />
HO HO<br />
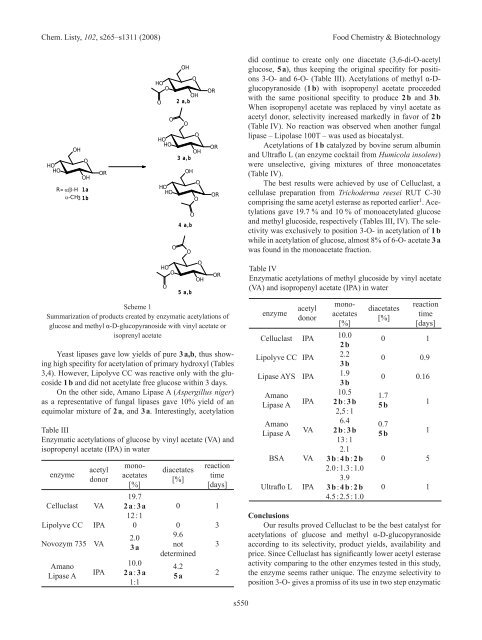
Yeast lipases gave low yields of pure 3 a,b, thus showing<br />
high specifity for acetylation of primary hydroxyl (Tables<br />
3,4). However, Lipolyve CC was reactive only with the glucoside<br />
1 b and did not acetylate free glucose within 3 days.<br />
On the other side, Amano Lipase A (Aspergillus niger)<br />
as a representative of fungal lipases gave 10% yield of an<br />
equimolar mixture of 2 a, and 3 a. Interestingly, acetylation<br />
O<br />
O<br />
HO HO<br />
O<br />
HO O<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
O<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
2 a,b<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
3 a,b<br />
OH<br />
4 a,b<br />
O<br />
5 a ,b<br />
Scheme 1<br />
Summarization of products created by enzymatic acetylations of<br />
glucose and methyl α-D-glucopyranoside with vinyl acetate or<br />
isoprenyl acetate<br />
Table III<br />
Enzymatic acetylations of glucose by vinyl acetate (VA) and<br />
isopropenyl acetate (IPA) in water<br />
enzyme<br />
acetyl<br />
donor<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
OR<br />
OR<br />
OR<br />
OR<br />
mono-<br />
diacetates reaction<br />
acetates<br />
[%]<br />
time<br />
[%] [days]<br />
Celluclast VA<br />
19.7<br />
2 a : 3 a<br />
12 : 1<br />
0 1<br />
Lipolyve CC IPA 0 0 3<br />
novozym 735 VA<br />
2.0<br />
9.6<br />
3 a<br />
3<br />
not<br />
determined<br />
Amano<br />
Lipase A<br />
IPA<br />
10.0<br />
2 a : 3 a<br />
1:1<br />
4.2<br />
5 a<br />
2<br />
s550<br />
did continue to create only one diacetate (3,6-di-O-acetyl<br />
glucose, 5 a), thus keeping the original specifity for positions<br />
3-O- and 6-O- (Table III). Acetylations of methyl α-Dglucopyranoside<br />
(1 b) with isopropenyl acetate proceeded<br />
with the same positional specifity to produce 2 b and 3 b.<br />
When isopropenyl acetate was replaced by vinyl acetate as<br />
acetyl donor, selectivity increased markedly in favor of 2 b<br />
(Table IV). no reaction was observed when another fungal<br />
lipase – Lipolase 100T – was used as biocatalyst.<br />
Acetylations of 1 b catalyzed by bovine serum albumin<br />
and Ultraflo L (an enzyme cocktail from Humicola insolens)<br />
were unselective, giving mixtures of three monoacetates<br />
(Table IV).<br />
The best results were achieved by use of Celluclast, a<br />
cellulase preparation from Trichoderma reesei RUT C-30<br />
comprising the same acetyl esterase as reported earlier 1 . Acetylations<br />
gave 19.7 % and 10 % of monoacetylated glucose<br />
and methyl glucoside, respectively (Tables III, IV). The selectivity<br />
was exclusively to position 3-O- in acetylation of 1 b<br />
while in acetylation of glucose, almost 8% of 6-O- acetate 3 a<br />
was found in the monoacetate fraction.<br />
Table IV<br />
Enzymatic acetylations of methyl glucoside by vinyl acetate<br />
(VA) and isopropenyl acetate (IPA) in water<br />
enzyme<br />
acetyl<br />
donor<br />
Celluclast IPA<br />
10.0<br />
2 b<br />
Lipolyve CC IPA<br />
2.2<br />
3 b<br />
Lipase AYS IPA<br />
1.9<br />
3 b<br />
Amano<br />
Lipase A<br />
IPA<br />
10.5<br />
2 b : 3 b<br />
2,5 : 1<br />
Amano<br />
Lipase A<br />
VA<br />
6.4<br />
2 b : 3 b<br />
13 : 1<br />
2.1<br />
BSA VA 3 b : 4 b : 2 b<br />
2.0 : 1.3 : 1.0<br />
<strong>3.</strong>9<br />
Ultraflo L IPA 3 b : 4 b : 2 b<br />
4.5 : 2.5 : 1.0<br />
mono-<br />
diacetates<br />
reaction<br />
acetates<br />
[%]<br />
time<br />
[%] [days]<br />
0 1<br />
0 0.9<br />
0 0.16<br />
1.7<br />
5 b<br />
0.7<br />
5 b<br />
Conclusions<br />
Our results proved Celluclast to be the best catalyst for<br />
acetylations of glucose and methyl α-D-glucopyranoside<br />
according to its selectivity, product yields, availability and<br />
price. Since Celluclast has significantly lower acetyl esterase<br />
activity comparing to the other enzymes tested in this study,<br />
the enzyme seems rather unique. The enzyme selectivity to<br />
position 3-O- gives a promiss of its use in two step enzymatic<br />
1<br />
1<br />
0 5<br />
0 1