- Page 2:
Olaf Schmidt Wood and Tree Fungi Bi
- Page 6:
Professor Dr. Olaf Schmidt Universi
- Page 10:
Preface This book is the updated re
- Page 14:
X Contents 5 Damages by Viruses and
- Page 18:
1 Introduction Wood is damaged by v
- Page 22:
2 Biology 2.1 Cytology and Morpholo
- Page 26:
2.1 Cytology and Morphology 5 10 nm
- Page 30:
2.1 Cytology and Morphology 7 The h
- Page 34:
2.1 Cytology and Morphology 9 Due t
- Page 38: 2.2 Growth and Spreading 11 velopme
- Page 42: 2.2 Growth and Spreading 13 Fig.2.6
- Page 46: 2.2 Growth and Spreading 15 Fig.2.7
- Page 50: 2.2 Growth and Spreading 17 Fig.2.8
- Page 54: 2.2 Growth and Spreading 19 Fig.2.1
- Page 58: 2.2 Growth and Spreading 21 shapedp
- Page 62: 2.2 Growth and Spreading 23 surface
- Page 66: 2.2 Growth and Spreading 25 and Ish
- Page 70: 2.3 Sexuality 27 the basidiospores
- Page 74: 2.3 Sexuality 29 Table 2.6. Pairing
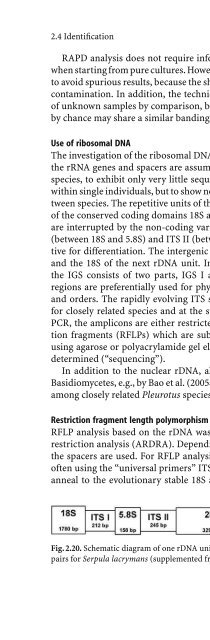
- Page 78: 2.4 Identification 31 In addition t
- Page 82: 2.4 Identification 33 2.4.2 Molecul
- Page 86: 2.4 Identification 35 antibodies. A
- Page 92: 38 2 Biology to conserved rDNA regi
- Page 96: 40 2 Biology Table 2.8. Sequenced a
- Page 100: 42 2 Biology Fig.2.22. Phylogeny of
- Page 104: 44 2 Biology Table 2.9. Species-spe
- Page 108: 46 2 Biology Fig.2.24. MALDI-TOF ma
- Page 112: 48 2 Biology nant and a vowel. The
- Page 116: 50 2 Biology or unitunicate ascus w
- Page 120: 52 2 Biology The Deuteromycetes are
- Page 124: 54 3 Physiology wounding a tree. A
- Page 128: 56 3 Physiology 1987, 1991). Transl
- Page 132: 58 3 Physiology durability of many
- Page 136: 60 3 Physiology at more than 20% CO
- Page 140:
62 3 Physiology of the water vapor
- Page 144:
64 3 Physiology intermolecular cavi
- Page 148:
66 3 Physiology 1974). Wood fungi a
- Page 152:
68 3 Physiology Table 3.8. Cardinal
- Page 156:
70 3 Physiology more thermotolerant
- Page 160:
72 3 Physiology Fig.3.2. pH value r
- Page 164:
74 3 Physiology Antrodia vaillantii
- Page 168:
76 3 Physiology Fig.3.3. Fruit body
- Page 172:
78 3 Physiology are only valuable i
- Page 176:
80 3 Physiology tree fungi (“biol
- Page 180:
82 3 Physiology The various competi
- Page 184:
84 3 Physiology 1989). The soil qua
- Page 188:
4 Wood Cell Wall Degradation 4.1 En
- Page 192:
4.1 Enzymes and Low Molecular Agent
- Page 196:
4.1 Enzymes and Low Molecular Agent
- Page 200:
4.3 Degradation of Hemicelluloses 9
- Page 204:
4.4 Cellulose Degradation 95 4.4 Ce
- Page 208:
4.4 Cellulose Degradation 97 metabo
- Page 212:
4.5 Lignin Degradation 99 The acces
- Page 216:
4.5 Lignin Degradation 101 vary als
- Page 220:
4.5 Lignin Degradation 103 (porphyr
- Page 224:
4.5 Lignin Degradation 105 genes en
- Page 228:
4.5 Lignin Degradation 107 that oxi
- Page 232:
110 5 Damages by Viruses and Bacter
- Page 236:
112 5 Damages by Viruses and Bacter
- Page 240:
114 5 Damages by Viruses and Bacter
- Page 244:
116 5 Damages by Viruses and Bacter
- Page 248:
118 5 Damages by Viruses and Bacter
- Page 252:
120 6 Wood Discoloration The wood-d
- Page 256:
122 6 Wood Discoloration Fig.6.2. M
- Page 260:
124 6 Wood Discoloration bark. Pulp
- Page 264:
126 6 Wood Discoloration Fig.6.3. B
- Page 268:
128 6 Wood Discoloration window con
- Page 272:
130 6 Wood Discoloration Fig.6.4. R
- Page 276:
132 6 Wood Discoloration is perform
- Page 280:
7 Wood Rot There are three types of
- Page 284:
7.1 Brown Rot 137 et al. 2004), and
- Page 288:
7.2 White Rot 139 tarius, T. versic
- Page 292:
7.2 White Rot 141 Fig.7.3. Manganes
- Page 296:
7.3 Soft Rot 143 Fig.7.4. Soft rot.
- Page 300:
7.3 Soft Rot 145 Further infection
- Page 304:
7.4 Protection 147 (Willeitner and
- Page 308:
7.4 Protection 149 preservatives. I
- Page 312:
7.4 Protection 151 ing efficacy and
- Page 316:
7.4 Protection 153 fungicides and p
- Page 320:
7.4 Protection 155 Table 7.9 shows
- Page 324:
7.4 Protection 157 unpleasant smell
- Page 328:
7.4 Protection 159 is a mixture of
- Page 332:
162 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi tophtho
- Page 336:
164 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi Table 8
- Page 340:
166 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi Fig.8.2
- Page 344:
168 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi cut sec
- Page 348:
170 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi ins; e.
- Page 352:
172 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi through
- Page 356:
174 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi After w
- Page 360:
176 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi Fig.8.8
- Page 364:
178 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi for bra
- Page 368:
180 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi Fig.8.1
- Page 372:
182 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi The typ
- Page 376:
184 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi by Armi
- Page 380:
186 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi schwein
- Page 384:
188 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi Fruit b
- Page 388:
190 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi (pine),
- Page 392:
192 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi Fig.8.1
- Page 396:
194 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi violet
- Page 400:
196 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi Fig.8.1
- Page 404:
198 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi Signifi
- Page 408:
200 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi 8.3.11
- Page 412:
202 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi inChap.
- Page 416:
204 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi Strands
- Page 420:
206 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi 8.4.5 S
- Page 424:
208 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi Fig.8.1
- Page 428:
210 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi timber
- Page 432:
212 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi 8.5.2 L
- Page 436:
214 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi 8.5.2.3
- Page 440:
216 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi Strands
- Page 444:
218 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi Oligopo
- Page 448:
220 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi 1985).
- Page 452:
222 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi Strands
- Page 456:
224 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi Occurre
- Page 460:
226 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi alive m
- Page 464:
228 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi Strands
- Page 468:
230 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi to penc
- Page 472:
232 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi with it
- Page 476:
234 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi most im
- Page 480:
236 8 Habitat of Wood Fungi 1991; R
- Page 484:
238 9 Positive Effects of Wood-Inha
- Page 488:
240 9 Positive Effects of Wood-Inha
- Page 492:
242 9 Positive Effects of Wood-Inha
- Page 496:
244 9 Positive Effects of Wood-Inha
- Page 500:
246 9 Positive Effects of Wood-Inha
- Page 504:
248 9 Positive Effects of Wood-Inha
- Page 508:
250 9 Positive Effects of Wood-Inha
- Page 512:
Appendix 1 Identification Key for S
- Page 516:
Appendix 1 255 thesebrighttobrown;v
- Page 520:
Appendix 1 257 22(13,17) recognizab
- Page 524:
Appendix 1 259 margin; sometimes wi
- Page 528:
262 Appendix 2 Candida utilis (Henn
- Page 532:
264 Appendix 2 Memnoniella echinata
- Page 536:
266 Appendix 2 Stereum rugosum (Per
- Page 540:
268 References Allen MF (1991) The
- Page 544:
270 References Bastawde KB (1992) X
- Page 548:
272 References Blanchette RA, Cease
- Page 552:
274 References Bucur V (2003) Nonde
- Page 556:
276 References Cooper JI, Edwards M
- Page 560:
278 References Dickinson DJ, Sorkho
- Page 564:
280 References Ellis EA (1976) Brit
- Page 568:
282 References Frankland JC, Hedger
- Page 572:
284 References Grinda M, Kerner-Gan
- Page 576:
286 References Haustrup ACS, Green
- Page 580:
288 References Holdenrieder O (1982
- Page 584:
290 References Jellison J, Chen Y,
- Page 588:
292 References Katayama S, Watanabe
- Page 592:
294 References Klein-Gebbinck HW, B
- Page 596:
296 References Laks PE, Park CG, Ri
- Page 600:
298 References Liese W, Kumar S (20
- Page 604:
300 References Martin F, Delaruelle
- Page 608:
302 References Moreth U, Schmidt O
- Page 612:
304 References Nilsson T, Obst JR,
- Page 616:
306 References Payne C, Petty JA, W
- Page 620:
308 References Rapp AO, Müller J (
- Page 624:
310 References Rösch R (1972) Phen
- Page 628:
312 References Schmidt H (2005) Au
- Page 632:
314 References Schmidt O, Schmitt U
- Page 636:
316 References Schwarze FWMR (2005)
- Page 640:
318 References Siepmann R (1970) Ar
- Page 644:
320 References Sutter H-P (2003) Ho
- Page 648:
322 References Uemura S, Ishihara M
- Page 652:
324 References Watanabe T, Sabrina
- Page 656:
326 References Wohlers A, Kowol T,
- Page 660:
Subject Index Abiotic wood discolor
- Page 664:
Subject Index 331 Fruit body format
- Page 668:
Subject Index 333 Phylogenetic anal