Diagnostic Ultrasound - Abdomen and Pelvis
Pancreas PANCREAS IN SITU Anatomy: Abdomen Stomach (cut & removed) Spleen Gastroduodenal artery Superior (dorsal) pancreatic artery Splenic artery Great pancreatic artery Posterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery Anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery Base of transverse mesocolon Duodenum Transverse colon Duodeno-jejunal junction Superior mesenteric artery & vein Base of small bowel mesentery Graphic shows the arterial supply to the body & tail of the pancreas through terminal branches of the splenic artery, which are variable in number & size. The two largest are usually the dorsal (superior) and great pancreatic arteries, which arise from the proximal & distal splenic artery, respectively. The arteries to the pancreatic head and duodenum come from the pancreaticoduodenal arcades that receive flow from the celiac and superior mesenteric arteries. The superior mesenteric vessels pass behind the neck of the pancreas and in front of the third portion of the duodenum. The root of the transverse mesocolon and small bowel mesentery arise from the surface of the pancreas and transmit the blood vessels to the small bowel & transverse colon. The splenic vein runs along the dorsal surface of the pancreas. The splenic vessels and pancreatic tail insert into the splenic hilum. 39
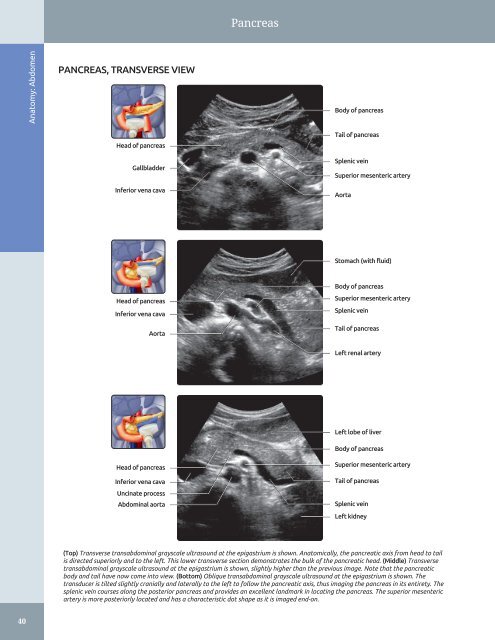
Pancreas Anatomy: Abdomen PANCREAS, TRANSVERSE VIEW Body of pancreas Head of pancreas Gallbladder Inferior vena cava Tail of pancreas Splenic vein Superior mesenteric artery Aorta Stomach (with fluid) Head of pancreas Inferior vena cava Aorta Body of pancreas Superior mesenteric artery Splenic vein Tail of pancreas Left renal artery Left lobe of liver Head of pancreas Inferior vena cava Uncinate process Abdominal aorta Body of pancreas Superior mesenteric artery Tail of pancreas Splenic vein Left kidney (Top) Transverse transabdominal grayscale ultrasound at the epigastrium is shown. Anatomically, the pancreatic axis from head to tail is directed superiorly and to the left. This lower transverse section demonstrates the bulk of the pancreatic head. (Middle) Transverse transabdominal grayscale ultrasound at the epigastrium is shown, slightly higher than the previous image. Note that the pancreatic body and tail have now come into view. (Bottom) Oblique transabdominal grayscale ultrasound at the epigastrium is shown. The transducer is tilted slightly cranially and laterally to the left to follow the pancreatic axis, thus imaging the pancreas in its entirety. The splenic vein courses along the posterior pancreas and provides an excellent landmark in locating the pancreas. The superior mesenteric artery is more posteriorly located and has a characteristic dot shape as it is imaged end-on. 40
- Page 10 and 11: Preface
- Page 12 and 13: Acknowledgements Text Editors Nina
- Page 14 and 15: Sections PART I - Anatomy SECTION 1
- Page 16 and 17: TABLE OF CONTENTS VASCULAR CONDITIO
- Page 18 and 19: TABLE OF CONTENTS 562 Perigraft Flu
- Page 20 and 21: TABLE OF CONTENTS 906 Hyperechoic G
- Page 22 and 23: Diagnostic Ultrasound
- Page 24 and 25: PART I SECTION 1 Abdomen Liver 4 Bi
- Page 26 and 27: Liver ○ Appear as echolucent defe
- Page 28 and 29: Liver Coronary ligament HEPATIC ATT
- Page 30 and 31: Liver Segment 8 HEPATIC SEGMENTS Se
- Page 32 and 33: Liver Rectus abdominis muscle LEFT
- Page 34 and 35: Liver Abdominal muscle LEFT LOBE OF
- Page 36 and 37: Liver Anterior right portal vein RI
- Page 38 and 39: Liver PORTA HEPATIS Anatomy: Abdome
- Page 40 and 41: Liver Inferior liver margin OTHER V
- Page 42 and 43: Biliary System • Harmonic imaging
- Page 44 and 45: Biliary System Left hepatic duct Ri
- Page 46 and 47: Biliary System Right rectus muscle
- Page 48 and 49: Biliary System COMMON BILE DUCT Ana
- Page 50 and 51: Biliary System LEFT INTRAHEPATIC DU
- Page 52 and 53: Spleen SPLEEN ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY
- Page 54 and 55: Spleen Fat in splenic hilum Left he
- Page 56 and 57: Spleen SPLENIC VESSELS Anatomy: Abd
- Page 58 and 59: Spleen Splenosis ANATOMICAL VARIANT
- Page 62 and 63: Pancreas PANCREAS, TRANSVERSE VIEW
- Page 64 and 65: Pancreas Left lobe of liver PANCREA
- Page 66 and 67: Kidneys - Normal peak systolic velo
- Page 68 and 69: Kidneys KIDNEY ARTERIES AND INTERIO
- Page 70 and 71: Kidneys RENAL FASCIA AND PERIRENAL
- Page 72 and 73: Kidneys Right hemidiaphragm RIGHT K
- Page 74 and 75: Kidneys RIGHT KIDNEY, CT CORRELATIO
- Page 76 and 77: Kidneys Right erector spinae muscle
- Page 78 and 79: Kidneys RIGHT INTRARENAL ARTERY AND
- Page 80 and 81: Kidneys LEFT KIDNEY, CT CORRELATION
- Page 82 and 83: Kidneys LEFT KIDNEY, CT CORRELATION
- Page 84 and 85: Kidneys Subcutaneous fat Left latis
- Page 86 and 87: Kidneys LEFT MAIN RENAL ARTERY AND
- Page 88 and 89: Kidneys Right lobe of liver MULTIPL
- Page 90 and 91: Bowel - Forms an incomplete ring in
- Page 92 and 93: Bowel Falciform ligament STOMACH AN
- Page 94 and 95: Bowel SMALL INTESTINE Anatomy: Abdo
- Page 96 and 97: Bowel Abdominal wall STOMACH Anatom
- Page 98 and 99: Bowel Rectus muscle SMALL BOWEL Ana
- Page 100 and 101: Bowel Abdominal wall musculature Ce
- Page 102 and 103: Bowel LARGE BOWEL Abdominal wall mu
- Page 104 and 105: Bowel Urinary bladder RECTOSIGMOID
- Page 106 and 107: Abdominal Lymph Nodes RETROPERITONE
- Page 108 and 109: Abdominal Lymph Nodes LYMPHANGIOGRA
Pancreas<br />
Anatomy: <strong>Abdomen</strong><br />
PANCREAS, TRANSVERSE VIEW<br />
Body of pancreas<br />
Head of pancreas<br />
Gallbladder<br />
Inferior vena cava<br />
Tail of pancreas<br />
Splenic vein<br />
Superior mesenteric artery<br />
Aorta<br />
Stomach (with fluid)<br />
Head of pancreas<br />
Inferior vena cava<br />
Aorta<br />
Body of pancreas<br />
Superior mesenteric artery<br />
Splenic vein<br />
Tail of pancreas<br />
Left renal artery<br />
Left lobe of liver<br />
Head of pancreas<br />
Inferior vena cava<br />
Uncinate process<br />
Abdominal aorta<br />
Body of pancreas<br />
Superior mesenteric artery<br />
Tail of pancreas<br />
Splenic vein<br />
Left kidney<br />
(Top) Transverse transabdominal grayscale ultrasound at the epigastrium is shown. Anatomically, the pancreatic axis from head to tail<br />
is directed superiorly <strong>and</strong> to the left. This lower transverse section demonstrates the bulk of the pancreatic head. (Middle) Transverse<br />
transabdominal grayscale ultrasound at the epigastrium is shown, slightly higher than the previous image. Note that the pancreatic<br />
body <strong>and</strong> tail have now come into view. (Bottom) Oblique transabdominal grayscale ultrasound at the epigastrium is shown. The<br />
transducer is tilted slightly cranially <strong>and</strong> laterally to the left to follow the pancreatic axis, thus imaging the pancreas in its entirety. The<br />
splenic vein courses along the posterior pancreas <strong>and</strong> provides an excellent l<strong>and</strong>mark in locating the pancreas. The superior mesenteric<br />
artery is more posteriorly located <strong>and</strong> has a characteristic dot shape as it is imaged end-on.<br />
40