Diagnostic Ultrasound - Abdomen and Pelvis
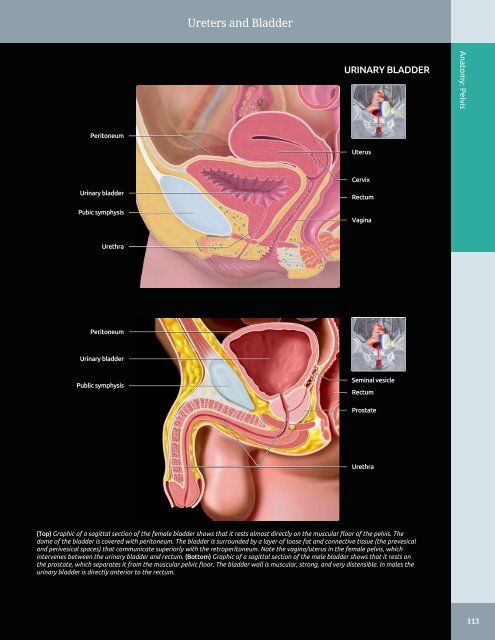
Ureters and Bladder URINARY BLADDER Anatomy: Pelvis Peritoneum Uterus Cervix Urinary bladder Pubic symphysis Rectum Vagina Urethra Peritoneum Urinary bladder Public symphysis Seminal vesicle Rectum Prostate Urethra (Top) Graphic of a sagittal section of the female bladder shows that it rests almost directly on the muscular floor of the pelvis. The dome of the bladder is covered with peritoneum. The bladder is surrounded by a layer of loose fat and connective tissue (the prevesical and perivesical spaces) that communicate superiorly with the retroperitoneum. Note the vagina/uterus in the female pelvis, which intervenes between the urinary bladder and rectum. (Bottom) Graphic of a sagittal section of the male bladder shows that it rests on the prostate, which separates it from the muscular pelvic floor. The bladder wall is muscular, strong, and very distensible. In males the urinary bladder is directly anterior to the rectum. 113
Ureters and Bladder Anatomy: Pelvis URINARY BLADDER, ULTRASOUND Bladder wall Bladder lumen Uterus Bladder Ovary Cervix Uterus Pouch of Douglas Bladder Partly seen left ureter jet Right ureteric jet (Top) Transverse transabdominal grayscale ultrasound shows the suprapubic region at the uterine body level. The transducer must be angled caudally to image the urinary bladder, especially when it is not well distended and assumes a retropubic location. (Middle) Longitudinal transabdominal grayscale ultrasound at the suprapubic region shows a well-distended urinary bladder with a posteriorly located uterus. Note the anechoic appearance of the urinary bladder due to its fluid-filled state, which acts as an acoustic window, permitting through transmission of the ultrasound beam and optimal visualization of posterior pelvic structures. (Bottom) Transverse color Doppler ultrasound of the bladder in the suprapubic region shows ureteral jets. 114
- Page 84 and 85: Kidneys Subcutaneous fat Left latis
- Page 86 and 87: Kidneys LEFT MAIN RENAL ARTERY AND
- Page 88 and 89: Kidneys Right lobe of liver MULTIPL
- Page 90 and 91: Bowel - Forms an incomplete ring in
- Page 92 and 93: Bowel Falciform ligament STOMACH AN
- Page 94 and 95: Bowel SMALL INTESTINE Anatomy: Abdo
- Page 96 and 97: Bowel Abdominal wall STOMACH Anatom
- Page 98 and 99: Bowel Rectus muscle SMALL BOWEL Ana
- Page 100 and 101: Bowel Abdominal wall musculature Ce
- Page 102 and 103: Bowel LARGE BOWEL Abdominal wall mu
- Page 104 and 105: Bowel Urinary bladder RECTOSIGMOID
- Page 106 and 107: Abdominal Lymph Nodes RETROPERITONE
- Page 108 and 109: Abdominal Lymph Nodes LYMPHANGIOGRA
- Page 110 and 111: Peritoneal Spaces and Structures PE
- Page 112 and 113: Peritoneal Spaces and Structures PE
- Page 114 and 115: Peritoneal Spaces and Structures Li
- Page 116 and 117: Peritoneal Spaces and Structures IN
- Page 118 and 119: Abdominal Wall ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL W
- Page 120 and 121: Abdominal Wall MUSCLES OF BACK IN S
- Page 122 and 123: Abdominal Wall Subcutaneous fat Rig
- Page 124 and 125: Abdominal Wall Right lobe of liver
- Page 126 and 127: Abdominal Wall Right rectus abdomin
- Page 128 and 129: Abdominal Wall Subcutaneous fat Rig
- Page 130 and 131: PART I SECTION 2 Pelvis Ureters and
- Page 132 and 133: Ureters and Bladder - Distended bla
- Page 136 and 137: Ureters and Bladder CT UROGRAM CORR
- Page 138 and 139: Ureters and Bladder Liver URETER An
- Page 140 and 141: Ureters and Bladder WEIGERT-MEYER L
- Page 142 and 143: Prostate ○ Sac-like structures su
- Page 144 and 145: Prostate ZONAL ANATOMY OF THE PROST
- Page 146 and 147: Prostate SEMINAL VESICLES AND VAS D
- Page 148 and 149: Prostate PROSTATE ANATOMY Anatomy:
- Page 150 and 151: Testes ○ Internal oblique muscle
- Page 152 and 153: Testes EPIDIDYMIS AND SCROTAL WALL
- Page 154 and 155: Testes TESTIS, SAGITTAL VIEW Anatom
- Page 156 and 157: Testes Scrotal wall EPIDIDYMIS, HEA
- Page 158 and 159: Testes TESTICULAR AND EPIDIDYMAL AP
- Page 160 and 161: Testes ARTERIAL AND VENOUS SUPPLY A
- Page 162 and 163: Uterus ARTERIES OF UTERUS AND ADJAC
- Page 164 and 165: Uterus NORMAL VARIATIONS, UTERINE P
- Page 166 and 167: Uterus UTERINE VARIATIONS WITH AGE
- Page 168 and 169: Uterus CYCLIC CHANGES OF ENDOMETRIU
- Page 170 and 171: Uterus FALLOPIAN TUBE Anatomy: Pelv
- Page 172 and 173: Cervix GRAPHICS OF CERVIX ANATOMY A
- Page 174 and 175: Cervix TRANSVAGINAL ULTRASOUND OF C
- Page 176 and 177: Cervix CHANGES OF CERVIX DURING PRE
- Page 178 and 179: Vagina GRAPHICS OF NORMAL VAGINAL A
- Page 180 and 181: Vagina Urinary bladder TRANSVERSE U
- Page 182 and 183: Vagina SPECTRAL WAVEFORM OF VAGINAL
Ureters <strong>and</strong> Bladder<br />
URINARY BLADDER<br />
Anatomy: <strong>Pelvis</strong><br />
Peritoneum<br />
Uterus<br />
Cervix<br />
Urinary bladder<br />
Pubic symphysis<br />
Rectum<br />
Vagina<br />
Urethra<br />
Peritoneum<br />
Urinary bladder<br />
Public symphysis<br />
Seminal vesicle<br />
Rectum<br />
Prostate<br />
Urethra<br />
(Top) Graphic of a sagittal section of the female bladder shows that it rests almost directly on the muscular floor of the pelvis. The<br />
dome of the bladder is covered with peritoneum. The bladder is surrounded by a layer of loose fat <strong>and</strong> connective tissue (the prevesical<br />
<strong>and</strong> perivesical spaces) that communicate superiorly with the retroperitoneum. Note the vagina/uterus in the female pelvis, which<br />
intervenes between the urinary bladder <strong>and</strong> rectum. (Bottom) Graphic of a sagittal section of the male bladder shows that it rests on<br />
the prostate, which separates it from the muscular pelvic floor. The bladder wall is muscular, strong, <strong>and</strong> very distensible. In males the<br />
urinary bladder is directly anterior to the rectum.<br />
113