"Front Matter". In: Organosilanes in Radical Chemistry - Index of
"Front Matter". In: Organosilanes in Radical Chemistry - Index of
"Front Matter". In: Organosilanes in Radical Chemistry - Index of
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
148 Consecutive <strong>Radical</strong> Reactions<br />
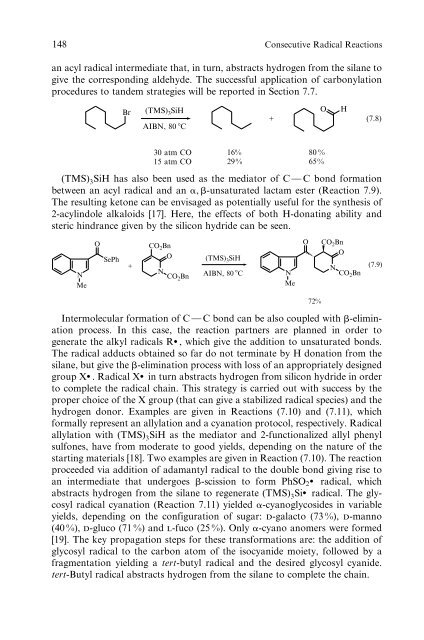
an acyl radical <strong>in</strong>termediate that, <strong>in</strong> turn, abstracts hydrogen from the silane to<br />
give the correspond<strong>in</strong>g aldehyde. The successful application <strong>of</strong> carbonylation<br />
procedures to tandem strategies will be reported <strong>in</strong> Section 7.7.<br />
Br (TMS) 3SiH AIBN, 80 �C<br />
+<br />
O H<br />
(7.8)<br />
30 atm CO<br />
15 atm CO<br />
16%<br />
29%<br />
80 %<br />
65%<br />
(TMS) 3SiH has also been used as the mediator <strong>of</strong> C w C bond formation<br />
between an acyl radical and an a, b-unsaturated lactam ester (Reaction 7.9).<br />
The result<strong>in</strong>g ketone can be envisaged as potentially useful for the synthesis <strong>of</strong><br />
2-acyl<strong>in</strong>dole alkaloids [17]. Here, the effects <strong>of</strong> both H-donat<strong>in</strong>g ability and<br />
steric h<strong>in</strong>drance given by the silicon hydride can be seen.<br />
N<br />
Me<br />
O<br />
SePh<br />
+<br />
CO2Bn O<br />
N<br />
CO2Bn (TMS) 3 SiH<br />
AIBN, 80 �C<br />
N<br />
Me<br />
O<br />
72%<br />
CO2Bn O<br />
N<br />
CO2Bn <strong>In</strong>termolecular formation <strong>of</strong> C w C bond can be also coupled with b-elim<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
process. <strong>In</strong> this case, the reaction partners are planned <strong>in</strong> order to<br />
generate the alkyl radicals R:, which give the addition to unsaturated bonds.<br />
The radical adducts obta<strong>in</strong>ed so far do not term<strong>in</strong>ate by H donation from the<br />
silane, but give the b-elim<strong>in</strong>ation process with loss <strong>of</strong> an appropriately designed<br />
group X:. <strong>Radical</strong> X: <strong>in</strong> turn abstracts hydrogen from silicon hydride <strong>in</strong> order<br />
to complete the radical cha<strong>in</strong>. This strategy is carried out with success by the<br />
proper choice <strong>of</strong> the X group (that can give a stabilized radical species) and the<br />
hydrogen donor. Examples are given <strong>in</strong> Reactions (7.10) and (7.11), which<br />
formally represent an allylation and a cyanation protocol, respectively. <strong>Radical</strong><br />
allylation with (TMS) 3SiH as the mediator and 2-functionalized allyl phenyl<br />
sulfones, have from moderate to good yields, depend<strong>in</strong>g on the nature <strong>of</strong> the<br />
start<strong>in</strong>g materials [18]. Two examples are given <strong>in</strong> Reaction (7.10). The reaction<br />
proceeded via addition <strong>of</strong> adamantyl radical to the double bond giv<strong>in</strong>g rise to<br />
an <strong>in</strong>termediate that undergoes b-scission to form PhSO2: radical, which<br />
abstracts hydrogen from the silane to regenerate (TMS) 3Si: radical. The glycosyl<br />
radical cyanation (Reaction 7.11) yielded a-cyanoglycosides <strong>in</strong> variable<br />
yields, depend<strong>in</strong>g on the configuration <strong>of</strong> sugar: d-galacto (73 %), d-manno<br />
(40 %), d-gluco (71 %) and l-fuco (25 %). Only a-cyano anomers were formed<br />
[19]. The key propagation steps for these transformations are: the addition <strong>of</strong><br />
glycosyl radical to the carbon atom <strong>of</strong> the isocyanide moiety, followed by a<br />
fragmentation yield<strong>in</strong>g a tert-butyl radical and the desired glycosyl cyanide.<br />
tert-Butyl radical abstracts hydrogen from the silane to complete the cha<strong>in</strong>.<br />
(7.9)