Integrated Cross-Sectorial Plan of Tirana-Durres Area
The Albanian Government and the National Spatial Plan have identified the Tiranë-Durrës area, as one of the most important economic areas of the country, and of the Balkan region. To ensure a sustainable territorial and urban development of this area, the Ministry of Urban Development in cooperation with the National Territorial Planning Agency has taken the initiative to draft a Cross-sectoral Integrated Plan for the economic area Tiranë – Durrës. The metropolitan region under study includes territories administered by 5 municipalities: Tiranë, Durrës, Vorë, Shijak, Kamëz. The Albanian Government and the National Spatial Plan have identified the Tiranë-Durrës area, as one of the most important economic areas of the country, and of the Balkan region. To ensure a sustainable territorial and urban development of this area, the Ministry of Urban Development in cooperation with the National Territorial Planning Agency has taken the initiative to draft a Cross-sectoral Integrated Plan for the economic area Tiranë – Durrës. The metropolitan region under study includes territories administered by 5 municipalities: Tiranë, Durrës, Vorë, Shijak, Kamëz.
• Creating a climate of trust, cooperation and teamwork among the actors; • Developing connections among businesses on common interest structures (cooperative and competitive), as complementary to one another; • Developing interactive networks and structures to promote innovation, with a view to obtaining globally competitive products and services. The main challenges in the formation of clusters: • Creating a climate of trust. Local, regional and central institutions should produce legal and fiscal incentives to support the creation of this climate, which is the main factor to the functioning of the cluster; • Creating a climate of cooperation. Through the mechanism of joint decision-making with governing boards, or legal or fiscal initiatives, the cooperation of actors involved in the cluster can and should be supported and Fazat zhvillimore të klasterit strengthened; • Agreeing on the use of product patents and innovative processes. If cooperation is guided by clear operating platforms, supported by legal instruments, then agreement can be reached; • The establishment of common approaches to disseminate knowledge and skills among actors in a cluster should be guided by independent public or private institutions; • The distribution of benefits should be run by management boards, where public institutions should be supportive actors; • The lack of time to deal with responsibilities and interact between actors needs to be addressed by promoting the use of electronic platforms. Given the complexity and challenges of cluster building, it is recommended to build combined and systematic strategies with all-inclusive approaches: Cluster development stages Cluster in creation Matured cluster Cluster in transition Champion at the national level World-class cluster Reborn cluster Cluster that supports emerging industries Public support for cluster development Specific programs and policies that address each stage of development Evaluation of developmental stages Standardization and evaluation Figure 4.7 Cluster development stages Let’s make a perfect cluster policy and 20 cluster programme, Berlin/Copenhagen, 2012 20 Let’s make a perfect cluster policy and cluster programme, Berlin/Copenhagen, 2012 82
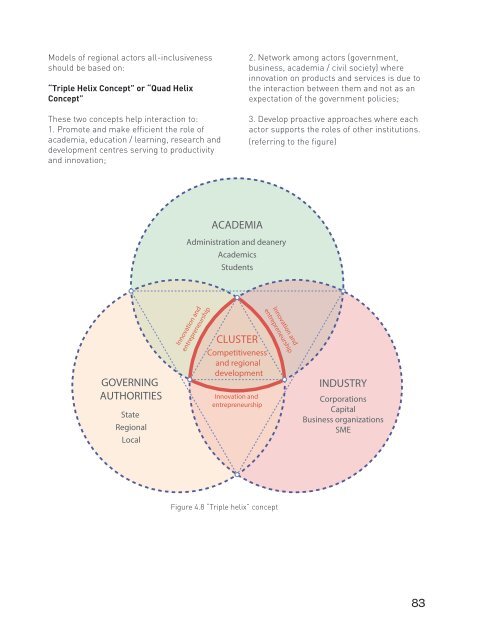
Models of regional actors all-inclusiveness should be based on: “Triple Helix Concept” or “Quad Helix Concept” These two concepts help interaction to: 1. Promote and make efficient the role of academia, education / learning, research and development centres serving to productivity and innovation; 2. Network among actors (government, business, academia / civil society) where innovation on products and services is due to the interaction between them and not as an expectation of the government policies; 3. Develop proactive approaches where each actor supports the roles of other institutions. (referring to the figure) ACADEMIA Administration and deanery Academics Students GOVERNING AUTHORITIES State Regional Local Innovation and entrepreneurship CLUSTER Competitiveness and regional development Innovation and entrepreneurship Innovation and entrepreneurship INDUSTRY Corporations Capital Business organizations SME Figure 4.8 “Triple helix” concept 83
- Page 34 and 35: Regional competitiveness profile: T
- Page 36 and 37: SARAJEVO ACCESSIBILITY AIR ROAD SEA
- Page 38 and 39: 1.2 Combination of the national pla
- Page 40 and 41: 1.3 Coordination of the plan After
- Page 42 and 43: 2SWOT analysis, territorial systems
- Page 44 and 45: 2.1 SWOT analysis The drafting of t
- Page 46 and 47: 2.2 Conclusions In conclusion of th
- Page 48 and 49: Scenario 1- Monocentric (Tirana) Th
- Page 50 and 51: Fushe Kruje Sukth Vore Kamez Durres
- Page 52 and 53: 3Vision and strategic objectives
- Page 54 and 55: Vision of the Integrated Cross-Sect
- Page 56 and 57: KRUJË VORË KAMËZ DURRËS SHIJAK
- Page 58 and 59: on the functions of the urban centr
- Page 60 and 61: Soft factors of regional and local
- Page 62 and 63: SO3. Improve infrastructure, transp
- Page 64 and 65: 4Regional development policies
- Page 66 and 67: 90 94 94 94 98 108 108 113 113 114
- Page 68 and 69: 138 138 139 141 142 143 143 143 143
- Page 70 and 71: Regional Development Policies The I
- Page 72 and 73: competitiveness, focusing on a glob
- Page 74 and 75: The governing structures should dev
- Page 76 and 77: EP3- Develop SMEs and innovation Th
- Page 78 and 79: Fund for Innovation. The board, thr
- Page 80 and 81: under the ground in order to avoid
- Page 82 and 83: Various services may be needed for
- Page 86 and 87: Dimensionet e ndryshme të një kla
- Page 88 and 89: There are a number of mechanisms wh
- Page 90 and 91: problems, to run R & D, or to devel
- Page 92 and 93: EP5- Territorial economic developme
- Page 94 and 95: For further economic development an
- Page 96 and 97: EP6- Regional branding and tourism
- Page 98 and 99: • Establishing areas for fairs, e
- Page 100 and 101: EP6.3- City and weekend tourism The
- Page 102 and 103: • Creating food festivals and com
- Page 104 and 105: Travel agents Tour operators Public
- Page 106 and 107: Guidelines for the development of u
- Page 108 and 109: participation of visitors intereste
- Page 110 and 111: 4.2 Urban development policies URBA
- Page 112 and 113: Metropolis Primary centre Secondary
- Page 114 and 115: Metropolis Primary centre Secondary
- Page 116 and 117: The plan promotes the consolidation
- Page 118 and 119: UP2.2- Regeneration of urban poles
- Page 120 and 121: Ishëm Thumanë Cudhi KRUJË Bubq F
- Page 122 and 123: Zonat informale për zhvillim dhe i
- Page 124 and 125: UP5- Comprehensive regional communi
- Page 126 and 127: further affect a better management
- Page 128 and 129: Adriatik Mamurras Ishëm Gramëz Th
- Page 130 and 131: Rural regeneration policies aim at
- Page 132 and 133: c) Marginal rural, agricultural-nat
Models <strong>of</strong> regional actors all-inclusiveness<br />
should be based on:<br />
“Triple Helix Concept” or “Quad Helix<br />
Concept”<br />
These two concepts help interaction to:<br />
1. Promote and make efficient the role <strong>of</strong><br />
academia, education / learning, research and<br />
development centres serving to productivity<br />
and innovation;<br />
2. Network among actors (government,<br />
business, academia / civil society) where<br />
innovation on products and services is due to<br />
the interaction between them and not as an<br />
expectation <strong>of</strong> the government policies;<br />
3. Develop proactive approaches where each<br />
actor supports the roles <strong>of</strong> other institutions.<br />
(referring to the figure)<br />
ACADEMIA<br />
Administration and deanery<br />
Academics<br />
Students<br />
GOVERNING<br />
AUTHORITIES<br />
State<br />
Regional<br />
Local<br />
Innovation and<br />
entrepreneurship<br />
CLUSTER<br />
Competitiveness<br />
and regional<br />
development<br />
Innovation and<br />
entrepreneurship<br />
Innovation and<br />
entrepreneurship<br />
INDUSTRY<br />
Corporations<br />
Capital<br />
Business organizations<br />
SME<br />
Figure 4.8 “Triple helix” concept<br />
83