Pharmacy Continence Care - Bladder and Bowel Website
Pharmacy Continence Care - Bladder and Bowel Website
Pharmacy Continence Care - Bladder and Bowel Website
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
measures impact of incontinence on the individual using seven questions. The IIQ was<br />
included as a set of questions within the body of the consumer baseline <strong>and</strong> follow-up<br />
questionnaires. A four-point rating scale was used in both waves of research to elicit<br />
responses, where 1=Not at all, 2=Slightly, 3=Moderately, 4=Greatly. In order to be<br />
comparable to the IIQ-7 3 , the scores were re-weighted (where 0=Not at all, 1=Slightly,<br />
2=Moderately, 3=Greatly) <strong>and</strong> an average score was taken <strong>and</strong> then multiplied by 33 1 /3 to<br />
put the score on a scale of 0 to 100.<br />
The results, presented in Table 2, indicate that the impact of incontinence between baseline<br />
<strong>and</strong> follow-up increased, in total, across all four key aspects: travel up 20 points; social<br />
activities up 13.4 points; physical activity up 11 points <strong>and</strong> emotional health up 10 points. In<br />
assessing this outcome, the project team consulted with expert panel members on factors<br />
which may contribute to or explain an increase in the perception of the difficulties caused by<br />
incontinence. The follow-up smaller sample comprised a significant proportion of consumers<br />
who reported an average length of persistence of incontinence 2.6 years greater than the<br />
average for the baseline group. That is, the consumer sample at follow-up comprised a<br />
greater proportion of individuals with long established incontinence.<br />
This group also reported a significantly lower level (40 per cent) of having visited or been<br />
visited by a health care professional about incontinence than did the group in the baseline<br />
survey. This is considered to be the likely explanation of the reported increase in difficulties –<br />
both in the proportion within the sample with long established <strong>and</strong> limiting incontinence, <strong>and</strong><br />
in the impact on the consumer perception of difficulty consequent upon the approach by <strong>and</strong><br />
engagement with the pharmacy staff.<br />
Given the follow-up sample included a higher proportion of older individuals, with longer<br />
established incontinence, who had had less contact with health professionals in respect of<br />
their incontinence; the increased perception of difficulty can be considered to reflect a<br />
“Hawthorne effect” – that is, the effect simply of being studied; <strong>and</strong> potentially of<br />
experimenter effects (Adair 1984). The Hawthorne effect has been held to potentially<br />
describe an experimental effect not in the direction expected, due to the participants’<br />
reactions to the experiment itself, that is, of the subject’s reaction to or new or increased<br />
awareness of the behaviour under study (Parsons 1974).<br />
The expert panel, <strong>and</strong> the project team, postulate that the follow-up sample of consumers<br />
comprised a higher proportion of consumers with long established <strong>and</strong> limiting incontinence<br />
than the baseline sample; <strong>and</strong>, that the follow-up sample had become more aware of the<br />
limiting nature of the incontinence (<strong>and</strong> perhaps of the potential for improvement) as a<br />
result of the interaction with pharmacy staff <strong>and</strong> participation in the baseline survey.<br />
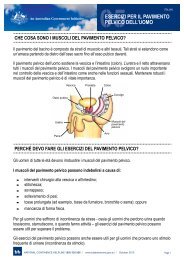
Has urine leakage affected your…<br />
Physical Activity<br />
Baseline Survey<br />
Score<br />
Ability to do household chores (cooking, housecleaning, laundry) 1.3 2.3<br />
Physical recreation such as walking, swimming, or other exercise 40.0 50.0<br />
Travel<br />
Entertainment activities (movies, concerts, etc) 33.3 40.0<br />
Ability to travel by car or bus more than 30 minutes from home 30.0 43.3<br />
Follow-up<br />
Survey Score<br />
3 The IIQ-7 provides a single index of life impact associated with urinary incontinence, which subsumes separate domains of<br />
physical activity (items 1 <strong>and</strong> 2), travel (items 3 <strong>and</strong> 4), social activities (item 5) <strong>and</strong> emotional health (items 6 <strong>and</strong> 7), <strong>and</strong> is<br />
scored as follows. The assigned values for the item responses are 0 for ‘not at all’, 1 for ‘slightly’, 2 for ‘moderately’ <strong>and</strong> 3 for<br />
‘greatly’. To account for missing responses, the average score of items responded to is taken, rather than the total number of<br />
responses. The average, which ranges from 0 to 3, is multiplied by 33 1/3 to put scores on a scale of 0 to 100.<br />
Final Report<br />
40<br />
NOVA Public Policy<br />
<strong>Pharmacy</strong> <strong>Continence</strong> <strong>Care</strong> Project