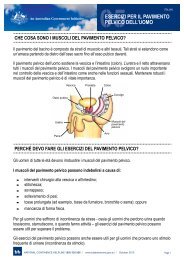
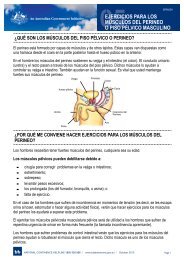
Pharmacy Continence Care - Bladder and Bowel Website
Pharmacy Continence Care - Bladder and Bowel Website
Pharmacy Continence Care - Bladder and Bowel Website
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Each pharmacy was asked to enrol, up to 10 customers to participate in the baseline <strong>and</strong><br />
follow-up survey by completing the consumer questionnaire, in the pharmacy, at enrolment,<br />
<strong>and</strong> by consenting to a follow-up telephone interview to complete the questionnaire at three<br />
months post enrolment.<br />
4.2 Effectiveness of the training<br />
The effectiveness of the training was evaluated through:<br />
• administration of the PIQ <strong>and</strong> PEQ survey questions (number 1-13, 42-47 <strong>and</strong> 61)<br />
• administration of the Evaluation of the PCCP training program Survey form, on<br />
completion of the training<br />
• collection of feedback from the training providers in relation to training delivery issues<br />
<strong>and</strong> activities that may have an impact on implementation of a future program.<br />
4.2.1 Administration of the PIQ <strong>and</strong> PEQ survey questions<br />
The results of the analysis of these three approaches are discussed in the Section 5. In<br />
summary, the training was perceived by both pharmacies <strong>and</strong> trainers as being effective,<br />
despite the mode of delivery. The revised materials, based on the training manuals from<br />
Stage One of the project, were well received by the users <strong>and</strong> provide a good framework for<br />
national roll-out of the PCCP.<br />
The PEQ <strong>and</strong> PIQ were used to evaluate the effectiveness of the training by recording<br />
responses of pharmacies before <strong>and</strong> after training to questions related to the following:<br />
• changes in knowledge/underst<strong>and</strong>ing of:<br />
o the urinary <strong>and</strong> gastrointestinal systems<br />
o normal bladder <strong>and</strong> bowel function<br />
o the different types of urinary incontinence<br />
o faecal incontinence<br />
o the risk factors for bladder <strong>and</strong> bowel incontinence<br />
o medicines used in the treatment of incontinence<br />
o medicines that may cause or exacerbate incontinence<br />
o self-management options for people with incontinence<br />
o incontinence products <strong>and</strong> how to match these to customer needs<br />
• changes in the level of confidence in:<br />
o initiating conversations with customers who may have incontinence<br />
o providing appropriate referrals for customers who may have continence problems<br />
o providing advice about continence self-management options such as diet <strong>and</strong><br />
exercise<br />
• changes in perceptions about the availability of suitable resources (e.g. information ) to<br />
assist in talking to customers about continence issues.<br />
It also sought an indication of preferred modes of training, before <strong>and</strong> after training delivery,<br />
to evaluate if there had been any shift.<br />
Final Report<br />
23<br />
NOVA Public Policy<br />
<strong>Pharmacy</strong> <strong>Continence</strong> <strong>Care</strong> Project