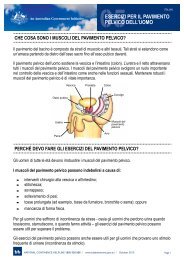
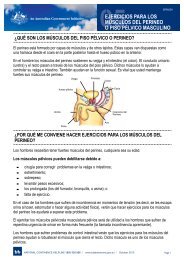
Pharmacy Continence Care - Bladder and Bowel Website
Pharmacy Continence Care - Bladder and Bowel Website
Pharmacy Continence Care - Bladder and Bowel Website
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
• evaluation of the pilot program <strong>and</strong> design of a draft national strategy, for consultation<br />
with the <strong>Pharmacy</strong> Guild Expert Advisory Group (EAG) <strong>and</strong> the <strong>Pharmacy</strong> Guild, in<br />
October <strong>and</strong> November 2005.<br />
This report presents a summary of each of the elements, the methodology applied, the<br />
findings <strong>and</strong> the application of those findings to the pilot program.<br />
Chapter 2, Methodology, discusses the literature review, information collection, expert<br />
advice, <strong>and</strong> stakeholder consultations undertaken to develop the materials for the training<br />
<strong>and</strong> evaluation components of this project. It also discusses the tools <strong>and</strong> methods applied in<br />
the training program for pharmacists <strong>and</strong> pharmacy assistants, <strong>and</strong> the evaluation of<br />
outcomes <strong>and</strong> effectiveness of the pilot program.<br />
Chapter 3 Implementation of the Pilot Program, summarises the implementation processes<br />
<strong>and</strong> results of the PCCP pilot program. The pilot relied on delivering training, <strong>and</strong> evaluating<br />
the effectiveness of that training, in a sample of pharmacies that was sufficient in size <strong>and</strong><br />
demographic distribution to provide reliable information that could be used to draw<br />
conclusions about a wider scale implementation. Consequently the project team undertook a<br />
recruitment strategy to achieve participation by pharmacies from all states <strong>and</strong> territories<br />
<strong>and</strong> all broad regional groupings: metropolitan, regional, rural, <strong>and</strong> remote. A recruitment<br />
target of 50 pharmacies across this range was set <strong>and</strong> achieved at commencement of<br />
training. Ten per cent (5) of these subsequently withdrew once training commenced, for a<br />
variety of reasons, mostly related to the availability of staff, time or both, <strong>and</strong> an additional<br />
pharmacy was included after a late response.<br />
The central purpose of this project was to assess the benefits of the pilot education <strong>and</strong><br />
training program, in continence health issues <strong>and</strong> continence care, to pharmacy practice, in<br />
pharmacy contribution to primary health care services, <strong>and</strong> to consumers. Chapter 4 reports<br />
on the Outcomes <strong>and</strong> Effectiveness evaluation that has been undertaken, based on parallel<br />
<strong>and</strong> two-stage surveys of participating pharmacies <strong>and</strong> of recruited consumer survey<br />
participants. NOVA team members conducted structured telephone interviews with<br />
nominated personnel in each participating pharmacy, at the inception of the program prior to<br />
the training provided in each pharmacy (the <strong>Pharmacy</strong> Intake Questionnaire - PIQ), <strong>and</strong><br />
again at the conclusion of the pilot program trial period in each pharmacy (the <strong>Pharmacy</strong> Exit<br />
Questionnaire - PEQ). A self-administered questionnaire providing pharmacy feedback on the<br />
training experience <strong>and</strong> outcomes was provided for completion by participating pharmacies<br />
at the conclusion of the program of training in each pharmacy.<br />
A recruitment target of 500 participating consumers was established, based on the estimated<br />
numbers <strong>and</strong> proportion of customers with incontinence or caring for a person with<br />
incontinence in the general population <strong>and</strong> the population attending community pharmacies.<br />
A follow-up survey by Computer Assisted Telephone Interview (CATI) with a r<strong>and</strong>omly<br />
selected sub-sample of 300 participating consumers was planned. Recruitment of consumers<br />
by pharmacies was very low, with only nine per cent of the target sample (45 consumers)<br />
recruited by pharmacies, despite various incentive <strong>and</strong> support strategies discussed in<br />
Chapter 4. The follow-up CATI survey was not undertaken r<strong>and</strong>omly, given the low<br />
participation rate, <strong>and</strong> 30 of the consumers who consented to follow-up were subsequently<br />
re-interviewed. Of these, 18 consented to further interview, <strong>and</strong> the project team will<br />
undertake a semi-structured interview with those of this group who are available during<br />
November 2005, to obtain further <strong>and</strong> personal detail that can be used as de-identified case<br />
study material in information for pharmacies <strong>and</strong> consumers, in the future national<br />
implementation of this training program.<br />
As part of the program, pharmacies were encouraged to seek feedback from their customers<br />
to gauge their satisfaction with the service they received from the pharmacy in relation to<br />
Final Report<br />
4<br />
NOVA Public Policy<br />
<strong>Pharmacy</strong> <strong>Continence</strong> <strong>Care</strong> Project