J17
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
1. (x + 3)(x + 1) 2. (x + 2)(x – 4)<br />
3. (x – 7)(x + 3) 4. (x – 4)(x – 3)<br />
5. (a + 8)(a – 3) 6. (p + 2)(p – 5)<br />
7. (x – 5)(x + 4) 8. (x + 5)(x + 4)<br />
9. (x + 2)(5x + 3) 10. (3x + 2)(x – 4)<br />
11. (2x – 7)(4x – 3) 12. (x +3)(x + 3)<br />
13. (a – 4)(a – 4) 14. (x + 7)(x – 7)<br />
15. (5t + 3)(3t + 2) 16. (2 – x)(3 – x)<br />
17. (3 + p)(5 – p) 18. (4 – 2y)(1 – 3y)<br />
19. (3x + 1)(8 – 2x) 20. (5 – 3x)(2 – 4x)<br />
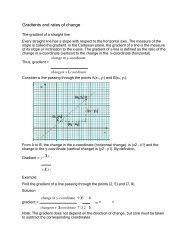
The quadratic identities<br />
1. Show that (a + b)(a + b) = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 .<br />
The product (a + b)(a + b) can be written as (a + b) 2 . Thus,<br />
(a + b) 2 = (a + b)(a + b)<br />
= a 2 + ab + ab + b 2<br />
= a 2 + 2ab + b 2<br />
This product is illustrated in the figure below.<br />
Consider a square with side (a + b) units. The square is divided into:<br />
(a) square A of side a,<br />
(b) square D of side b,<br />
(c) rectangle B of sides a and b,<br />
(d) rectangle C of sides a and b.<br />
Area of the big square = (a + b) 2<br />
Area of: square A = a 2<br />
rectangle B = ab<br />
rectangle C = ab<br />
square D = b 2<br />
Rectangles B and C are identical.<br />
The area of A + B + C + D = a 2 + ab + ab + b 2<br />
Therefore, (a + b) 2 = a 2 + ab + ab + b 2<br />
= a 2 + 2ab + b 2