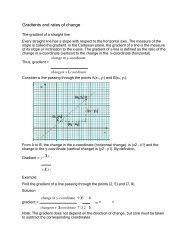
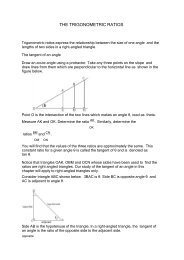
J17
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Example<br />
Factorize x 2 + 7x + 6 = 0. Hence solve the equation.<br />
Solution<br />
x 2 + 7x + 6 = 0<br />
Factorizing, x 2 +7x + 6, gives (x + 6)(x + 1) = 0.<br />
Therefore, x + 6 = 0 or x + 1 = 0; which means x = -6 or x = -1<br />
These are the only two values of x which satisfy the equation x 2 + 7x + 6 = 0. We can<br />
check these solutions by substituting each of them in the equation.<br />
Thus, when x = -6,<br />
(-6) 2 + 7(-6) + 6 = 36 – 42 + 6 = 0<br />
And when x = -1<br />
(-1) 2 + 7(-1) + 6 = 1 – 7 + 6 = 0<br />
Note: Every quadratic equation has two solutions.<br />
Example<br />
Solve: x 2 + x – 72 = 0<br />
Solution<br />
x 2 + x – 72 = 0<br />
(x – 8)(x + 9) = 0. x – 8 = 0 or x + 9 = 0<br />
x = 8 or x = -9.<br />
Example<br />
Solve: x 2 – x – 29 = 1<br />
Solution<br />
Always ensure that the quadratic expression is equated to zero. This is the only time the<br />
method used in the examples above can apply.<br />
Thus, x 2 – x – 29 = 1 should be rewritten as x 2 – x – 29 – 1 = 0. That is,<br />
x 2 – x – 30 = 0.<br />
The factors of 30, whose sum is 1, are -6 and 5.<br />
Therefore, (x – 6)(x + 5) = 0.<br />
Either x – 6 = 0 or x + 5 = 0<br />
x = 6 or x = -5<br />
The roots are -5 and 6.<br />
Example<br />
Solve:<br />
(a) x 2 – 49 = 0 (b) x 2 – 6x = 0<br />
(c) x 2 – 16x + 64 = 0 (d) 6x 2 + 5x – 4 = 0<br />
Solutions<br />
(a) x 2 – 49 = 0 can be written as x 2 – 7 2 = 0<br />
(x – 7)(x + 7) = 0