TCP vs UDP
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Difference between <strong>TCP</strong> and <strong>UDP</strong><br />
Transmissions Control Protocol (<strong>TCP</strong>) and User datagram Protocol (<strong>UDP</strong>) are 2 most<br />
commonly used protocol in <strong>TCP</strong>/IP. In this article you will see the complete comparison<br />
between <strong>TCP</strong> and <strong>UDP</strong>.<br />
In nutshell, <strong>TCP</strong> is a reliable protocol and offers are guaranteed delivery, However <strong>UDP</strong> is un<br />
reliable and does not provide any guarantee of deliver. Go here for complete <strong>UDP</strong> and <strong>TCP</strong><br />
comparison and click this link for <strong>TCP</strong>, <strong>UDP</strong> details.<br />
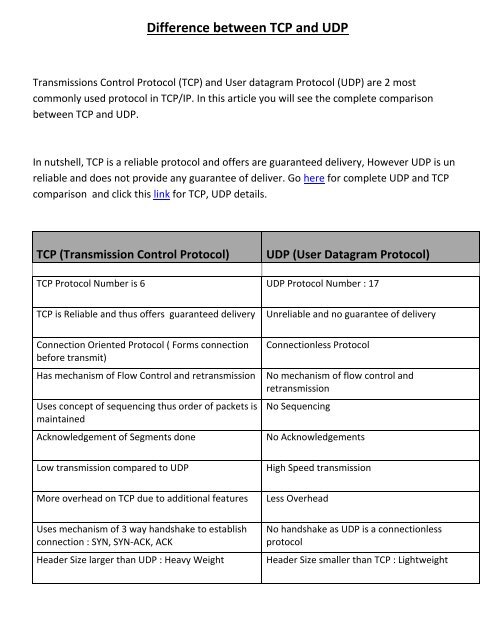
<strong>TCP</strong> (Transmission Control Protocol)<br />
<strong>UDP</strong> (User Datagram Protocol)<br />
<strong>TCP</strong> Protocol Number is 6 <strong>UDP</strong> Protocol Number : 17<br />
<strong>TCP</strong> is Reliable and thus offers guaranteed delivery<br />
Unreliable and no guarantee of delivery<br />
Connection Oriented Protocol ( Forms connection<br />
before transmit)<br />
Has mechanism of Flow Control and retransmission<br />
Uses concept of sequencing thus order of packets is<br />
maintained<br />
Acknowledgement of Segments done<br />
Connectionless Protocol<br />
No mechanism of flow control and<br />
retransmission<br />
No Sequencing<br />
No Acknowledgements<br />
Low transmission compared to <strong>UDP</strong><br />
High Speed transmission<br />
More overhead on <strong>TCP</strong> due to additional features<br />
Less Overhead<br />
Uses mechanism of 3 way handshake to establish<br />
connection : SYN, SYN-ACK, ACK<br />
Header Size larger than <strong>UDP</strong> : Heavy Weight<br />
No handshake as <strong>UDP</strong> is a connectionless<br />
protocol<br />
Header Size smaller than <strong>TCP</strong> : Lightweight
<strong>TCP</strong> offers Error correction<br />
Used for other applications like webpages or<br />
critical applications<br />
Fields in Header: Source Port, Destination Port,<br />
Sequence number, ACK number, Data Offset,<br />
Reserved, Control bit (Flags), Window, Checksum,<br />
Urgent Pointer, Options, Padding<br />
Protocol Examples: FTP, HTTP, SMTP, DNS etc.<br />
<strong>UDP</strong> does error checking but no correction or<br />
recovery done in case of errors found<br />
Used for Streaming Audio & Video<br />
Fields in Header: Source Port, Destination Port,<br />
Length, <strong>UDP</strong> Checksum<br />
Protocol Example: DNS, SNMP, TFTP, BOOTP<br />
etc.<br />
---x---