Staff Members of the Institute of Biochemistry, TU - Institut für ...
Staff Members of the Institute of Biochemistry, TU - Institut für ...
Staff Members of the Institute of Biochemistry, TU - Institut für ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
carotenoids, while 110 o C, 120 o C and 130 o C were favorable for triacylglycerol oxidation.<br />
Stability <strong>of</strong> triacylglycerols decrease with <strong>the</strong> increased formation <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> oxidation products <strong>of</strong><br />
β-carotene.<br />
Intensity<br />
100<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
20<br />
Trilinolein<br />
288<br />
263<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
+ [ M + Na]<br />
901<br />
[ M + NH 4]<br />
+<br />
896<br />
+ [ M + H]<br />
879<br />
0<br />
200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900<br />
O<br />
O<br />
m/z<br />
LL +<br />
599<br />
DAGs<br />
Intensity<br />
1-Oleoyl-2-linoleoyl-3-linoleoyl glycerol<br />
100<br />
O<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
20<br />
Intensity<br />
1-Oleoyl-2-linoleoyl-3-oleoyl glycerol<br />
100<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
20<br />
+<br />
[ M-<br />
O + H + Li]<br />
874<br />
288<br />
263<br />
+ [ M + H]<br />
883<br />
0<br />
200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
LL<br />
599<br />
+<br />
+ [ M + Na]<br />
903<br />
[ M + NH4]<br />
+<br />
898<br />
+<br />
[ M-<br />
O + H+<br />
Li]<br />
288<br />
+ 872<br />
[ M + H]<br />
263<br />
881<br />
0<br />
200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900<br />
O<br />
m/z<br />
O<br />
OL<br />
601<br />
+<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
m/z<br />
O<br />
O<br />
OL +<br />
601<br />
OO<br />
603<br />
+<br />
0 5 10 15 20 25 30<br />
Time (min)<br />
35<br />
[ M + Na]<br />
+ 905<br />
[ M + NH4]<br />
+<br />
900<br />
Intensity<br />
4<br />
603<br />
[ M + NH ] +<br />
100 OO 902<br />
+<br />
O<br />
Triolein<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
20<br />
+<br />
[ M-<br />
O + H + Li]<br />
876<br />
+ [ M + H]<br />
263<br />
883<br />
0<br />
200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900<br />
O<br />
O<br />
m/z<br />
Intensity<br />
1-Oleoyl-2-oleoyl-3-stearoyl glycerol<br />
100<br />
O<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
20<br />
[ M + Na]<br />
+<br />
907<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
OO<br />
603<br />
+<br />
OS<br />
605<br />
+<br />
[ M + NH4]<br />
+<br />
909<br />
[ M + Na]<br />
+<br />
904<br />
288<br />
+<br />
[ M + H]<br />
887<br />
0<br />
200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900<br />
O<br />
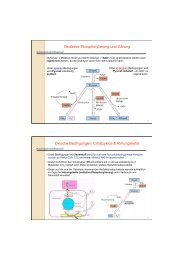
HPLC-MS<br />
Figure 1. Separation and Identification <strong>of</strong> Triacylglycerols using HPLC-ESI-MS.<br />
Diploma Theses completed<br />
Thomas Binder: Effects <strong>of</strong> blanching and enzyme treatment on <strong>the</strong> amount <strong>of</strong> asparagine in<br />
potato slices<br />
The overall aim <strong>of</strong> this work was to find different ways to reduce <strong>the</strong> asparagine content in<br />
raw potato slices. This was done by studying <strong>the</strong> effect <strong>of</strong> blanching and enzyme treatments<br />
on <strong>the</strong> asparagine content in raw and blanched potato slices. A fur<strong>the</strong>r important objective was<br />
to find a good treatment for lowering <strong>the</strong> asparagine content in potato slices which also can be<br />
used in <strong>the</strong> food industry. For this reason <strong>the</strong> cooking value was calculated for <strong>the</strong> different<br />
blanching treatments.<br />
Katrin Julia Greimel: Absolute quantification <strong>of</strong> soy in animal feed<br />
The quantification <strong>of</strong> technically unavoidable contaminations in animal feed (especially soy)<br />
is necessary due to <strong>the</strong> threshold values determined by law. However, it turns out to be a great<br />
challenge for analytical laboratories. In this work, two different methods for <strong>the</strong> absolute<br />
quantification <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> soy percentage in animal feed have been developed. One method for<br />
detection is based on molecular biology <strong>the</strong> real-time polymerase chain reaction (real-time<br />
PCR), <strong>the</strong> o<strong>the</strong>r is a standard method <strong>of</strong> classical analytical chemistry, namely <strong>the</strong> high<br />
performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Sensitive and specific primers were developed<br />
for <strong>the</strong> PCR-method and were additionally used with suitable hydrolysis probes in a<br />
multiplex-PCR. The optimisation <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> method made it possible to quantify low percentage<br />
soy in animal feed products. The quantification by HPLC was carried out by means <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> two<br />
is<strong>of</strong>lavones daidzein and genistein, that are especially present in soybeans. Both were chosen