DISSERTATION
resolver
resolver
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
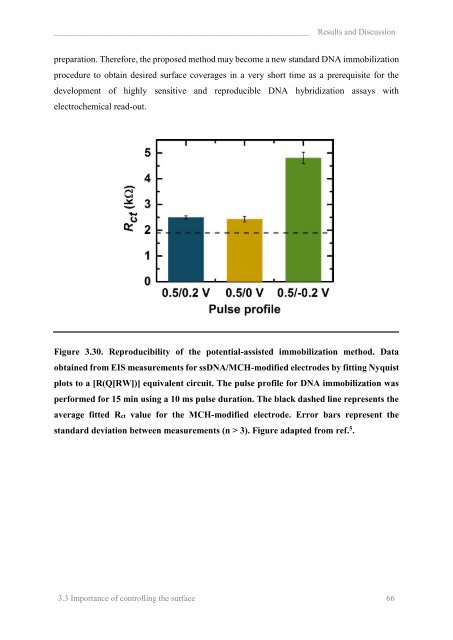
_____________________________________________________________ Results and Discussion<br />
3.3.2 Formation of compact thiol SAMs within minutes<br />
Data analysis was done based on discussions with Dr. Felipe Conzuelo and Dr. Arturo Estrada-<br />
Vargas. Parts of this section were published in ref. 89 : “D. Jambrec, F. Conzuelo, A. Estrada-<br />
Vargas, W. Schuhmann, ChemElectroChem 2016, 3, 1484-1489.” written by the author. Figure<br />
adapted from ref. 89 .<br />
A typical approach for a DNA sensor buildup is a two-step immobilization strategy, in which<br />
initially a probe DNA is grafted on the surface and subsequently the electrode is covered by a<br />
thiol SAM. Thiol passivation forces the grafted DNA to lift up and to obtain a more favorable<br />
orientation for the hybridization process concomitantly removing unspecifically bound DNA<br />
strands. Additionally, the blocking ability of the passivation step in the DNA sensor preparation<br />
plays an important role in the efficiency of an envisaged DNA sensing scheme. It prevents<br />
unspecific adsorption of undesired molecules employed in the detection scheme and determines<br />
the signal of the negative control. Therefore, controlling of the blocking ability of the modified<br />
surface is crucial for construction of very sensitive and reproducible DNA sensors.<br />
3.3 Importance of controlling the surface 67