DISSERTATION
resolver
resolver
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
_____________________________________________________________<br />
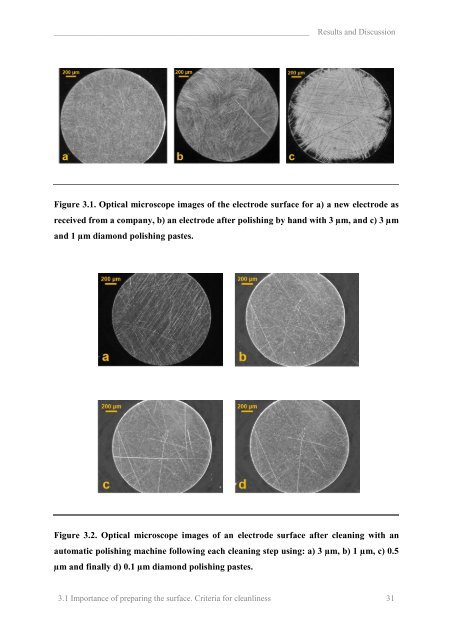
Results and Discussion<br />
In addition to the roughness factor (for its determination see Section 5.3), the criterion for<br />
efficiency of electrochemical cleaning in H2SO4 was the shape of the CV. The electrode surface<br />
was considered clean only if the oxidation peaks of individual gold facets 69 were observed upon<br />
electrochemical cleaning as shown in Figure 3.3.<br />
Figure 3.3. Representative CV of a clean gold electrode. Electrochemical cleaning was<br />
performed in 0.5 M H2SO4 at a scan rate of 100 mV/s.<br />
Following the mechanical and electrochemical cleaning of the electrode surface, EIS and CV<br />
using the ferro/ferricyanide couple as redox probe were used to verify the electrode cleanliness<br />
and to allow for a comparison of separate electrodes. Afterwards, criteria were selected for the<br />
desired charge transfer resistance (Rct) derived from EIS and the peak current in the CV as a<br />
prerequisite for the use of prepared electrodes for subsequent surface modification.<br />
Representative EIS and CV of clean gold electrodes are shown in Figure 3.4.<br />
Modification of electrodes was performed immediately after mechanical and electrochemical<br />
cleaning and characterization of the bare electrodes since it was observed by EIS that upon<br />
storage of bare gold electrodes in air, H2SO4 or HClO4 unknown contaminants adsorb on the<br />
electrode surface (data not shown).<br />
3.1 Importance of preparing the surface. Criteria for cleanliness 32