DISSERTATION
resolver
resolver
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
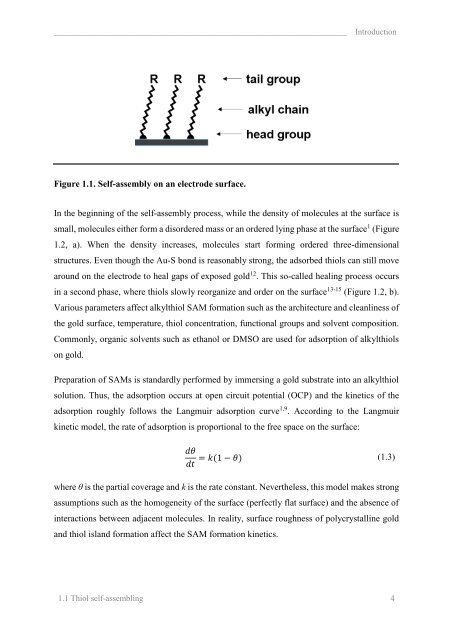
______________________________________________________________________ Introduction<br />
Externally applied potentials affect already formed SAMs, causing the change of their<br />
structure 16 , change of wettability 17 or desorption 18,19 . The desorption of SAMs can occur by<br />
applying rather high positive or negative potentials. Nevertheless, the potential value required<br />
to invoke SAM desorption depends on the type of alkylthiols used (length of the alkyl chain,<br />
head group repulsion) and the coverage, since they influence the stability of the SAM 12 . Longer<br />
alkylthiols and more compact layers are more stable SAMs and therefore, more difficult to<br />
desorb. Furthermore, the possibility of controlling SAM formation by applying an external<br />
potential was observed in the 1990s 20 . Application of anodic constant potentials seems to<br />
accelerate the kinetics of SAM formation 13,21-24 . However, this phenomenon is still poorly<br />
understood.<br />
Figure 1.2. Self-assembly on an electrode surface occurs through two phases: a) in the first<br />
phase (lying phase) molecules randomly lie on the surface, and in b) the second phase<br />
(healing phase) they slowly reorganize to form highly compact monolayers.<br />
1.1 Thiol self-assembling 5