DISSERTATION
resolver
resolver
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
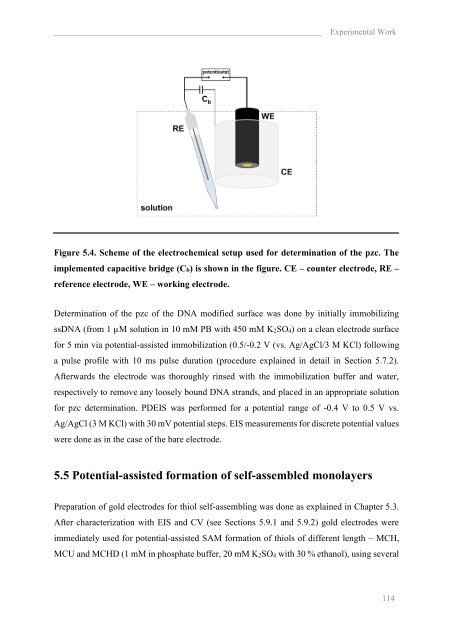
________________________________________________________________ Experimental Work<br />
pulse profiles: 0.3/-0.1 V, 0.5/-0.2 V and 0.5/-0.4 V (vs. Ag/AgCl/3 M KCl) with various pulse<br />
durations of 1 ms, 10 ms, 100 ms and 10 s.<br />
Real-time impedance measurements were performed during potential-assisted SAM formation<br />
to investigate the kinetics of self-assembly. This was done in a way that the applied pulse<br />
profiles were considered as DC potentials which were superimposed with an AC signal of 1<br />
kHz frequency and 5 mVrms amplitude. Experiments were performed using a setup that<br />
consisted of a potentiostat with a summing amplifier (IPS AJ, Germany), a function generator<br />
(Agilent 33120A, USA), a lock-in amplifier (EG&G Instruments 7265 DSP, USA) and a 16 bit<br />
CIO-DAS 1602/16 AD/DA board (Plug-In electronic, Germany).<br />
Determination of the capacitance was done by calculating initially the imaginary impedance<br />
component (-Z'') using the recorded magnitude (|Z|) and phase (θ) values:<br />
|Z| =<br />
A AC<br />
k|Z| meas<br />
(5.5)<br />
−Z ′′ = |Z|sinθ<br />
where AAC is AC amplitude, k is the correction coefficient taking into account the current range<br />
of the potentiostat (10 mA/10 V) and |Z|meas is the measured value of the magnitude. Using the<br />
value of the imaginary impedance component the capacitance was calculated using the<br />
following expression, derived from an RC series equivalent electrical circuit:<br />
C = −1<br />
ωZ ′′ (5.6)<br />
Data sampling was done at a rate of 100 ms per data point and recorded with a home-made<br />
software. Oscillations of the recorded signals coming from the applied pulse potential were<br />
suppressed by applying a digital filter to the experimental plots. Data analysis and curve fitting<br />
was performed with Origin.<br />
5.6 Potential-assisted desorption<br />
Potential-assisted desorption was performed using ssDNA-, MCU- or ssDNA/MCU-modified<br />
electrodes. The experiment was done in 10 mM PB with 450 mM K2SO4 by applying a 0.9/-0.9<br />
115