Distinctive Features - Speech Resource Pages - Macquarie University
Distinctive Features - Speech Resource Pages - Macquarie University
Distinctive Features - Speech Resource Pages - Macquarie University
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
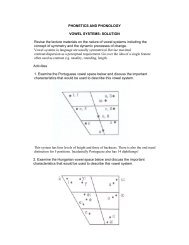
1. syllabic / non-syllabic [syll]: Syllabic sounds constitute a syllable peak<br />
(sonority peak). [+syll] refers to vowels and to syllabic consonants. [-syll]<br />
refers to all non-syllabic consonants (including semi-vowels).<br />
2. consonantal / non-consonantal [cons]: Consonantal sounds are<br />
produced with at least approximant stricture. That is consonantal sounds<br />
involve vocal tract constriction significantly greater that that which occurs<br />
for vowels. [+cons] refers to all consonants except for semi-vowels (which<br />
often have resonant stricture). [-cons] refers to vowels and semi-vowels.<br />
3. sonorant / obstruent [son]: Sonorant sounds are produced with vocal<br />
tract configuration that permits air pressure on both sides of any<br />
constriction to be approximately equal to the air pressure outside the<br />
mouth. Obstruents possess constriction (stricture) that is sufficient to result<br />
in significantly greater air pressure behind the constriction than occurs in<br />
front of the constriction and outside the mouth. [+son] refers to vowels and<br />
approximants (glides and semi-vowels). [-son] refers to stops, fricatives<br />
and affricates.<br />
4. coronal / non-coronal [cor]: "Coronal sounds are produced by raising the<br />
tongue blade toward the teeth or the hard palate; noncoronal sounds are<br />
produced without such a gesture." (HC) This feature is intended for use with<br />
consonants only. [+cor] refers to dentals (not including labio-dentals)<br />
alveolars, post-alveolars, palato-alveolars, palatals. [-cor] refers to labials,<br />
velars, uvulars, pharyngeals.<br />
5. anterior / posterior [ant]: "Anterior sounds are produced with a primary<br />
constriction at or in front of the alveolar ridge. Posterior sounds are<br />
produced with a primary constriction behind the alveolar ridge." (HC) This<br />
feature is intended to be applied to consonants. [+ant] refers to labials,<br />
dentals and alveolars. [-ant] refers to post-alveolars, palato-alveolars,<br />
retroflex, palatals, velars, uvulars, pharyngeals.<br />
6. labial / non-labial [lab]: Labial sounds involve rounding or constriction at<br />
the lips. [+lab] refers to labial and labialised consonants and to rounded<br />
vowels. [-lab] refers to all other sounds.<br />
7. distributed / non-distributed [distr]: "Distributed sounds are produced<br />
with a constriction that extends for a considerable distance along the<br />
midsaggital axis of the oral tract; nondistributed sounds are produced with<br />
a constriction that extends for only a short distance in this direction." (HC)<br />
[+distr] refers to sounds produced with the blade or front of the tongue, or<br />
bilabial sounds. [-distr] refers to sounds produced with the tip of the<br />
tongue. This feature can distinguish between palatal and retroflex sounds,<br />
between bilabial and labiodental sounds, between lamino-dental and apicodental<br />
sounds.<br />
8. high / non-high [high]: "High sounds are produced by raising the body of<br />
the tongue toward the palate; nonhigh sounds are produced without such a<br />
gesture." (HC) [+high] refers to palatals, velars, palatalised consonants,<br />
velarised consonants, high vowels, semi-vowels. [-high] refers to all other<br />
sounds. Note, however, the discussion above on how this feature is used in<br />
combination with [mid] to describe the distinction between four contrastive<br />
vowel heights.<br />
9. mid / non-mid [mid]: Mid sounds are produced with tongue height<br />
approximately half way between the tongue positions appropriate for<br />
[+high] and [+low]. This vowel height feature is only required when a<br />
language has four levels of height contrast and remains unspecified for<br />
languages with fewer vowel height contrasts. [+mid] refers to vowels with<br />
intermediate vowel height. [-mid] refers to all other sounds.<br />
10. low / non-low [low]: "Low sounds are produced by drawing the body of<br />
the tongue down away from the roof of the mouth; nonlow sounds are