BASIC PROFICIENCY TOPIC 13 GRADE 9 Title Ming Dynasty and Ottoman Empire
Ming Dynasty and Ottoman Empire - JonesHistory.net
Ming Dynasty and Ottoman Empire - JonesHistory.net
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>BASIC</strong> <strong>PROFICIENCY</strong> <strong>TOPIC</strong> <strong>13</strong><br />
<strong>GRADE</strong><br />
9<br />
<strong>Title</strong>: <strong>Ming</strong> <strong>Dynasty</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Ottoman</strong> <strong>Empire</strong><br />
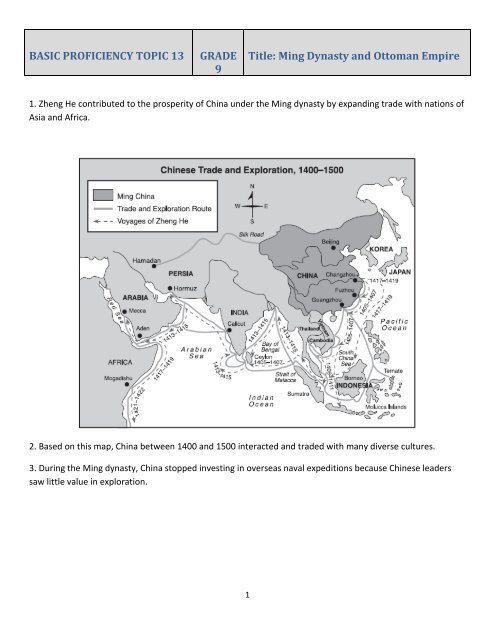
1. Zheng He contributed to the prosperity of China under the <strong>Ming</strong> dynasty by exp<strong>and</strong>ing trade with nations of<br />
Asia <strong>and</strong> Africa.<br />
2. Based on this map, China between 1400 <strong>and</strong> 1500 interacted <strong>and</strong> traded with many diverse cultures.<br />
3. During the <strong>Ming</strong> dynasty, China stopped investing in overseas naval expeditions because Chinese leaders<br />
saw little value in exploration.<br />
1
4. During the <strong>Ming</strong> dynasty, as a result of the travels of Zheng He, advanced navigation technology was<br />
available in China.<br />
5. <strong>Ming</strong> <strong>Dynasty</strong> Events:<br />
• Foreign rulers were overthrown.<br />
• Admiral Zheng He established trade links.<br />
• Civil service exams were reinstated.<br />
2
6. The generalization is best supported by the information in this map is that by the 1500s, the <strong>Ottoman</strong><br />
<strong>Empire</strong> controlled parts of the Middle East, North Africa, <strong>and</strong> eastern Europe.<br />
7. The golden ages of the Roman, Byzantine, <strong>and</strong> <strong>Ottoman</strong> <strong>Empire</strong>s can be attributed in part to stable<br />
governments.<br />
8. King Louis XIV of France, Peter the Great of Russia, <strong>and</strong> Suleiman the Magnificent of the <strong>Ottoman</strong> <strong>Empire</strong><br />
were all considered absolute rulers because they determined government policies without the consent of<br />
their people.<br />
9. In 1453, the <strong>Ottoman</strong> <strong>Empire</strong> rose to power by defeating the Byzantine <strong>Empire</strong>.<br />
10. One similarity between the Roman <strong>Empire</strong> <strong>and</strong> the <strong>Ottoman</strong> <strong>Empire</strong> is that both declined because of<br />
corruption in government.<br />
11. One similarity in the rule of Peter the Great, Suleiman I, <strong>and</strong> Louis XIV is that each leader exp<strong>and</strong>ed his<br />
territory.<br />
12. One way in which Suleiman the Magnificent <strong>and</strong> Akbar the Great are similar is that they both brought<br />
about periods of political stability <strong>and</strong> religious tolerance.<br />
<strong>13</strong>. One way in which Asoka, Mansa Musa, <strong>and</strong> Suleiman the Magnificent are similar is that they ruled during<br />
times of prosperity.<br />
14. “Absolutist” is the form of political leadership is most closely associated with Ivan the Terrible, Suleiman<br />
the Magnificent, <strong>and</strong> Philip II of Spain.<br />
3