Estonian Human Development Report
Estonian Human Development Report - Eesti Koostöö Kogu
Estonian Human Development Report - Eesti Koostöö Kogu
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
significantly among Russian-speaking youth in recent<br />
years, while the corresponding percentage among <strong>Estonian</strong>-speaking<br />
youth has increased noticeably (ESPAD).<br />
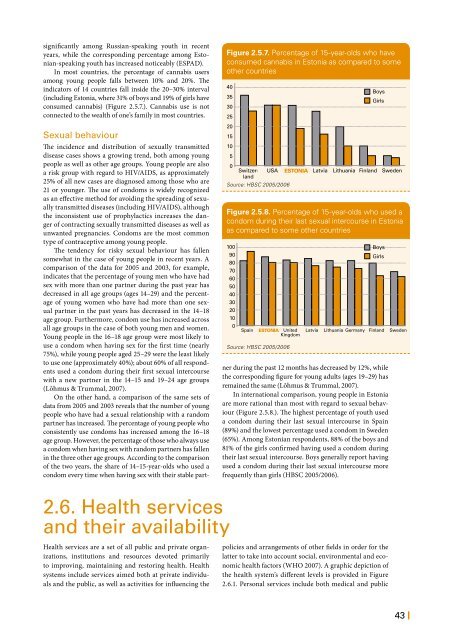
In most countries, the percentage of cannabis users<br />
among young people falls between 10% and 20%. The<br />
indicators of 14 countries fall inside the 20–30% interval<br />
(including Estonia, where 31% of boys and 19% of girls have<br />
consumed cannabis) (Figure 2.5.7.). Cannabis use is not<br />
connected to the wealth of one’s family in most countries.<br />
Sexual behaviour<br />
Figure 2.5.7. Percentage of 15-year-olds who have<br />
consumed cannabis in Estonia as compared to some<br />
other countries<br />
40<br />
35<br />
30<br />
25<br />
20<br />
15<br />
10<br />
5<br />
0<br />
The incidence and distribution of sexually transmitted<br />
disease cases shows a growing trend, both among young<br />
people as well as other age groups. Young people are also<br />
a risk group with regard to HIV/AIDS, as approximately<br />
25% of all new cases are diagnosed among those who are<br />
21 or younger. The use of condoms is widely recognized<br />
as an effective method for avoiding the spreading of sexually<br />
transmitted diseases (including HIV/AIDS), although<br />
the inconsistent use of prophylactics increases the danger<br />
of contracting sexually transmitted diseases as well as<br />
unwanted pregnancies. Condoms are the most common<br />
type of contraceptive among young people.<br />
The tendency for risky sexual behaviour has fallen<br />
somewhat in the case of young people in recent years. A<br />
comparison of the data for 2005 and 2003, for example,<br />
indicates that the percentage of young men who have had<br />
sex with more than one partner during the past year has<br />
decreased in all age groups (ages 14–29) and the percentage<br />
of young women who have had more than one sexual<br />
partner in the past years has decreased in the 14–18<br />
age group. Furthermore, condom use has increased across<br />
all age groups in the case of both young men and women.<br />
Young people in the 16–18 age group were most likely to<br />
use a condom when having sex for the first time (nearly<br />
75%), while young people aged 25–29 were the least likely<br />
to use one (approximately 40%); about 60% of all respondents<br />
used a condom during their first sexual intercourse<br />
with a new partner in the 14–15 and 19–24 age groups<br />
(Lõhmus & Trummal, 2007).<br />
On the other hand, a comparison of the same sets of<br />
data from 2005 and 2003 reveals that the number of young<br />
people who have had a sexual relationship with a random<br />
partner has increased. The percentage of young people who<br />
consistently use condoms has increased among the 16–18<br />
age group. However, the percentage of those who always use<br />
a condom when having sex with random partners has fallen<br />
in the three other age groups. According to the comparison<br />
of the two years, the share of 14–15-year-olds who used a<br />
condom every time when having sex with their stable part-<br />
Switzerland<br />
Source: HBSC 2005/2006<br />
Boys<br />
Girls<br />
USA ESTONIA Latvia Lithuania Finland Sweden<br />
Figure 2.5.8. Percentage of 15-year-olds who used a<br />
condom during their last sexual intercourse in Estonia<br />
as compared to some other countries<br />
100<br />
90<br />
80<br />
70<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
0<br />
Spain ESTONIA United<br />
Kingdom<br />
Source: HBSC 2005/2006<br />
Boys<br />
Girls<br />
Latvia Lithuania Germany Finland Sweden<br />
ner during the past 12 months has decreased by 12%, while<br />
the corresponding figure for young adults (ages 19–29) has<br />
remained the same (Lõhmus & Trummal, 2007).<br />
In international comparison, young people in Estonia<br />
are more rational than most with regard to sexual behaviour<br />
(Figure 2.5.8.). The highest percentage of youth used<br />
a condom during their last sexual intercourse in Spain<br />
(89%) and the lowest percentage used a condom in Sweden<br />
(65%). Among <strong>Estonian</strong> respondents, 88% of the boys and<br />
81% of the girls confirmed having used a condom during<br />
their last sexual intercourse. Boys generally report having<br />
used a condom during their last sexual intercourse more<br />
frequently than girls (HBSC 2005/2006).<br />
2.6. Health services<br />
and their availability<br />
Health services are a set of all public and private organizations,<br />
institutions and resources devoted primarily<br />
to improving, maintaining and restoring health. Health<br />
systems include services aimed both at private individuals<br />
and the public, as well as activities for influencing the<br />
policies and arrangements of other fields in order for the<br />
latter to take into account social, environmental and economic<br />
health factors (WHO 2007). A graphic depiction of<br />
the health system’s different levels is provided in Figure<br />
2.6.1. Personal services include both medical and public<br />
43 |