Bibliometric Analysis Asia-Pacific Research Area ... - JuSER
Bibliometric Analysis Asia-Pacific Research Area ... - JuSER
Bibliometric Analysis Asia-Pacific Research Area ... - JuSER
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Central Library<br />
of all Indonesian publications in 1998 were produced within the research area analysed.<br />
Indonesia’s most important cooperation partners are Japan, Australia and Thailand. Its most<br />
important international partner is the USA. Germany features as its forth most important<br />
international partner. With 402 publications, Indonesia has the second lowest scientific output<br />
within the research area studied; Vietnam has the lowest. With 78,514 published journal articles,<br />
Japan, in contrast, was well ahead of all other countries in South <strong>Asia</strong> in 1998. However, only<br />
3 % of its total output was published in cooperation with one of the other countries. The most<br />
important partners for Japanese scientists came from the USA, Germany and the United<br />
Kingdom. In forth place, China features as the first South-East <strong>Asia</strong>n cooperation partner. In<br />
seventh and eight place are South Korea and Australia. As can be seen from the share of the<br />
total output of South-East <strong>Asia</strong>n countries in Table 8, Japan was responsible for more than half<br />
of the publications in the region with its high publication output in 1998. Australia and China<br />
follow with 17 % and 13 %, respectively. Ten years later, this relationship changed: thanks to its<br />
almost exponential increase in publications, China became the most important country studied<br />
with 34 %. Japan, New Zealand and Australia lost some of their influence to all of the other<br />
countries analysed. Despite this, cooperation between these countries and the other countries<br />
excluding China increased disproportionately in relation to the total publication output. The drop<br />
of 4.55 % in China’s share of publications by South-East <strong>Asia</strong> in the countries’ total output<br />
compared to 1998 can be explained by a huge increase in the number of publications. Between<br />
1998 and 2007, the number of Chinese publications increased by around 370 %. Copublications<br />
with the other South-East <strong>Asia</strong>n countries increased from 1,737 to 7,835,<br />
representing an increase of 350 %. China therefore cooperated less in relation to its total output<br />
in 2007 than it did with the research area in 1998. This statement must be considered in relation<br />
to China’s total output and its exponential increase.<br />
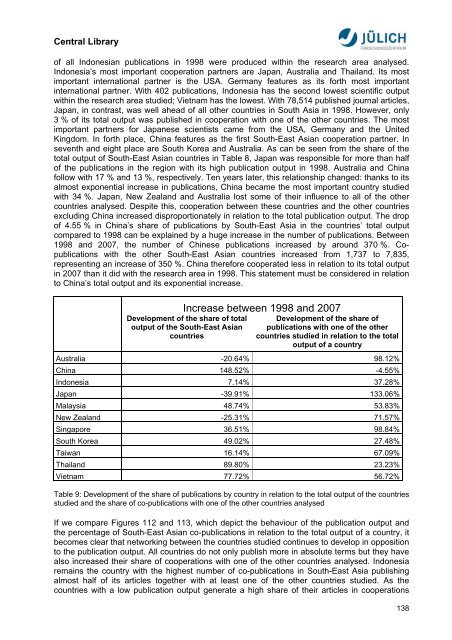
Increase between 1998 and 2007<br />
Development of the share of total<br />
output of the South-East <strong>Asia</strong>n<br />
countries<br />
Development of the share of<br />
publications with one of the other<br />
countries studied in relation to the total<br />
output of a country<br />
Australia -20.64% 98.12%<br />
China 148.52% -4.55%<br />
Indonesia 7.14% 37.28%<br />
Japan -39.91% 133.06%<br />
Malaysia 48.74% 53.83%<br />
New Zealand -25.31% 71.57%<br />
Singapore 36.51% 98.84%<br />
South Korea 49.02% 27.48%<br />
Taiwan 16.14% 67.09%<br />
Thailand 89.80% 23.23%<br />
Vietnam 77.72% 56.72%<br />
Table 9: Development of the share of publications by country in relation to the total output of the countries<br />
studied and the share of co-publications with one of the other countries analysed<br />
If we compare Figures 112 and 113, which depict the behaviour of the publication output and<br />
the percentage of South-East <strong>Asia</strong>n co-publications in relation to the total output of a country, it<br />
becomes clear that networking between the countries studied continues to develop in opposition<br />
to the publication output. All countries do not only publish more in absolute terms but they have<br />
also increased their share of cooperations with one of the other countries analysed. Indonesia<br />
remains the country with the highest number of co-publications in South-East <strong>Asia</strong> publishing<br />
almost half of its articles together with at least one of the other countries studied. As the<br />
countries with a low publication output generate a high share of their articles in cooperations<br />
138