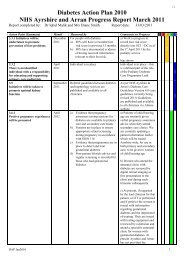
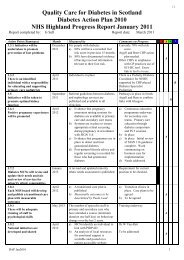
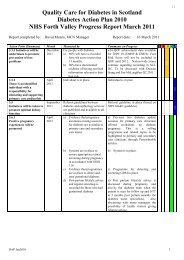
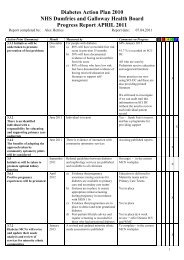
DIABETES ACTION PLAN 2010
Diabetes Action Plan 2010 - Scottish Government
Diabetes Action Plan 2010 - Scottish Government
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>DIABETES</strong> <strong>ACTION</strong> <strong>PLAN</strong> <strong>2010</strong><br />
QUALITY CARE FOR <strong>DIABETES</strong> IN SCOTLAND<br />
Type 2 diabetes develops when the body can still produce some insulin, though not<br />
enough for its needs, or when the insulin that the body produces does not work properly.<br />
Type 2 diabetes usually appears in people over the age of 40 and its rise in prevalence is<br />
closely linked to rising obesity levels, the aging population and reduced activity. Most<br />
people with type 2 diabetes manage to control blood glucose levels with lifestyle changes<br />
and oral medication, but some may also require insulin therapy.<br />
Since the previous Action Plan was published in 2006, Scotland has continued to see a<br />
steady increase in the prevalence of diabetes (Fig. 1). Although much of the rise can be<br />
attributed to better monitoring and data collection, it still represents a serious concern.<br />
This undesirable trend reflects what is happening in the rest of the UK and in other parts<br />
of the world. The number of people with type 2 diabetes in Scotland is currently<br />
increasing at a rate of 4% per year.<br />
Fig. 1. Prevalence of diabetes in Scotland<br />
250,000<br />
200,000<br />
Number of people<br />
150,000<br />
100,000<br />
50,000<br />
0<br />
2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009<br />
Year<br />
Source: SDS 2009 (www.diabetesinscotland.org.uk/publications)<br />
Diabetes has been recognised for at least the last 10 years as an exemplar long term<br />
condition, both in terms of the growing number of people with type 2 diabetes and in<br />
terms of the serious and expensive complications it can bring in its train. Maintaining and<br />
improving the quality of diabetes services against a backdrop of increased incidence and<br />
prevalence, and the consequent pressure on those services, forms the key challenge facing<br />
NHSScotland.<br />
Diabetes care is thought to account for some 10% of all NHS expenditure; this high level<br />
of investment emphasises the importance of ensuring care is in line with cost-effective and<br />
evidence-based treatment.<br />
12